An Act to make provision for and in relation to an occupational superannuation scheme for, and the payment of other benefits to, members of the Defence Force, and for related purposes
Part 1—Preliminary
1 Short title
This Act may be cited as the Military Superannuation and Benefits Act 1991.
2 Commencement
(1) Parts 1, 2, 6 and 7 and sections 42, 47 and 50 to 52 commence on the day on which this Act receives the Royal Assent.
(2) Section 61 commences on 1 September 1991.
(3) The remaining provisions of this Act commence on 1 October 1991.
3 Interpretation
(1) In this Act, unless the contrary intention appears:
associate benefit means a benefit that is payable under provisions of the Trust Deed that are authorised by section 5A.
Board means the Military Superannuation and Benefits Board of Trustees No. 1 established by section 18, as in force before its repeal by item 110 of Schedule 1 to the Superannuation Legislation (Consequential Amendments and Transitional Provisions) Act 2011.
CSC (short for Commonwealth Superannuation Corporation) has the same meaning as in the Governance of Australian Government Superannuation Schemes Act 2011.
DFRDB Act means the Defence Force Retirement and Death Benefits Act 1973.
Fund means the fund established, and vested in the Board, by the Trust Deed.
Note: From 1 July 2011, the fund is vested in CSC.
member of the Scheme has the meaning given by sections 6 and 7.
Rules means the Rules for the administration of the Scheme set out in the Schedule to the Trust Deed.
Scheme means the superannuation scheme established by the Trust Deed.
Trust Deed means the deed referred to in section 4 and includes that deed as subsequently amended under section 5.
(2) Unless the contrary intention appears, a word or expression:
(a) defined, for the purposes of the Rules, in Schedule 1 to the Rules; and
(b) used in a provision of this Act other than the Deed;
has in that provision the same meaning as it has in the Rules.
3A Application of the Criminal Code
Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code applies to all offences against this Act.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
Part 2—The Trust Deed
4 Deed to establish Superannuation Scheme etc.
(1) Not later than 30 days after the commencement of this Act, the Minister must, for and on behalf of the Commonwealth, by deed:
(a) establish an occupational superannuation scheme for the benefit of persons who, on and after the commencement of Part 3, will be, under that Part, members of the scheme; and
(b) establish, and vest in the Board, a fund for the purposes of the superannuation scheme; and
(c) set out the functions and powers of the Board.
(2) The deed must be in the form set out in the Schedule.
5 Amendment of Trust Deed
(1) The Minister may, by legislative instrument signed by the Minister, amend the Trust Deed.
(1AA) Without limiting subsection (1), the Minister may amend the Trust Deed to:
(a) authorise CSC to:
(i) accept particular kinds of amounts in respect of particular kinds of people who are not members of the Scheme; and
(ii) deal with those amounts under the Deed; and
(b) define the functions of CSC in relation to those amounts; and
(c) include provisions in the Rules dealing with:
(i) the manner in which those amounts will be dealt with; and
(ii) the benefits that are to become payable in relation to those amounts; and
(iii) the circumstances in which entitlements to receive those benefits will arise; and
(iv) any other matter relating to those amounts or those benefits.
(1A) The Minister may not amend the Trust Deed unless:
(a) CSC has consented to the amendment; or
(b) the amendment:
(i) relates to a payment of an employer contribution that will, after the making of the amendment, be required or permitted to be made under this Act; or
(ii) relates solely to the termination of the Scheme; or
(iii) is made in circumstances covered by regulations made for the purposes of subparagraph 60(1)(b)(iii) of the Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Act 1993.
(1B) For the purposes of subparagraph (1A)(b)(i), a payment under the Trust Deed is taken to be a payment of an employer contribution.
(2) If compliance with a provision of the Trust Deed as amended under subsection (1) would have the effect that the Scheme:
(a) would not be a regulated superannuation fund within the meaning of the Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Act 1993; or
(b) would not comply with that Act;
that provision is invalid.
5A Amendments of Trust Deed to implement family law interest splitting
(1) Without limiting subsection 5(1), amendments under that subsection:
(a) may provide that, when a splitting agreement or splitting order is received by CSC in respect of a superannuation interest under this Act:
(i) the non‑member spouse is entitled to benefits determined in accordance with the Rules; and
(ii) the benefits of the member spouse are reduced in accordance with the Rules; and
(b) may provide that, when a splitting agreement or splitting order is received by CSC in respect of a superannuation interest under:
(i) section 52 of the Defence Act 1903; or
(ii) the Defence Force Retirement and Death Benefits Act 1973;
the non‑member spouse is entitled to benefits determined in accordance with the Rules; and
(c) may make any other provision that is related to, or consequential on, provisions referred to in paragraph (a) or (b).
(2) Subparagraph (1)(b)(ii) does not apply in a case covered by subsection 49B(2) of the Defence Force Retirement and Death Benefits Act 1973.
(3) Subsection 12(2) (retrospective application of legislative instruments) of the Legislation Act 2003 does not apply to amendments referred to in subsection (1) of this section.
(4) In this section:
member spouse has the same meaning as in Part VIIIB of the Family Law Act 1975.
non‑member spouse has the same meaning as in Part VIIIB of the Family Law Act 1975.
splitting agreement means:
(a) a superannuation agreement (within the meaning of Part VIIIB of the Family Law Act 1975); or
(b) a flag lifting agreement (within the meaning of Part VIIIB of the Family Law Act 1975) that provides for a payment split (within the meaning of Part VIIIB of the Family Law Act 1975).
splitting order has the same meaning as in Part VIIIB of the Family Law Act 1975.
superannuation interest has the same meaning as in Part VIIIB of the Family Law Act 1975.
Part 3—Members of Superannuation Scheme
6 Membership of Superannuation Scheme
(1) Each of the following persons is a member of the Scheme:
(a) a person who is a member of the Permanent Forces;
(b) a member of the Reserves who is rendering a period of continuous full‑time service.
(2) This section is subject to section 7.
7 Persons excluded from membership of Superannuation Scheme
Defence Force Retirement and Death Benefits scheme
(1) A person is not a member of the Scheme if the person is an eligible member of the Defence Force for the purposes of the DFRDB Act.
Those commencing on or after 1 July 2016
(2) A person is not a member of the Scheme if:
(a) the person does not have a preserved benefit that includes an amount of employer benefit; and
(b) on or after 1 July 2016:
(i) the person becomes a member of the Permanent Forces; or
(ii) the person, as a member of the Reserves, begins to render continuous full‑time service.
Those choosing Australian Defence Force Superannuation
(3) A person is not a member of the Scheme if the person has chosen to become an ADF Super member under section 12 of the Australian Defence Force Superannuation Act 2015 (whether or not the person is still an ADF Super member).
8 Cases where person taken not to have ceased to be a member
Where a person ceases to be a member and, immediately after so ceasing, again becomes a member, the person is taken, for the purposes of this Act, not to have ceased to be a member.
Part 4—Contributions
9 Contributions of members to Superannuation Scheme etc. to be deducted from salary
Any contribution payable by a member under the Rules may be deducted from the member’s salary and paid to CSC.
10 Contributions to Superannuation Scheme etc. by Department
(1) The Department must pay to CSC, in accordance with the Rules, all contributions that under the Rules are payable by the Department in respect of a member.
(2) Where any amount payable by the Department under subsection (1) remains unpaid after the day on which payment was due, the Department is liable to pay to CSC interest on that amount at such rate as CSC determines from time to time.
Part 5—Payment of benefits
11 Interpretation
In this Part, a reference, in relation to a person who has ceased to be a member, to a member benefit, or to the part of a member benefit, that is totally funded is a reference to a member benefit, or to that part of a member benefit that consists only of:
(a) contributions that have been paid by the person to CSC on or after the day on which the person became, or last became, a member; and
(b) the interest on those contributions.
12 Member benefits
Where a member benefit becomes payable under the Rules to a person who has ceased to be a member:
(a) if the member benefit is totally funded—the member benefit is payable to the person by CSC; or
(b) if paragraph (a) does not apply:
(i) an amount equal to the part of the member benefit that is totally funded is payable by CSC to the Commonwealth; and
(ii) the member benefit is payable to the person by the Commonwealth.
13 Employer benefits
Where an employer benefit becomes payable under the Rules to a person who has ceased to be a member:
(a) an amount equal to the funded employer benefit in relation to the person is payable by CSC to the Commonwealth; and
(b) any benefit to which the person is entitled is payable to the person by the Commonwealth.
14 Preserved benefits
(1) Where:
(a) a preserved benefit, or part of a preserved benefit, applicable to a person who has ceased to be a member becomes payable; and
(b) the preserved benefit, or the part of the preserved benefit, consists only of an amount of member benefit;
then:
(c) if the preserved benefit consists only of an amount of member benefit that is totally funded—the preserved benefit, or the part of the preserved benefit, is payable to, or in respect of, the person by CSC; or
(d) if paragraph (c) does not apply:
(i) an amount equal to:
(A) if the total amount of preserved benefit is payable—the part of the member benefit that is totally funded; or
(B) if a part of a preserved benefit is payable—a corresponding part of the part of the member benefit that is totally funded;
is payable by CSC to the Commonwealth; and
(ii) the preserved benefit, or the part of the preserved benefit, is payable to, or in respect of, the person by the Commonwealth.
(2) Where:
(a) a preserved benefit applicable to a person who has ceased to be a member becomes payable; and
(b) the preserved benefit includes both an amount of member benefit and an amount of employer benefit;
then:
(c) an amount equal to the sum of:
(i) the part of the member benefit included in the preserved benefit that is totally funded; and
(ii) so much of the funded employer benefit in relation to the person as is included in the preserved benefit;
is payable by CSC to the Commonwealth; and
(d) the preserved benefit is payable to, or in respect of, the person by the Commonwealth.
15 Payment by or to the Commonwealth on reclassification of invalidity pensioner
(1) Where a person who is an invalidity pensioner classified as Class A or Class B is reclassified as Class C, the Commonwealth must pay to CSC an amount equal to the amount of the funded employer benefit in relation to the person at the time when the person was retired on the ground of invalidity.
(2) Where:
(a) a person who was an invalidity pensioner classified as Class A or Class B was reclassified as Class C; and
(b) the person is subsequently reclassified as Class A or Class B;
CSC must pay to the Commonwealth an amount equal to the funded employer benefit in relation to the person.
16 Payment by Commonwealth where an invalidity pensioner again becomes a member
Where a person who is an invalidity pensioner again becomes a member, the Commonwealth must pay to CSC an amount equal to the amount of the funded employer benefit in relation to the person at the time when the person was retired on the ground of invalidity.
16A Payments relating to associate benefits
(1) Where an associate benefit becomes payable under the Rules, the Commonwealth must pay the benefit to such person or persons as are appropriate under the Rules.
(2) CSC must pay to the Commonwealth any amount that CSC is required under the Rules to pay to the Commonwealth in respect of an associate benefit.
16B Recoverable payments
(1) If, apart from this subsection, the Commonwealth does not have power, under this Act, to pay an amount (the relevant amount) to a person (the recipient) purportedly as a benefit under the Rules, then the Commonwealth may pay the relevant amount to the recipient.
Recovery
(2) If a payment is made under subsection (1) to the recipient, the relevant amount:
(a) is a debt due to the Commonwealth by the recipient; and
(b) may be recovered by CSC, on behalf of the Commonwealth, in a court of competent jurisdiction.
(3) If:
(a) a payment is made under subsection (1) to the recipient; and
(b) the recipient is receiving, or is entitled to receive, a benefit under the Rules;
then:
(c) the relevant amount; or
(d) such part of the relevant amount as the Board of CSC determines;
may, if the Board of CSC so directs, be recovered by deduction from that benefit.
16C Recoverable death payments
(1) If, apart from this subsection, the Commonwealth does not have power under this Act to pay an amount (the relevant amount) in any of the following circumstances:
(a) the relevant amount is deposited to an account kept in the name of a deceased person;
(b) the relevant amount is deposited to an account kept in the names of a deceased person and another person;
(c) the relevant amount is paid by way of a cheque made out to a deceased person;
the Commonwealth may pay the relevant amount in the circumstances mentioned in paragraph (a), (b) or (c), so long as:
(d) on the last day on which changes could reasonably be made to the payment of the relevant amount, the chief executive officer (however described) of CSC did not know that the deceased person had died; and
(e) apart from this subsection, the relevant amount would have been payable as a benefit to the deceased person if the deceased person had not died.
(2) If a payment is made under subsection (1), the relevant amount is taken to have been paid to the deceased person’s estate.
Recovery
(3) If a payment is made under subsection (1), the relevant amount:
(a) is a debt due to the Commonwealth by the legal personal representative of the deceased person; and
(b) may be recovered by CSC, on behalf of the Commonwealth, in a court of competent jurisdiction.
16D Reports about recoverable payments and recoverable death payments
(1) CSC must cause a report of the following information to be published, in such manner as the Board of CSC thinks fit:
(a) the number of payments that any employee of CSC was aware of that were made under subsection 16B(1) or 16C(1) during the reporting period (see subsection (2) of this section);
(b) the total amount of payments referred to in paragraph (a);
(c) the number of payments made under subsection 16B(1) or 16C(1) that any employee of CSC became aware of during the reporting period that were made during an earlier reporting period;
(d) the total amount of payments referred to in paragraph (c);
(e) for each payment referred to in paragraph (c)—the reporting period in which the payment was made.
(2) The reporting period is:
(a) a financial year; or
(b) if a shorter recurring period is prescribed under paragraph (5)(a)—that period.
(3) A report is not required if no employee of CSC is aware of any payments referred to in paragraph (1)(a) or (c).
When report must be provided
(4) The report must be provided before the end of the following period:
(a) 4 months after the end of the reporting period;
(b) if a lesser number of months has been prescribed for the reporting period under paragraph (5)(b)—that number of months after the end of the reporting period.
Power to make legislative instruments
(5) The Minister may, by legislative instrument, prescribe:
(a) a period for the purposes of paragraph (2)(b); or
(b) a number of months for a reporting period for the purposes of paragraph (4)(b).
17 Appropriation
Any payment by the Commonwealth under this Part is to be made out of the Consolidated Revenue Fund, which is appropriated accordingly.
Part 6—CSC
18 Functions and powers
(1) The functions and powers of CSC are those set out in the Trust Deed.
Note: For other functions of CSC, see section 8 of the Governance of Australian Government Superannuation Schemes Act 2011.
(2) CSC is also responsible for the general administration of this Act.
Part 9—Miscellaneous
42 Cost of administration of Act etc.
The costs of the administration of this Act and of the Trust Deed, excluding the costs of and incidental to the management of the Fund by CSC and the investment of its money, are to be paid out of money appropriated from time to time by Parliament for the purpose.
42A CSC liable to pay surcharge under the Superannuation Contributions Tax (Assessment and Collection) Act 1997
(1) To remove any doubt, it is stated that:
(a) for the purposes of the Superannuation Contributions Tax (Assessment and Collection) Act 1997, CSC in its capacity as a superannuation provider is an entity distinct from the Commonwealth; and
(b) consequently, section 33 of that Act does not affect the liability of CSC under that Act to pay surcharge on the surchargeable contributions of members.
(2) Amounts payable by CSC under subsection 16(6) of the Superannuation Contributions Tax (Assessment and Collection) Act 1997 are to be paid out of the Consolidated Revenue Fund, which is appropriated accordingly.
43 Recovery of unpaid contributions etc.
(1) Any amount (including an amount of contributions) that is payable to CSC under this Act or the Rules may be recovered by CSC in a court of competent jurisdiction as a debt.
(2) Any contribution payable by a person to CSC under the Rules that remains unpaid when the person ceases to be a member may be deducted from any payment or payments of benefit payable under the Rules to, or in respect of, the person.
(3) Where for any reason (including the making of, or cancellation of, an election under the Rules), CSC had paid an amount of benefit that is, or has become, not payable:
(a) the amount so paid may be recovered by CSC in a court of competent jurisdiction as a debt; or
(b) where the person to whom that amount was paid is receiving, or is entitled to receive, a benefit under the Rules, the amount so paid, or such part of that amount as CSC determines, may, if CSC in its discretion so directs, be recovered by deduction from that benefit.
44 Payment of fees
(1) Such fees as are prescribed are payable to the Commonwealth by a person who, under the Rules, requests CSC to reconsider one of its decisions.
(2) The regulations may make provision for and in relation to the refund of any fees paid under subsection (1).
45 Assignment of benefits
No pension or other benefit payable under the Rules is capable of being assigned.
46 Member etc. bound by Rules
(1) A person who is, or has ceased to be, a member is subject to the Rules to the extent that they are applicable in relation to the person.
(1A) A person who is, or has ceased to be, an associate is subject to the Rules to the extent that they are applicable in relation to the person. For this purpose, associate means a person to whom an associate benefit is payable.
(2) The Commonwealth is subject to the Rules to the extent that they are applicable in relation to the Commonwealth.
47 Indemnification
(1) Any matter or thing done, or omitted to be done, in good faith by:
(d) a member of an Incapacity Classification Committee established under the Rules; or
(e) a member of a Reconsideration Advisory Committee established under the Rules;
does not subject him or her personally to any action, liability, claim or demand.
(2) Subsection (1) does not preclude CSC from being subject to any action, liability, claim or demand.
48 Bank not liable in respect of certain payments out of account of deceased pensioner
(1) In this section:
bank includes, but is not limited to, a body corporate that is an ADI (authorised deposit‑taking institution) for the purposes of the Banking Act 1959.
primary pension means a pension payable to a pensioner.
(2) Where:
(a) after the death of a retirement pensioner, an amount purporting to be an instalment of primary pension payable to the pensioner on a pension pay day not later than the 7th pension pay day after his or her death is paid into an account of the pensioner with a bank; and
(b) the bank pays, out of that account, to the spouse of the deceased pensioner an amount not exceeding the amount so paid into the account;
then, in spite of any other law, the bank is not liable to the Commonwealth, the personal representative of the deceased pensioner or anyone else for any loss incurred because of the payment of that amount to the spouse of the pensioner.
48A CSC may rely on information supplied by the Department
(1) For the purposes of the Trust Deed in its application to or in respect of a person who is or has been a member of the Scheme, CSC may presume that any information provided to CSC by the Department is correct.
(2) If a tribunal, authority or person is empowered:
(a) to review a decision of CSC under this Act, the regulations or the Trust Deed; and
(b) to vary, or make a decision in substitution for, CSC’s decision under this Act, the regulations or the Trust Deed;
the tribunal, authority or person is not bound by any presumption made by CSC under subsection (1).
49 Amendments to Trust Deed disallowable under the Legislation Act 2003
Despite regulations made for the purposes of paragraph 44(2)(b) of the Legislation Act 2003, section 42 (disallowance) of that Act applies to an instrument amending the Trust Deed.
51 Delegation by Minister
The Minister may, by signed instrument, delegate all or any of his or her powers under this Act or the regulations to:
(a) CSC or an employee of CSC; or
(aa) a director (within the meaning of the Governance of Australian Government Superannuation Schemes Act 2011); or
(b) an officer of the Department; or
(d) an officer of the Defence Force.
51A Transitional—MSB Instrument No. 3 of 1993 to have retrospective effect
Application
(1) This section applies to a member benefit that was or is payable under the Rules to a person because the person ceased to be a member during either of the following periods:
(a) the period beginning on 1 October 1991 and ending at the end of 26 May 1992;
(b) the period beginning on 9 September 1992 and ending at the end of 21 April 1993.
Retrospective effect
(2) In calculating the member benefit, the Rules have effect as if MSB Instrument No. 3 of 1993 had been made, and had come into force, on 1 October 1991.
Repayment of excess
(3) If:
(a) the member benefit has been paid to the person; and
(b) the amount paid exceeds the amount that the person would have been entitled to be paid if MSB Instrument No. 3 of 1993 had been made, and had come into force, on 1 October 1991;
the person is liable to repay the amount of the excess.
Recovery of repayment
(4) If a person is liable to repay an amount under subsection (3):
(a) the amount may be recovered as a debt due to the Board or the Commonwealth, as the case may be; and
(b) the amount may be deducted from any other amount that is payable to the person by the Board or the Commonwealth, as the case may be.
Definition
(5) In this section:
MSB Instrument No. 3 of 1993 means Instrument No. 3 of 1993 made under subsection 5(1) on 19 April 1993 and notified in the Gazette on 22 April 1993.
51B Transitional—recoverable payments relating to retention benefit
(1) If, apart from this subsection, the Commonwealth does not have power, under repealed Part 8 of this Act as continued in force by item 4 of Schedule 4 to the Defence Legislation Amendment Act (No. 1) 2005, to pay an amount (the relevant amount) to a person (the recipient) purportedly as a retention benefit, then the Commonwealth may pay the relevant amount to the recipient.
Recovery
(2) If a payment is made under subsection (1) to the recipient, the relevant amount:
(a) is a debt due to the Commonwealth by the recipient; and
(b) may be recovered by the Secretary of the Department, on behalf of the Commonwealth, in a court of competent jurisdiction.
(3) If:
(a) a payment is made under subsection (1) to the recipient; and
(b) the recipient is receiving, or is entitled to receive, an amount under a determination made under Part IIIA of the Defence Act 1903;
then:
(c) the relevant amount; or
(d) such part of the relevant amount as the Secretary of the Department determines;
may, if the Secretary of the Department so directs, be recovered by deduction from the amount mentioned in paragraph (b).
Appropriation
(4) For the purposes of repealed section 39 of this Act as continued in force by item 4 of Schedule 4 to the Defence Legislation Amendment Act (No. 1) 2005, a payment under subsection (1) of this section is taken to be a retention benefit.
Retention benefit
(5) For the purposes of this section, retention benefit means retention benefit under repealed Part 8 of this Act as continued in force by item 4 of Schedule 4 to the Defence Legislation Amendment Act (No. 1) 2005.
51C Transitional—reports about recoverable payments
(1) During the applicable publication period for a reporting period, the Secretary of the Department must cause to be published, in such manner as the Secretary thinks fit, a report that sets out:
(a) the number of payments made under subsection 51B(1) during the reporting period; and
(b) the total amount of those payments.
(2) However, a report is not required if the number mentioned in paragraph (1)(a) is zero.
Deferred reporting
(3) Subsection (1) of this section does not require a report to deal with a payment unless, before the preparation of the report, a Departmental official was aware the payment was made under subsection 51B(1).
(4) For the purposes of this section, if:
(a) a payment was made under subsection 51B(1) in a reporting period; and
(b) because of subsection (3) of this section, subsection (1) of this section did not require a report to deal with the payment; and
(c) during a later reporting period, a Departmental official becomes aware that the payment was made under subsection 51B(1);
the payment is subject to a deferred reporting obligation in relation to the later reporting period.
(5) If one or more payments made under subsection 51B(1) during a reporting period are subject to a deferred reporting obligation in relation to a later reporting period, the Secretary of the Department must, during the applicable publication period for the later reporting period:
(a) prepare a report that sets out:
(i) the number of those payments; and
(ii) the total amount of those payments; and
(iii) the reporting period during which the payments were made; and
(b) if a report is required under subsection (1) in relation to the later reporting period—include the paragraph (a) report in the subsection (1) report; and
(c) if paragraph (b) does not apply—publish, in such manner as the Secretary thinks fit, the paragraph (a) report.
Reporting period
(6) For the purposes of this section, a reporting period is:
(a) a financial year; or
(b) if a shorter recurring period is specified in a legislative instrument made by the Minister—that period.
Applicable publication period
(7) For the purposes of this section, the applicable publication period for a reporting period is the period of:
(a) 4 months; or
(b) if a lesser number of months is specified, in relation to the reporting period, in a legislative instrument made by the Minister—that number of months;
beginning immediately after the end of the reporting period.
Departmental official
(8) For the purposes of this section, Departmental official means an official (within the meaning of the Public Governance, Performance and Accountability Act 2013) of the Department.
52 Regulations
(1) The Governor‑General may make regulations, not inconsistent with this Act, prescribing all matters that:
(a) are required or permitted to be prescribed by this Act; or
(b) are necessary or convenient to be prescribed for carrying out or giving effect to this Act.
(2) Regulations may not be made after the commencement of this subsection unless:
(a) CSC has consented to the making of the regulations; or
(b) the regulations:
(i) relate to a payment of an employer contribution that will, after the making of the regulations, be required or permitted to be made under this Act; or
(ii) relate solely to the termination of the Scheme; or
(iii) are made in circumstances covered by regulations made for the purposes of subparagraph 60(1)(b)(iii) of the Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Act 1993.
(3) For the purposes of subparagraph (2)(b)(i), a payment under the Trust Deed is taken to be a payment of an employer contribution.
(2) Interpretations of the following matters, for the purposes of these Rules, are provided in Parts 6 to 9 of Schedule 1:
Part 6 Parts of speech and grammatical forms
Part 7 Number
Part 8 Reckoning of time
Part 9 Attainment of particular age.
Part 2—Contributions
Contributions by members
3. (1) A member is required to pay a contribution each fortnight in accordance with this Division.
(2) Where contributions by a member fall due during a period when he or she is on leave without pay, the member, or a person acting on his or her behalf, is to pay those contributions:
(a) each fortnight; or
(b) in such instalments and at such times as CSC approves; or
(c) with the approval of CSC, in a lump sum.
Amount of contributions
4. (1) Subject to subrule (2), the amount of the contribution payable by a member in a fortnight is an amount equal to the relevant percentage of the amount of the salary paid to the member in that fortnight.
(2) Where a member elects under subrule (10) to vary the amount of the contribution payable by him or her, that election has effect in relation to the first salary fortnight in relation to which it can be applied in the ordinary course of business.
(3) Where a member makes an election under subrule (10), the member is not entitled to make a further election until the expiration of a period of three months after the day on which the earlier election was made.
(4) For the purposes of subrule (1), salary is taken not to be paid to a member in respect of a day included in a period that, in accordance with Schedule 2, is a prescribed period.
(5) Where:
(a) the salary and allowances of a member in respect of a period are forfeited, in whole or in part, under regulations made under the Defence Act 1903; and
(b) the period does not exceed 21 consecutive days;
the amounts of the contributions payable by the member in respect of that period are to be calculated as if the member were on full pay.
(6) Subject to subrule (7), where a member who is granted:
(a) long service leave on half pay; or
(b) leave without pay for a period not exceeding 21 days;
the amounts of the contributions payable by the member in respect of that period are to be calculated as if the member were on full pay.
(7) In a case to which paragraph (6) (b) applies, the member’s salary for the purpose of calculating the contribution payable by the member is taken not to include higher duties allowance unless:
(a) higher duties allowance was payable to the member on the day immediately preceding the commencement of the period; and
(b) an appropriate authority of the Defence Force has notified CSC that, but for the member’s absence on leave without pay, higher duties allowance would have been payable to the member in respect of the whole of the period of his or her absence on that leave.
(8) In calculating the amount of a contribution payable by a member, the calculation is to be made as if no deductions were made from the member’s salary.
(9) Where the amount of a contribution payable by a member includes a fraction of a cent:
(a) if the fraction is less than one‑half of a cent—the contribution is taken to be reduced by the amount of the fraction; or
(b) if the fraction is one‑half of a cent or more—the contribution is taken to be increased by treating the fraction as one cent.
(10) In this rule:
“relevant percentage”, in relation to a member, means:
(a) the percentage, being a whole number that is not less than 5 and not more than 10, elected by the member; or
(b) if the member has not made an election—5 per centum.
Cessation of contributions on reaching maximum benefit limit
5. (1) A member is not entitled to pay contributions after he or she has been notified that his or her total benefit equals or exceeds his or her pension maximum benefit limit.
(2) At any time after a member is notified that his or her total benefit equals or exceeds his or her lump sum maximum benefit limit, he or she may elect to cease paying contributions.
(3) This rule applies in spite of anything in this Part.
Contributions while on leave without pay in connection with birth of child etc.
6. A member who is on leave without pay for a period exceeding 21 days which was granted to him or her in connection with:
(a) the birth of a child of the member; or
(b) other termination of the pregnancy of the member; or
(c) the adoption of a child by the member;
may elect to pay contributions, calculated as if the member were on full pay, in respect of so much of that period, not exceeding 9 months, as is specified in the election.
Contributions while on other leave without pay
7. (1) This rule does not apply to a period of leave without pay to which rule 6 applies.
(2) Where a member who is on leave without pay for a period exceeding 21 days which was granted to him or her:
(a) for the purpose of the member:
(i) engaging, with the approval of the appropriate authority of the Defence Force, in full time employment; or
(ii) undertaking further education; or
(iii) undergoing training; or
(iv) engaging in some other activity;
and, in the case of subparagraph (ii), (iii) or (iv), an appropriate authority of the Defence Force has notified CSC that the education, training or other activity is relevant to the requirements of the Defence Force; or
(b) because the member was for the time being physically or mentally incapable of performing his or her duties;
the member may, with the approval of CSC, elect to pay contributions, calculated as if the member were on full pay, in respect of so much of the period as is specified in the election.
(3) Where:
(a) leave without pay is granted to a member (in this subrule called the “inactive member”) whose spouse (in this subrule called the “active member”):
(i) is also a member; or
(ii) is an eligible member of the Defence Force within the meaning of the 1973 Act; and
(b) the active member is posted to a locality to which the inactive member is unable to obtain a posting; and
(c) the inactive member is granted the leave without pay in order not to be separated from the active member;
the inactive member may elect to pay contributions, calculated as if the member were on full pay, in respect of so much of that period, not exceeding 2 years, as is specified in the election.
(4) In this rule:
“spouse”, in relation to a member, means a person who is legally married to the member and includes a person who, although not legally married to the member, ordinarily lives with the member as his or her husband or wife, as the case may be, on a permanent and bona fide domestic basis and is not of the same sex as the member.
General conditions applicable to contributions under rules 6 and 7
8. (1) The provisions of rule 4 apply to an election made under rule 6 or 7 as if:
(a) the reference in that rule to the amount of salary paid to the member in a fortnight were a reference to the amount of salary that would have been paid to the member in that fortnight if the member had been on full pay; and
(b) the salary so assumed to be paid did not include higher duties allowance unless:
(a) higher duties allowance was payable to the member on the day immediately before the commencement of the period; and
(b) an appropriate authority of the Defence Force has notified CSC that, but for the member’s absence on leave without pay, higher duties allowance would have been payable to the member in respect of the whole of the period of his or her absence on that leave.
(2) A member who has made an election under rule 6 or 7 may revoke the election at any time after the expiration of a period of 3 months after the election was made.
Member contributions to be paid to CSC
9. Contributions payable by a member are to be paid to CSC by or on behalf of the member.
Liability of Department to pay employer contributions
10. (1) The Department must, on each salary pay‑day on which a member pays contributions, pay to CSC an employer contribution in relation to the member.
(2) In spite of a member paying contributions during a period of leave without pay to which rule 7 applies, subrule (1) does not apply:
(a) in the case of a period of leave without pay referred to in subrule 7 (2) which exceeds 12 months—to any part of the excess period in respect of which no amount is paid under a prescribed arrangement; or
(b) in the case of a period of leave without pay referred to in subrule 7 (3).
(3) The amount of an employer contribution payable by the Department in relation to a member is an amount that is 3 per centum of the amount of the salary payable to the member in respect of the relevant fortnight.
(4) In this rule:
“member’s employer”, in relation to a member who is engaged in employment referred to in subparagraph 7 (2) (a) (i), means the person who is the employer of the member in respect of that employment.
“prescribed arrangement”, in relation to a member who is engaged in employment referred to in subparagraph 7 (2) (a) (i), means an arrangement between the Commonwealth and the member’s employer under which the employer agrees to pay to the Commonwealth an employer contribution, in relation to the member:
(a) in respect of each salary fortnight in the period of that employment; or
(b) in respect of each salary fortnight in a specified part of that period;
as the case may be, in respect of which the member pays a contribution under this Part.
Payment of contributions into Fund
11. CSC must pay all member and employer contributions received by it into the Fund.
Part 3—Members’ Benefits
Division 1—Benefits other than Invalidity Benefits
Benefits on retirement before reaching 55 years of age or earlier retiring age, otherwise than for redundancy or retrenchment etc.
12. (1) This rule applies to a member who retires:
(a) in the case of a member whose retiring age is less than 55 years—before reaching his or her retiring age; or
(b) in any other case—before reaching the age of 55 years;
not being a member who is:
(c) retired on the ground of redundancy or retrenchment; or
(d) entitled to an invalidity pension.
(2) Subject to rule 15, in the case of a person to whom this rule applies:
(a) his or her member benefit is payable to him or her as a lump sum; and
(b) there is applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of the amount of his or her employer benefit.
(3) Subject to rule 15, a person who is entitled to be paid a member benefit under paragraph (2) (a) may elect that, instead of that benefit being paid to him or her, there be applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of the amount of the member benefit and if he or she so elects:
(a) the member benefit is not payable to him or her as a lump sum; and
(b) there is applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of that amount.
Benefits on retirement for redundancy or retrenchment or on attaining retiring age of less than 55 years
13. (1) Where a member is retired on the ground of redundancy or retrenchment and he or she is not entitled to an invalidity pension:
(a) his or her member benefit is payable to him or her as a lump sum; and
(b) there is applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of the amount of his or her employer benefit.
(2) Where a member retires and, on that retirement:
(a) he or she has reached his or her retiring age;
(b) that retiring age is less than 55 years; and
(c) he or she is not entitled to an invalidity pension;
then:
(d) his or her member benefit is payable to him or her as a lump sum; and
(e) there is applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of the amount of his or her employer benefit.
(3) A person who is entitled to be paid a member benefit under paragraph (1) (a) or (2) (d) may elect that, instead of that benefit being paid to him or her, there be applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of the amount of the member benefit and if he or she so elects:
(a) the member benefit is not payable to him or her as a lump sum; and
(b) there is applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of that amount.
(4) A person to whom a preserved benefit is applicable under paragraph (1) (b) or (2) (e) may elect that, instead of that benefit being so preserved, it be converted into a pension payable to him or her and if he or she so elects:
(a) a preserved benefit of the amount of the benefit is not applicable to him or her; and
(b) the benefit is converted into a pension payable to him or her.
(5) Where:
(a) a member retired and, on that retirement, subrule (2) applied to him or her; and
(b) he or she again became a member and again retires; and
(c) on the last‑mentioned retirement the member is not entitled to an invalidity pension;
then, for the purposes of these Rules, the person is taken to be a person to whom subrule (2) applies.
Benefits on retirement on or after attaining age of 55 years
14. Where a member retires:
(a) on or after attaining the age of 55 years; and
(b) he or she is not entitled to an invalidity pension;
there is applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of the amount of his or her member benefit and employer benefit.
Payment of benefits where rule 12 applies and person has less than 12 months’ eligible service
15. (1) This rule applies to a person to whom rule 12 applies who has less than 12 months’ eligible service and whose employer benefit consists wholly of funded employer benefit.
(2) Where the person’s employer benefit is an amount to which the preservation standards set out in the Occupational Superannuation Standards Regulations apply, he or she may elect that, instead of his or her employer benefit being preserved in the Fund, it is paid to a preservation fund, or used to purchase a deferred annuity, of his or her choice, and if he or she does so:
(a) his or her employer benefit is payable to that preservation fund or to be used to purchase that annuity, as the case may be; and
(b) he or she is not entitled to elect under subrule 12 (3) to have applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of the amount of his or her member benefit.
(3) Where the person’s employer benefit is an amount to which the preservation standards set out in the Occupational Superannuation Standards Regulations do not apply, he or she may elect that his or her employer benefit is paid to him or her as a lump sum, and if he or she so elects:
(a) his or her employer benefit is payable to him or her as a lump sum; and
(b) he or she is not entitled to elect under subrule 12 (3) to have applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of his or her member benefit.
(4) In spite of anything in this rule or in rule 12, where a person to whom this rule applies does not elect that there be applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of the amount of his or her member benefit, there is not applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of his or her employer benefit, but instead:
(a) if the employer benefit is an amount referred to in subrule (2), it is payable to a preservation fund, or used to purchase a deferred annuity, of his or her choice; or
(b) in any other case, it is payable to him or her as a lump sum.
(5) In this rule:
“preservation fund” means a fund that is required, in accordance with the standards set out in the Occupational Superannuation Standards Regulations, to preserve benefits transferred to the fund from a superannuation fund in accordance with those regulations.
Limitation on certain benefits in case of certain transferees who retire before completing 731 days’ service after 30 September 1991
16. (1) Where a person who transferred from the 1973 Scheme before 1 October 1992 retires before completing 731 days of contributory service after 30 September 1991 otherwise than:
(a) on reaching his or her retiring age; or
(b) on the ground of invalidity, redundancy or retrenchment;
the amount of member benefit which he or she would, but for this rule, be entitled to be paid is reduced by substituting for the amount of interest applicable in relation to him or her under the relevant provisions an amount calculated in accordance with the formula:
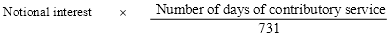
where:
“Notional interest” means the amount of interest applicable in relation to the person under the relevant provisions; and
“Number of days of contributory service” means the number of days of contributory service by the person after 30 September 1991.
(2) A reference in this rule to a person who retires on the ground of invalidity is taken not to include a reference to a person who, by reason of rule 31, 32 or 33, is not entitled to invalidity benefits.
(3) In this rule:
“contributory service”, in relation to a person, means service by the person in respect of which the person paid contributions under Part 2 or contributions under section 17 of the 1973 Act;
“relevant provisions” means subparagraph (e) (ii) of Schedule 9 and paragraph 1(b) of Schedule 10.
Division 2—Invalidity Benefits
Subdivision A—Incapacity Classification
Establishment of Incapacity Classification Committee
17. CSC must establish an Incapacity Classification Committee.
Membership of Committee
18. (1) The Committee comprises such number of persons as CSC determines.
(2) The qualifications of each member of the Committee are such as CSC determines.
Functions of Committee
19. (1) The functions of the Committee are to exercise, at the request of CSC and subject to any directions given by CSC, the powers and functions under rules 22 and 23.
(2) When determining the classification of, or reclassifying, an invalidity retiree, the Committee:
(a) must take into account any evidence relating to that retiree that is made available or submitted to it; and
(b) may take steps to obtain any other evidence that it considers necessary to properly determine the classification.
(3) CSC must make available to the Committee any medical or other evidence that it has concerning the invalidity retiree whose classification or reclassification is being considered and that is relevant to his or her classification.
Proceedings of Committee
20. Subject to any directions given by CSC, the Committee may regulate its proceedings as the Committee thinks fit.
Decisions by Committee
21. The Committee must notify CSC of its decision as to the classification or reclassification of an invalidity retiree, giving reasons for its decision.
Classification in respect of incapacity
22. (1) Where a member is retired on the ground of invalidity, CSC or the Committee must determine the percentage of incapacity in relation to civil employment of the invalidity retiree and must classify the retiree according to the percentage of incapacity as follows:
Percentage of Incapacity | Class |
60% or more | A |
30% or more but less than 60% | B |
Less than 30% | C |
(2) In determining, for the purposes of subrule (1), the percentage of incapacity in relation to civil employment of an invalidity retiree, CSC or the Committee must have regard to the following matters only:
(a) the vocational, trade and professional skills, qualifications and experience of the retiree;
(b) the kinds of civil employment which a person with the skills, qualifications and experience referred to in paragraph (a) might reasonably undertake;
(c) the degree to which the physical or mental impairment of the retiree that is the cause of the invalidity by reason of which he or she has been retired has diminished his or her capacity to undertake the kinds of civil employment referred to in paragraph (b).
(3) The death of a person after he or she has been retired on the ground of invalidity does not prevent the classifying of the person under subrule (1).
(4) This rule does not apply to a person who, by reason of rule 31, 32 or 33, is not entitled to invalidity benefits.
Reclassification in respect of incapacity
23. (1) Where CSC or the Committee, at any time, is satisfied that there has been such a change in the percentage of incapacity in relation to civil employment of an invalidity pensioner that his or her classification should be altered, CSC or the Committee may reclassify him or her in the appropriate classification set out in rule 22 according to the percentage of his or her incapacity in relation to civil employment.
(2) Where an invalidity pensioner has attained the age of 55 years and the invalidity pensioner is classified:
(a) as Class A—subrule (1) does not apply to him or her; or
(b) as Class B—subrule (1) is taken not to empower CSC to reclassify him or her as Class C.
(3) In determining, for the purposes of subrule (1), the percentage of incapacity in relation to civil employment of an invalidity pensioner, CSC or the Committee must have regard to the following matters only:
(a) the vocational, trade and professional skills, qualifications and experience of the pensioner;
(b) the kinds of civil employment which a person with skills, qualifications and experience referred to in paragraph (a) might reasonably undertake;
(c) the degree to which any physical or mental impairment of the pensioner, being a prescribed physical or mental impairment, has diminished his or her capacity to undertake the kinds of civil employment referred to in paragraph (b).
(4) Where CSC or the Committee reclassifies a person under this rule, CSC or the Committee must specify the date from which the reclassification has effect and, on and after that date, the person is, for the purposes of these Rules, taken to be classified under rule 22 accordingly.
(5) Where CSC or the Committee reclassifies a person under this rule, the date specified by CSC or the Committee as the date from which the reclassification has effect is not to be a date earlier than the date on which CSC or the Committee reclassifies the member unless:
(a) the person is reclassified as Class A or, having been classified as Class C, is reclassified as Class B; and
(b) CSC or the Committee is satisfied that special circumstances exist that justify an earlier date being so specified.
(6) Where a person who was retired otherwise than on the ground of invalidity is, by virtue of rule 30, treated as if he or she had been retired on the ground of invalidity, CSC or the Committee may, despite subrule (5), on the same day on which it classifies him or her under rule 22, reclassify him or her under this rule with effect from a date after the date of his or her retirement but before the date on which CSC or the Committee makes the reclassification.
(7) The death of a person after he or she has been classified under rule 22 or reclassified under this rule does not prevent the reclassifying of the person under subrule (1).
(8) For the purposes of this rule, a person who:
(a) is classified as Class C; and
(b) immediately before being so classified was an invalidity pensioner;
is taken to be an invalidity pensioner.
(9) This rule does not apply to a person who has attained the age of 65 years.
(10) In this rule:
“prescribed physical or mental impairment”, in relation to an invalidity pensioner, means:
(a) a physical or mental impairment of the pensioner that was the cause, or one of the causes, of the invalidity by reason of which he or she was retired, whether or not that impairment has changed, for better or worse, since that retirement; or
(b) any other physical or mental impairment of the pensioner causally connected with a physical or mental impairment referred to in paragraph (a).
Decision as to classification or reclassification to be notified to invalidity retiree
24. CSC must notify an invalidity retiree in writing of any decision under rule 22 or 23 as to the classification or reclassification of the retiree and the reasons for that decision.
Power of CSC to require persons to be medically examined etc.
25. (1) CSC may, by notice in writing given to a person in receipt of an invalidity pension, require him or her:
(a) to submit himself or herself for medical examination by a legally qualified medical practitioner at a time and place specified in the notice; or
(b) to furnish in writing to CSC, within such period as is specified in the notice, such information as is required by the notice with respect to any employment (whether as an employee or on his or her own account) in which he or she has been engaged during such period as is specified in the notice.
(2) A notice under subrule (1) must set out the effect of subrule (3).
(3) Where a person fails to comply with a notice given under subrule (1) and CSC is not satisfied that there was a reasonable excuse for the failure, CSC may, by notice in writing given to the person, suspend the person’s invalidity pension with effect from a day determined by CSC, being a day not earlier than:
(a) in a case where the first‑mentioned notice required the person to submit to a medical examination on a day specified in the notice—the day next following that day; or
(b) in a case where the first‑mentioned notice required the person to furnish information within a period specified in the notice—the day next following the end of that period.
(4) A notice to a person under subrule (3) must set out the effect of subrules (7), (9) and (10).
(5) An invalidity pension is not payable in respect of a period during which a suspension under subrule (3) is in force.
(6) Where:
(a) the invalidity pension of a person is suspended under subrule (3); and
(b) CSC, having regard to such matters as it considers relevant, is of the opinion that the suspension should be revoked;
CSC may, by notice in writing given to the person, revoke the suspension with effect from a day determined by CSC, being a day not later than the day on which the notice is given.
(7) Without limiting subrule (6), where the invalidity pension of a person is suspended under subrule (3), the person may, by notice in writing given to CSC, request CSC to revoke the suspension and, where such a request is made, CSC must, by notice in writing given to the person:
(a) if the invalidity pension has been suspended by virtue of the relevant person’s having failed to comply with a notice requiring the person to submit to a medical examination—require the person to submit to a medical examination by a medical practitioner at a time and place specified in the second‑mentioned notice; or
(b) if the invalidity pension has been suspended by virtue of the person’s having failed to comply with a notice requiring the person to give information to CSC (in this paragraph called “the original notice”)—require the person to give in writing to CSC, within such period as is specified in the second‑mentioned notice, such information as was required by the original notice to be given.
(8) A notice given by CSC under subrule (7) must set out the effect of subrules (9) and (10).
(9) Where:
(a) because of a request having been made to revoke the suspension of the invalidity pension of a person, a notice under subrule (7) is given to the person: and
(b) either:
(i) the person complies with the notice; or
(ii) the person fails to comply with the notice but CSC is satisfied that there was a reasonable excuse for the failure;
CSC must, by notice in writing given to the person, revoke the suspension with effect from a day determined by CSC, being a day not later than:
(c) in a case to which subparagraph (b) (i) applies—the day on which the person so complied with the notice; or
(d) in a case to which subparagraph (b) (ii) applies:
(i) the day on which CSC became so satisfied; or
(ii) if CSC is satisfied that it would be equitable in the circumstances of the case for the revocation to have effect from an earlier day—from that earlier day.
(10) Where:
(a) because of a request having been made to revoke the suspension of the invalidity pension of a person, a notice under subrule (7) is given to the person; and
(b) the person fails to comply with the notice and CSC is not satisfied that there was a reasonable excuse for the failure;
CSC must, by notice in writing given to the person, refuse to revoke the suspension.
(11) A notice required or permitted to be given:
(a) to a person by CSC under subrule (6), (7), (9) or (10) may be given to a person acting on his or her behalf; or
(b) to CSC by a person under this rule may be given by a person acting on his or her behalf.
(12) Where CSC is required by this rule to give a person a notice, the notice is taken to have been given to the person if:
(a) the notice is served on the person personally; or
(b) the notice is sent to the person by pre‑paid post as a letter and the person acknowledges receipt of the letter; or
(c) where CSC has caused all reasonable steps to be taken to ascertain a reliable address of the person, the notice is sent to the person by prepaid post to:
(i) in a case where CSC is satisfied that at least one reliable address of the person has been ascertained—that address or one of those addresses; or
(ii) in any other case—the last address of the person known to CSC.
(13) A reference in subrule (12) to a reliable address of a person is a reference to an address where, if a letter were sent to the person by pre‑paid post to the address, the person would probably receive the letter.
Subdivision B—Invalidity Benefits
Entitlement to invalidity benefits
26. A person who is classified as Class A or Class B under rule 22 (whether on his or her retirement or by reason of his or her having been reclassified under rule 23) is entitled to invalidity benefits in accordance with this Division.
Invalidity benefits for person classified as Class A
27. (1) Where a person who is entitled to invalidity benefits is classified as Class A:
(a) his or her member benefit is payable to him or her as a lump sum; and
(b) his or her employer benefit is converted into a pension payable to him or her.
(2) A person who is entitled to be paid a member benefit under subrule (1) may elect that, instead of that benefit being paid to him or her, there be applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of the amount of the benefit and if he or she so elects:
(a) the member benefit is not payable to him or her as a lump sum; and
(b) there is applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of that amount.
Invalidity benefits for person classified as Class B
28. (1) Where a person who is entitled to invalidity benefits is classified as Class B:
(a) his or her member benefit is payable to him or her as a lump sum; and
(b) a pension is payable to him or her at an annual rate equal to:
(i) half the rate of the pension which would have been payable to him or her if he or she had been classified as Class A; or
(ii) the rate of the pension which would have been payable to him or her if he or she:
(A) had been retired otherwise than on the ground of invalidity; and
(B) were entitled to elect to convert his or her employer benefit into a pension and had elected to do so;
whichever is the greater.
(2) A person who is entitled to be paid a member benefit under subrule (1) may elect that, instead of that benefit being paid to him or her, there be applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of the amount of the benefit and if he or she so elects:
(a) the member benefit is not payable to him or her as a lump sum; and
(b) there is applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of that amount.
Effect of change of invalidity classification on pension and preserved benefit
29. (1) Where a person who is classified as Class A or Class B is reclassified as Class C:
(a) the pension payable to him or her under rule 27 or 28 is cancelled; and
(b) there is applicable to him or her a preserved benefit of the amount of his or her employer benefit.
(2) If a person referred to in subrule (1) is subsequently reclassified as Class A or Class B:
(a) the preserved benefit referred to in that subrule ceases to be applicable to him or her; and
(b) a pension is payable to him or her in accordance with rule 27 or 28, as the case may be, from the date specified under rule 23 by CSC or the Committee, as the case may be, as the date from which the reclassification has effect.
Person may be treated as having been retired on ground of invalidity
30. (1) Where a person has been retired otherwise than on the ground of invalidity but, after his or her retirement, CSC is satisfied that, at the time the person was retired, grounds existed on which he or she could have been retired on the ground of invalidity, CSC may, for the purposes of these Rules, treat the person as if he or she had been retired on the last‑mentioned ground.
(2) Where, because of action taken under subrule (1), a person is classified as Class A or Class B under rule 22:
(a) so much of the preserved benefit applicable to him or her under rule 12, 13 or 14 as consists of employer benefit ceases to be applicable to him or her; and
(b) a pension is payable to him or her in accordance with rule 27 or 28, as the case may be.
Subdivision C—Invalidity Benefits Not Payable
Person classified as Class C
31. A person who is classified as Class C is not entitled to invalidity benefits under this Division.
Pre‑existing condition
32. (1) Where:
(a) a member is, within a period of 2 years after becoming a member, retired on the ground of invalidity; and
(b) CSC is satisfied that:
(i) the invalidity was caused, or was substantially contributed to, by a physical or mental condition that existed at the time when he or she became a member; and
(ii) the condition was not materially aggravated by his or her service after becoming a member;
the person is not entitled to invalidity benefits under this Division.
(2) Where:
(a) a person who has retired again becomes a member after a break in the continuity of his or her service; and
(b) he or she is not a person who again became a member pursuant to the Parliamentary Candidates Act; and
(c) he or she is subsequently retired on the ground of invalidity;
the person is, for the purposes of subrule (1), treated as if he or she had first become a member at the time when he or she again became a member.
Invalidity due to intentional act
33. (1) Where:
(a) a member is retired on the ground of invalidity; and
(b) CSC is satisfied that the invalidity was due to an intentional act on his or her part for the purpose of obtaining invalidity benefits under this Division;
he or she is not entitled to invalidity benefits under this Division.
(2) Subrule (1) does not apply in a case where CSC is of the opinion:
(a) that the condition which formed the ground on which the person was retired was not wholly due to the intentional act of the person; or
(b) that the action of the person was caused by his or her physical or mental condition.
Invalidity arising during absence without leave exceeding 21 days
34. (1) Where:
(a) a member is retired on the ground of invalidity; and
(b) CSC is satisfied that the invalidity was caused, or was substantially contributed to, by an occurrence that happened at a time when he or she was absent without leave and had been so absent for a period exceeding 21 consecutive days; and
(c) the salary and allowances of the member in respect of the period were forfeited under regulations made under the Defence Act 1903 and an amount equal to the amount of the salary and allowances so forfeited was not subsequently paid, and is not payable, under those regulations to him or her;
he or she is not entitled to invalidity benefits under this Division.
(2) This rule does not apply in a case where CSC is satisfied that the absence of the member was due to sufficiently mitigating circumstances.
Division 3—Person Rejoining the Scheme
Suspension of pension of retirement pensioner other than invalidity retiree
35. Where a person who is in receipt of a pension under Division 1 again becomes a member, the pension is suspended for the duration of his or her membership and is not payable while it is suspended.
Cancellation of pension etc. of invalidity retiree
36. Where a person, who was a member and was retired on the ground of invalidity, again becomes a member:
(a) any determination of his or her incapacity in relation to civil employment and consequent classification or reclassification, under rule 22 or 23, is cancelled; and
(b) if he or she was, immediately before again becoming a member, a person to whom an invalidity pension was payable, his or her entitlement to that pension is cancelled; and
(c) when the person again retires, he or she is not treated as having been retired on the ground of invalidity only by reason of his or her retirement on that ground from his or her earlier period of service.
Continuation of previous election to cease paying contributions
37. Where:
(a) immediately before a person ceased to be a member, the person was, in consequence of an election made by him or her under subrule 5 (2), not paying contributions; and
(b) the person again becomes a member;
that election is taken to be again in force in relation to the member as if it had been made after the member again became a member.
Part 5—Spouses’ and Children’s Benefits
Division 1—Death of a Member
Applicability of benefits
38. Where a member dies and is survived by a spouse or spouses or an eligible child or children, benefits are payable in accordance with this Division.
Payment of deceased member’s member benefit
39. A deceased member’s member benefit is payable as a lump sum as follows:
(a) if the deceased member is survived by a spouse, the benefit is payable to the spouse;
(b) if the deceased member is not survived by a spouse but is survived by an eligible child or children, the benefit is payable to, or for the benefit of, the child or children;
(c) if the deceased member is not survived by a spouse or an eligible child and he or she had notified CSC in writing that:
(i) he or she had a person or persons dependent on him or her who would not be eligible to receive benefits as a spouse or eligible child; and
(ii) he or she had made provision for that person or those persons in his or her will;
the benefit is payable to, or for the benefit of, the person or persons;
(d) in any other case the benefit is payable to the deceased member’s personal representative.
Payment of deceased member’s employer benefit
40. (1) A deceased member’s employer benefit or a pension is payable as follows:
(a) if the deceased member is survived by a spouse with or without an eligible child or children, the employer benefit is payable to the spouse as a lump sum;
(b) if the deceased member is not survived by a spouse but is survived by an eligible child or children, a pension is payable to, or for the benefit of, the child or children at an annual rate equal to the relevant percentage in Table 2 in Schedule 4 of the deceased member’s notional invalidity pension;
(c) if the deceased member is not survived by a spouse or an eligible child and he or she had notified CSC in writing that:
(i) he or she had a person or persons dependent on him or her who would not be eligible to receive benefits as a spouse or eligible child; and
(ii) he or she had made provision for that person or those persons in his or her will;
the employer benefit is payable to, or for the benefit of, the person or persons as a lump sum;
(d) in any other case the employer benefit is payable to the deceased member’s personal representative as a lump sum.
(2) A spouse who is entitled to be paid an employer benefit under paragraph (1) (a) may elect that:
(a) instead of that employer benefit being paid to him or her, it be converted into a pension payable to him or her at an annual rate equal to the relevant percentage in Table 1 in Schedule 4 of the deceased member’s notional invalidity pension and if he or she so elects the benefit is so converted; or
(b) instead of that employer benefit being paid in full to him or her, a specified part of that benefit, being not less than one‑half of the benefit, be converted into a pension payable to him or her at an annual rate equal to the relevant percentage in Table 1 in Schedule 4 of the deceased member’s reduced notional invalidity pension and if he or she so elects:
(i) that part of the benefit is so converted; and
(ii) the balance of the benefit is payable to him or her as a lump sum.
(3) An employer benefit payable under subrule (1) is calculated as if, on the date of the death of the deceased member, he or she had become entitled to invalidity benefits under Division 2 of Part 3 and had been classified as Class A under rule 22.
(4) Subrules (2) and (3) do not apply where:
(a) a member dies and, at the time of his or her death, he or she was absent without leave and had been so absent for a period that exceeds 21 consecutive days; and
(b) the salary and allowances of the deceased member in respect of the period of absence without leave were forfeited under regulations made under the Defence Act 1903 and an amount equal to the amount of the salary and allowances forfeited was not subsequently paid, and is not payable, under those regulations to the deceased member’s personal representative;
unless CSC is satisfied that the absence of the member was due to sufficiently mitigating circumstances.
(5) In this rule:
“notional invalidity pension”, in relation to a deceased member, means the invalidity pension that would have been payable to the deceased member if, on the date of his or her death, he or she had become entitled to invalidity benefits under Division 2 of Part 3 and had been classified as Class A under rule 22;
“reduced notional invalidity pension”, in relation to a deceased member, means the invalidity pension that would have been payable to the deceased member if, on the date of his or her death:
(a) he or she had become entitled to invalidity benefits under Division 2 of Part 3; and
(b) he or she had been classified as Class A under rule 22; and
(c) the amount of his or her employer benefit were the amount which his or her spouse elected under paragraph (2) (b) to convert into a pension.
Division 2—Death of Retirement Pensioner
Applicability of benefits
41. Where a retirement pensioner dies and is survived by a spouse or spouses or an eligible child or children, benefits are payable in accordance with this Division.
Pensions payable
42. (1) Where a deceased retirement pensioner is survived by a spouse with or without eligible children, a pension is payable to the spouse at an annual rate equal to the relevant percentage in Table 1 in Schedule 4 of the deceased retirement pensioner’s pension.
(2) In spite of subrule (1), on each of the 7 pension paydays immediately following the death of a retirement pensioner referred to in that subrule, the rate at which pension is payable to the spouse of the deceased retirement pensioner is the rate at which pension would have been payable to the deceased retirement pensioner on that day if he or she had not died.
(3) Where a deceased retirement pensioner is not survived by a spouse but is survived by an eligible child or children, a pension is payable to, or for the benefit of, the child or children at an annual rate equal to the relevant percentage in Table 2 in Schedule 4 of the deceased retirement pensioner’s pension.
(4) In this rule:
“deceased retirement pensioner’s pension”, in relation to a deceased retirement pensioner, means the pension that was payable to the deceased retirement pensioner immediately before his or her death.
Final benefit payable in relation to deceased retirement pensioner
43. (1) Where a retirement pensioner dies not later than 10 years after his or her pension became payable to him or her and he or she is not survived by a spouse or eligible child to whom, or for the benefit of whom, benefits are payable under this Division, there is payable to the deceased retirement pensioner’s personal representative as a lump sum an amount equal to:
(a) where the deceased retirement pensioner was an invalidity pensioner:
(i) the amount (if any) by which the deceased invalidity pensioner’s employer benefit exceeds the amount of pension paid to the deceased invalidity pensioner since he or she last ceased to be a member; or
(ii) the amount of pension which would have been paid to the invalidity pensioner (if he or she had not died) from the date of his or her death until the expiration of a period of 10 years after the invalidity pensioner’s pension became payable to him or her;
whichever is the less; or
(b) in any other case—the amount (if any) by which so much of the deceased retirement pensioner’s employer benefit as was funded exceeds the amount of pension paid to the deceased retirement pensioner since he or she last ceased to be a member.
(2) Where a retirement pensioner dies, and:
(a) he or she is survived by a spouse or eligible child to whom, or for the benefit of whom, a pension is payable under this Division; and
(b) that surviving person, or the last of those surviving persons, dies not later than 10 years after the retirement pensioner’s pension became payable to him or her;
there is payable to the deceased spouse’s or eligible child’s personal representative as a lump sum an amount equal to:
(c) where the deceased retirement pensioner was an invalidity pensioner—the amount (if any) by which the deceased invalidity pensioner’s employer benefit exceeds the total of the amounts of pension paid to the deceased invalidity pensioner and his or her spouse, and to, or for the benefit of, his or her child or children, since he or she last ceased to be a member; or
(d) in any other case—the amount (if any) by which so much of the deceased retirement pensioner’s employer benefit as was funded exceeds the total of the amounts of pension paid to the deceased retirement pensioner and his or her spouse, and to, or for the benefit of, his or her child or children, since he or she last ceased to be a member.
Death in certain cases due to retirement disabilities
44. Where a person who:
(a) is classified as Class B; or
(b) is classified as Class C as a result of a reclassification under rule 23;
dies, and CSC is satisfied that his or her death was due to:
(c) the physical condition that was the cause of his or her retirement on the ground of invalidity; or
(d) a physical condition that was causally connected with that condition;
he or she is taken, for the purposes of this Division, to have been, immediately before his or her death, an invalidity pensioner classified as Class A and in receipt of pension at a rate calculated accordingly.
Effect of death of invalidity pensioner while pension suspended
45. Where a person whose invalidity pension has been suspended under rule 25 dies before the invalidity pension again becomes payable, he or she is taken, for the purposes of this Division, to have been an invalidity pensioner in receipt of pension immediately before his or her death.
Division 3—Death of Spouse
Child’s benefit upon death of spouse
46. (1) Where a spouse of a deceased member, being a spouse who:
(a) is in receipt of a spouse’s pension; and
(b) has an eligible child or children;
dies, a pension is payable to, or for the benefit of, the child or children at an annual rate equal to the relevant percentage in Table 2 of Schedule 4 of the deceased person’s notional pension.
(2) In this rule:
“deceased person” has the same meaning as in paragraph 8 of Schedule 1;
“deceased person’s notional pension” means:
(a) where the spouse was in receipt of a pension under subrule 40 (2)—the deceased person’s notional invalidity pension, or reduced notional invalidity pension, on the date of the member’s death; or
(b) where the spouse was in receipt of a pension under subrule 42 (1)—the deceased person’s pension on the date of the member’s death;
as if the rate of that pension had been increased from time to time in accordance with Division 2 of Part 6;
“notional invalidity pension” and “reduced notional invalidity pension” have the same respective meanings as in rule 40.
Division 4—Miscellaneous
Entitlements where two spouses
47. (1) In spite of anything in this Part, where a deceased member or retirement pensioner is survived by 2 spouses, the amount of member benefit (if any) and the amount of employer benefit payable to each spouse is to be determined by CSC but so that not less than 37.5 per centum of the member benefit (if any) and 37.5 per centum of the employer benefit is payable to each spouse.
(2) The total amount of member benefit (if any) and the total amount of employer benefit determined under subrule (1) is not to exceed the amount of the deceased person’s member benefit (if any) or employer benefit, respectively.
(3) Where, under a provision of this Part, a spouse is entitled to make an election in relation to a benefit, then, in a case where a deceased person is survived by 2 spouses, each of those spouses is entitled to make such an election in relation to so much of the benefit as is applicable to him or her.
Payment of balance of benefit where pension becomes payable to child in certain cases
48. (1) Where a pension becomes payable to, or for the benefit of, an eligible child or children of a deceased member under paragraph 40 (1) (b), an amount equal to the amount (if any) by which the employer benefit of the deceased member exceeds the amount that CSC determines to be the capital value of the pension payable to, or for the benefit of, the child or children is payable in accordance with subrule (4).
(2) Where a pension becomes payable to, or for the benefit of, an eligible child or children of a deceased retirement pensioner (other than an invalidity pensioner) under subrule 42 (3), an amount equal to the amount (if any) by which the funded employer benefit of the deceased retirement pensioner exceeds an amount equal to the sum of:
(a) the amounts of pension paid to the deceased retirement pensioner and his or her spouse, and to, or for the benefit of, his or her child or children, since he or she last ceased to be a member; and
(b) the amount that CSC determines to be the capital value of the pension payable to, or for the benefit of, the child or children;
is payable in accordance with subrule (4).
(3) Where a pension becomes payable to, or for the benefit of, an eligible child or children of a deceased invalidity pensioner under subrule 42 (3), an amount equal to the amount (if any) by which the employer benefit of the deceased pensioner exceeds an amount equal to the sum of:
(a) the amounts of pension paid to the deceased invalidity pensioner and his or her spouse, and to, or for the benefit of, his or her child or children, since he or she last ceased to be a member; and
(b) the amount that CSC determines to be the capital value of the pension payable to, or for the benefit of, the child or children;
is payable in accordance with subrule (4).
(4) Where an amount is payable under subrule (1), (2) or (3):
(a) if the deceased person had notified CSC in writing that:
(i) he or she had a person or persons dependent on him or her who would not be eligible to receive benefits as a spouse or eligible child; and
(ii) he or she had made provision for that person or those persons in his or her will;
the amount is payable to, or for the benefit of the person or persons as a lump sum; or
(b) in any other case, the amount is payable to the deceased person’s personal representative as a lump sum.
(5) In determining the capital value of a pension under this rule, CSC must obtain, and have regard to, the advice of an actuary.
Part 5—Payment of Preserved Benefits
Drawing on member benefit included in preserved benefit
49. (1) Subject to subrule (2), where a preserved benefit is applicable to a person and the preserved benefit includes an amount of member benefit, he or she may, at any time, elect to have the whole or a part of that member benefit paid to him or her as a lump sum and:
(a) if he or she elects to have the whole of the member benefit paid—the whole of the member benefit is payable to him or her; or
(b) if he or she elects to have part of the member benefit paid—the amount specified in the election is payable to him or her;
and the amount of the preserved benefit applicable to the person is reduced by a corresponding amount.
(2) Where a person elects under this rule to have part of the member benefit paid:
(a) that part must be an amount of $10,000 or a whole number multiple of that amount; and
(b) he or she is not permitted, except with the approval of CSC, to make another election under this rule until 6 months has elapsed since the last election made by him or her.
Fee for payment of part of person’s member benefit
50. (1) Where a person elects under rule 49 to have part of his or her member benefit paid to him or her, there is payable to CSC by the person a fee determined by CSC but not exceeding the administrative costs incurred by CSC in relation to that payment.
(2) A fee is not payable in respect of the first payment of part of a person’s member benefit.
Payment of employer benefit included in preserved benefit before person attains age of 55 years
51. Where, in relation to a person:
(a) to whom a preserved benefit applies; and
(b) who has not attained the age of 55 years;
one of the following paragraphs applies, the employer benefit included in that preserved benefit becomes payable to him or her as a lump sum on the date specified in that paragraph:
(c) CSC decides that by reason of the person’s physical or mental incapacity, the person has become unlikely ever to be able to work again in employment for which he or she is reasonably qualified by education, training or experience or for which the person could reasonably be qualified after retraining—on the date on which CSC so decided;
(d) the person intends to leave Australia permanently and CSC is satisfied that that intention will be carried out—on the date on which CSC became so satisfied;
(e) the Insurance and Superannuation Commissioner approves the payment of the benefit in other circumstances—the date which is the later of:
(i) the date of the approval; or
(ii) the date on which the circumstances apply.
Payment of employer benefit included in preserved benefit to person who has attained 55 years of age
52. Where a preserved benefit is applicable to a person who has attained the age of 55 years, he or she may, at any time:
(a) elect to have that preserved benefit paid to him or her as a lump sum and if he or she so elects the benefit is payable to him or her; or
(b) instead of the employer benefit included in the preserved benefit being paid to him or her, elect that it be converted into a pension payable to him or her and if he or she so elects:
(i) the employer benefit is so converted; and
(ii) the member benefit (if any) included in the preserved benefit is payable to the person as a lump sum; or
(c) instead of the employer benefit being paid in full to him or her, elect that a specified part of the employer benefit, being not less than one half of the employer benefit, be converted into a pension payable to him or her and if he or she so elects:
(i) that part of the employer benefit is so converted; and
(ii) the balance of the preserved benefit is payable to him or her as a lump sum.
Compulsory payment of preserved benefit to person on attaining 65 years of age
53. Where a person in relation to whom a preserved benefit is applicable does not make an election under paragraph 52 (b) or (c) on or before attaining the age of 65 years, the preserved benefit is payable to the person as a lump sum.
Payment of deceased former member’s preserved benefit
54. (1) Upon the death of a person who had been a member but at the time of his or her death was not a member or a retirement pensioner (in this rule called the “deceased former member”), his or her preserved benefit or a pension is payable in accordance with this rule.
(2) A deceased former member’s preserved benefit or a pension is payable as follows:
(a) if the deceased former member is survived by a spouse, the preserved benefit is payable to the spouse as a lump sum;
(b) if the deceased former member is not survived by a spouse but is survived by an eligible child or children, a pension is payable to, or for the benefit of, the child or children at an annual rate equal to the relevant percentage in Table 2 in Schedule 4 of the deceased former member’s notional pension;
(c) if the deceased former member is not survived by a spouse or an eligible child and he or she had notified CSC in writing that:
(i) he or she had a person or persons dependent on him or her who would not be eligible to receive benefits as a spouse or eligible child; and
(ii) he or she had made provision for that person or those persons in his or her will;
the preserved benefit is payable to, or for the benefit of, the person as a lump sum;
(d) in any other case, the preserved benefit is payable to the deceased member’s personal representatives as a lump sum.
(3) Where a pension becomes payable under paragraph (2) (b), the member benefit (if any) included in the preserved benefit is payable, as a lump sum, to, or for the benefit of, the eligible child or children.
(4) A spouse who is entitled to be paid an employer benefit under paragraph (2) (a) may elect that:
(a) instead of that employer benefit being paid to him or her, it be converted into a pension payable to him or her at an annual rate equal to the relevant percentage in Table 1 in Schedule 4 of the deceased member’s notional pension and if he or she so elects the benefit is so converted; or
(b) instead of that employer benefit being paid in full to him or her, a specified part of that benefit, being not less than one‑half of the benefit, be converted into a pension payable to him or her at an annual rate equal to the relevant percentage in Table 1 in Schedule 4 of the deceased member’s reduced notional pension and if he or she so elects:
(i) that part of the employer benefit is so converted; and
(ii) the balance of the preserved benefit is payable to him or her as a lump sum.
(5) In this rule:
“notional pension”, in relation to a deceased former member, means the pension that would have been payable to the deceased former member if, on the date of his or her death, he or she had become entitled, under Division 1 of Part 3, to elect to have his or her employer benefit converted into a pension and had elected to do so;
“reduced notional pension”, in relation to a deceased former member, means the pension that would have been payable to the deceased former member if, on the date of his or her death, he or she:
(a) had become entitled, under Division 1 of Part 3, to elect to have part of his or her employer benefit converted into a pension; and
(b) had elected to convert into a pension the same amount of his or her employer benefit as his or her spouse elected under paragraph (4) (b) to convert into a pension.
Part 6—Increases in Maximum Benefit Limits, Pensions and Certain Unfunded Preserved Benefits
Division 1—Increases in Maximum Benefit Limits
Increases in maximum benefit limits
55. (1) This rule is to have effect, on 1 July 1991 and each subsequent 1 July, as if there were substituted for:
(a) each amount referred to in the definition of “lump sum maximum benefit multiple” in Schedule 3; and
(b) each amount referred to in the definition of “pension maximum benefit multiple” in Schedule 3;
or for the amount last substituted for that amount under this rule (in this rule called the “base amount”) a new amount calculated by:
(c) multiplying the base amount by the index number for the March quarter immediately preceding that 1 July; and
(d) dividing the product by the index number for the previous March quarter.
(2) Subject to subrule (3), if at any time, whether before or after the commencement of these Rules, the Statistician publishes an index number in respect of a particular March quarter in substitution for an index number previously published, that later index number is disregarded for the purposes of this rule.
(3) If at any time the Statistician changes the reference base for the index numbers, regard is to be had, for the purposes of the operation of this rule after the change took place, only to index numbers published in terms of the new reference base.
(4) Where an amount to be substituted under this rule is not a multiple of $10, it is increased to the nearest multiple of $10.
(5) In this rule:
“index number”, in relation to a quarter, means the amount of the full‑time adult average weekly ordinary time earnings first published by the Statistician for the middle month of that quarter.
Division 2—Increases in Pensions and Certain Unfunded Preserved Benefits
Increases in pensions and certain unfunded preserved benefits
56. (1) Subject to this Part, if the all groups consumer price index number for the weighted average of the 8 capital cities published by the Statistician in respect of the March quarter of the year immediately preceding a prescribed year exceeds the highest all groups consumer price index number for the weighted average of the 8 capital cities published by the Statistician in respect of the March quarter of any earlier year, not being a year earlier than the year that commenced on 1 July 1989, then:
(a) a person (in this section called the “pensioner”) who was in receipt of a pension immediately before the commencement of that prescribed year is entitled to an increase in the rate at which the pension was payable immediately before the commencement of that prescribed year; and
(b) where, immediately before the commencement of that prescribed year, a preserved benefit is applicable to a person, or has become payable in respect of a deceased person but has not been paid, the amount of the unfunded employer benefit included in the preserved benefit in relation to that person immediately before the commencement of that year is increased.
(2) The increase provided for by subrule (1) in the rate at which a pension was payable to a person, or in the amount of the unfunded preserved benefit in relation to a person, immediately before the commencement of a prescribed year (in this rule called the “relevant prescribed year”), is the percentage of that rate or amount that represents A – B expressed as a percentage of B, where:
A is the all groups consumer price index number for the weighted average of the 8 capital cities published by the Statistician in respect of the March quarter of the year immediately preceding the prescribed year; and
B is the highest all groups consumer price index number for the weighted average of the 8 capital cities published by the Statistician in respect of the March quarter of any year earlier than the year that commenced on 1 July 1990.
(3) Where, by reason of the death on 30 June in the year immediately preceding a prescribed year of a person in receipt of a pension, a pension becomes payable on the following day to another person, that other person is entitled to such an increase in the rate of that pension as he or she would have been entitled to had the pension become payable to him or her on that 30 June.
Application of increase to suspended pension
57. Where a pension would, but for its suspension under rule 25, be payable to a person immediately before the commencement of a prescribed year, that pension is, for the purposes of this Part, taken to have been payable to that person immediately before the commencement of that prescribed year but any increase in the rate of that pension by virtue of this Part does not take effect until the day on which the pension again becomes payable.
Proportionate increase for part of a year
58. (1) This rule applies to a pension where:
(a) the person to whom the pension is payable would, but for this rule, be entitled to an increase, in accordance with rule 56, in the rate at which the pension was payable to him or her immediately before the commencement of the prescribed year; and
(b) the person is:
(i) a retirement pensioner and the pension became payable to him or her during the preceding year; or
(ii) the spouse of, or eligible child in relation to, a deceased person who was a member immediately before his or her death and the pension became payable to the spouse or child, as the case may be, during the preceding year; or
(iii) the spouse of, or eligible child in relation to, a deceased person who was a retirement pensioner immediately before his or her death and the deceased person’s pension became payable to the deceased person during the preceding year.
(2) If:
(a) the pension; or
(b) where subparagraph (1) (b) (iii) applies—the pension that was payable to the deceased person in relation to whom the person was a spouse or eligible child;
became payable after 16 June in the preceding year, the person is not entitled to the increase.
(3) If:
(a) the pension; or
(b) where subparagraph (1) (b) (iii) applies—the pension that was payable to the deceased person in relation to whom the person was a spouse or eligible child;
became payable on or before 16 June in the preceding year, the amount of the increase is an amount calculated in accordance with the formula:

where:
“Full increase” means the amount of the increase that would have been applicable but for this subrule.
“Number of months in period” means the number of months in the period that began on the day on which the pension referred to in paragraph (a) or (b) became payable and ended on 30 June in the preceding year.
(4) If the period referred to in subrule (3) is less than 1 month, that period is treated as 1 month.
(5) If the period referred to in subrule (3) consists of a number of whole months and a part of a month:
(a) where the number of days in that part of that month is less than one‑half of the number of days in that month—that part is disregarded; and
(b) where the number of days in that part of that month is more than one‑half of the number of days in that month—that part is treated as a whole month.
(6) Where a preserved benefit:
(a) became applicable to a person; or
(b) became payable or was converted into a pension;
during the most recent prescribed year, that part of the preserved benefit that is an unfunded employer benefit is increased to the extent determined by CSC, consistent with the principle of subrule 56 (2).
(7) In this rule:
“preceding year”, in relation to a pension to which this rule applies, means the year immediately preceding the prescribed year.
Adjustment in connection with invalidity reclassification
59. (1) Where:
(a) a person to whom an invalidity pension is payable is reclassified from Class A to Class B or vice versa under rule 23 during a prescribed year; and
(b) the person became entitled at the beginning of that year to an increase under this Part in the rate at which that invalidity pension was payable to him or her immediately before the beginning of that year;
the rate at which the pension is payable to him or her on and after the date from which the reclassification has effect is the rate at which the pension would have been payable to him or her at the beginning of the year if his or her classification, on and after the date on which he or she became entitled to the pension, had been in accordance with the reclassification.
(2) Where:
(a) a person to whom an invalidity pension was payable ceased to be entitled to an invalidity pension because of his or her reclassification under rule 23; and
(b) in consequence of a further reclassification under that rule during a prescribed year he or she again becomes entitled to an invalidity pension;
the rate at which the pension is payable to him or her on and after the date from which the latter reclassification has effect is the rate at which the pension would have been payable to him or her if:
(c) he or she had not ceased to be entitled to an invalidity pension in consequence of the first mentioned reclassification; and
(d) his or her classification, on and after the date on which he or she first became entitled to an invalidity pension, had been in accordance with the further reclassification.
(3) Where:
(a) a person to whom an invalidity pension was payable ceased to be entitled to an invalidity pension because of his or her reclassification under rule 23; and
(b) in consequence of a further reclassification under that rule after his or her death he or she would, had he or she not died, have again become entitled to an invalidity pension;
then, for the purpose of calculating benefits for any surviving spouse or eligible child of the invalidity pensioner, the invalidity pensioner is to be taken to have been, immediately before his or her death, in receipt of an invalidity pension at the rate at which that pension would have been payable to him or her if:
(c) he or she had not ceased to be entitled to invalidity pension in consequence of the first‑mentioned reclassification; and
(d) his or her classification, on and after the date on which he or she first became entitled to an invalidity pension, had been in accordance with the further reclassification.
(4) Upon a preserved benefit becoming applicable to a person under subrule 29 (1), the unfunded employer benefit included in that preserved benefit is increased as if:
(a) that preserved benefit had become applicable to the person on the person’s retirement; and
(b) this Part had applied, since that retirement, to the unfunded employer benefit included in the preserved benefit.
Date of effect of increase
60. (1) An increase by virtue of this Part in the rate of a pension that:
(a) was payable; or
(b) under subrule 56 (3) is treated as having been payable;
to a person on 30 June in a year applies in relation to the instalment of pension falling due on the first pension pay‑day occurring after that day and in relation to all subsequent instalments.
(2) An increase by virtue of this Part in the amount of an unfunded preserved benefit applies with effect from:
(a) in the case of an increase under subrule 58 (6)—the date on which the preserved benefit became payable; or
(b) in any other case—1 July of the prescribed year.
Interpretation
61. (1) Subject to subrule (2), if at any time, whether before or after the commencement of these Rules, the Statistician has published or publishes in respect of a particular March quarter an all groups consumer price index number for the weighted average of the 8 capital cities in substitution for an index number previously published by him or her in respect of that quarter, the publication of the later index number is disregarded for the purposes of this Part.
(2) If at any time, whether before or after the commencement of these Rules, the Statistician has changed or changes the reference base for the Consumer Price Index, then, for the purposes of the application of this Part after the change took place or takes place, regard is to be had only to index numbers published in terms of the new reference base.
(3) If the percentage for the purposes of rule 56 is or includes a fraction of one tenth of 1 per centum:
(a) where that fraction is less than one half of one tenth—that fraction is disregarded; and
(b) where that fraction is not less than one half of one tenth—that fraction is treated as one tenth.
Part 7—Candidates at Parliamentary Elections
Re‑instated member
62. (1) Where a person who resigned to contest an election:
(a) again becomes a member; and
(b) is a person referred to in a relevant provision of the Parliamentary Candidates Act; and
(c) repays to CSC, before the expiration of 60 days after the day on which he or she again became a member, the amount of any benefit paid to him or her under these Rules upon him or her resigning to contest the election;
the person is taken for the purposes of these Rules:
(d) to have been a member; and
(e) despite the operation of the relevant provision, not to have been absent on leave without pay;
during the relevant period.
(2) Where subrule (1) applies to a person:
(a) any benefit that became payable to him or her under these Rules upon him or her ceasing to be a member is taken not to have been payable; and
(b) the fortnightly contributions that the person is required to make in respect of the relevant period are in accordance with the election by him or her that was in force immediately before the beginning of that period.
Death or physical or mental incapacity of person
63. When a person who resigned to contest an election:
(a) dies; or
(b) in the opinion of CSC, becomes physically or mentally incapacitated to the extent that he or she would have been retired on the ground of invalidity if he or she had remained a member;
he or she is, where considered appropriate by CSC, taken not to have ceased to be a member but to have died or retired on the ground of invalidity while a member at a time determined by CSC.
Part 8—General Provisions Applicable to Contributions and Benefits
Provisions applicable to elections under the Rules
64. (1) An election under these Rules is to be in writing.
(2) Where a person is about to become, or has become, entitled:
(a) to benefits under Part 3 or Part 5; and
(b) to make an election in relation to the nature of those benefits;
he or she may make that election not earlier than 3 months before he or she is due to become entitled to the benefits and not later than 3 months after becoming entitled to the benefits.
(3) Where an election under these Rules is made by a person after the expiration of the period allowed for the making of the election and CSC is satisfied that, in all the circumstances of the case, it is desirable that the election be recognised, CSC may direct that the election be allowed and if it does so these Rules have effect as if the election had been made within the period allowed.
(4) Where a person who is entitled to make an election under these Rules is, by reason of physical or mental incapacity, unable to make that election, CSC may allow such other person as it thinks appropriate to make the election within such period as CSC allows and if it does so and the other person so makes the election these Rules have effect as if the election had been made by the first‑mentioned person within the period allowed.
(5) Where:
(a) an election under Part 3, 4 or 5 is made by the person entitled to make the election or, in accordance with subrule (3), by another person on behalf of the first‑mentioned person; and
(b) the person who made the election makes an application to CSC, not later than 3 months after the day on which the election is made or within such further period as CSC in special circumstances allows, requesting that CSC cancel the election; and
(c) CSC, having regard to such matters as it considers relevant, is satisfied that the election should be cancelled;
CSC may direct that the election is cancelled and if it does so these Rules have effect as if the election had not been made.
(6) Where a person who is, or has been, a member is entitled to make an election under Part 3 or 5 and dies without making such an election:
(a) if the person is survived by a spouse—the spouse may make the election within 3 months after the person’s death; or
(b) if the person is not survived by a spouse, or is survived by a spouse but the spouse dies without making such an election, but the person is survived by an eligible child—the election may be made within that period by such person as CSC permits;
and if the spouse, or the person permitted by CSC, does so, these Rules have effect as if the election had been made by the first‑mentioned person.
Rate of pension where lump sum converted into pension
65. (1) Where a person is entitled under these Rules to have an amount of his or her employer benefit converted into a pension, the annual rate of that pension is calculated in accordance with Schedule 5.
Benefits in unusual or exceptional circumstances
66. Where, in a particular case, CSC is of the opinion that:
(a) the operation of these Rules, other than this rule, with regard to a point at issue produces a result in relation to a person that is not in the spirit of the Rules; and
(b) the relevant circumstances of the case are unusual or exceptional;
CSC may, in relation to that case, having regard to the circumstances of the case, the principles in these Rules and the need to maintain equity between members, determine the point at issue in favour of that person.
Instalments of pensions
67. (1) Pensions are to be paid in fortnightly instalments on pension pay‑days.
(2) The amount of a fortnightly instalment of pension is an amount ascertained by dividing the amount per annum of the pension by 26.
(3) Where the amount of a fortnightly instalment of pension includes a fraction of a cent:
(a) if the fraction is less than one‑half of a cent—the amount of the instalment is taken to be reduced by the amount of the fraction; or
(b) if the fraction is one‑half of a cent or more—the amount of the instalment is taken to be increased by treating the fraction as 1 cent.
(4) The amount of pension payable in respect of a day is one‑fourteenth of the amount of a fortnightly instalment of the pension.
Set off against pension in certain cases
68. Where:
(a) the spouse of a deceased pensioner to whom retirement pension or invalidity pension (in this rule called the “primary pension”) was payable is entitled to spouse’s pension in accordance with subrule 42 (2); and
(b) an amount, purporting to be an instalment of primary pension payable to the pensioner in respect of a period in respect of which spouse’s pension is payable in accordance with that subrule, is paid into an account with a bank, credit union or building society (in this rule called the “financial institution”); and
(c) the financial institution pays, out of that account, to the spouse of the deceased pensioner an amount not exceeding the amount so paid into the account;
CSC may make arrangements under which the amount so paid to the spouse may be offset against any amount of pension payable to the spouse in accordance with subrule 42 (2).
Interest payable where payment of benefit delayed
69. (1) Where a benefit is payable as a lump sum to a person and the payment of the benefit is delayed, CSC may, in accordance with this rule, approve an increase, by an amount of interest, in the amount of the benefit payable to the person.
(2) Where a pension is payable to, or for the benefit of a person and the commencement of the payment of that pension is delayed, CSC may, in accordance with this rule, approve an increase, by an amount of interest, in the rate of the pension payable to the person for such period as CSC determines.
(3) A pension is not to be increased under subrule (2) if CSC is of the opinion that the amount of the increase would not be significant.
(4) Interest applicable under this rule is calculated in such manner as CSC determines:
(a) in the case of a lump sum payment—in respect of the period of the delay; and
(b) in the case of a pension—in respect of:
(i) each instalment of the pension delayed; and
(ii) the period of delay of that instalment.
(5) In this rule:
“benefit” means employer benefit or member benefit.
Payment of benefit otherwise than to person entitled
70. (1) Where, in the opinion of CSC, the part of:
(a) an instalment of spouse’s pension; or
(b) a spouse’s lump sum payment;
attributable to an eligible child or eligible children, or any portion of that part, should, by reason of the child or children not being in the custody, care and control of the spouse, or for any other reason which CSC thinks proper, be paid to a person other than the spouse, CSC may authorise payment of that part, or a portion of the part, to the other person and if CSC does so payment is to be made to the other person accordingly.
(2) For the purposes of subrule (1), the part of a spouse’s lump sum payment attributable to that eligible child or those eligible children is taken to be the amount obtained by multiplying the spouse’s lump sum payment by the percentage applicable in respect of an eligible child or children under rule 43 in relation to a pension.
(3) Where, in the opinion of CSC:
(a) an instalment, or part of an instalment, of a pension; or
(b) an amount of any other benefit;
should:
(c) by reason of the person who, but for this rule, would be entitled to the payment being a child, or being a person who is of unsound mind or undergoing imprisonment or otherwise being under a disability; or
(d) for any other reason which CSC thinks proper;
be paid to a person other than the person who would be so entitled to the payment, CSC may authorise payment to the other person and if CSC does so payment is to be made to the other person accordingly.
(4) It is the intention of this rule that:
(a) the part, or a portion of the part, of an instalment of spouse’s pension attributable to an eligible child that, by virtue of subrule (1), is paid to a person other than the child to which that part or portion is attributable; or
(b) an instalment of pension payable to a child that, by virtue of subrule (3), is paid to a person other than the child;
be applied for the maintenance, education or other benefit of the child.
Withholding payment of benefit where required information not provided
71. CSC may withhold payment of the whole, or a part, of a benefit in relation to a person where that person does not provide, or arrange to be provided, to CSC information required by CSC in connection with the determination of the person’s entitlement to benefits under these Rules or the determination of the amount of those benefits.
Part 9—Reconsideration of Decisions
Establishment of Reconsideration Advisory Committees
72. (1) CSC must establish a Reconsideration Advisory Committee.
(2) CSC may establish more than one Committee.
Membership of Committee
73. (1) A Committee comprises such number of persons as CSC determines.
(2) The qualifications or experience of each member are such as CSC determines.
(3) A person who is a member of CSC is not disqualified by reason of that fact from being appointed to a Committee.
Functions of Committee
74. (1) The functions of a Committee are:
(a) to review any decision referred to it under this Part; and
(b) to make recommendations to CSC in relation to the decision.
(2) When reviewing a decision, a Committee:
(a) must take into account any evidence relevant to the decision that is made available or submitted to it; and
(b) may also take steps to obtain any other evidence that it considers necessary for a proper review of the decision.
Proceedings of Committee
75. Subject to any directions given by CSC, a Committee may regulate its proceedings as the Committee thinks fit.
Reconsideration of decision made by delegate
76. (1) A person affected by a decision made by a delegate of CSC may apply to CSC for reconsideration of the decision.
(2) An application may be:
(a) in writing addressed to CSC and setting out the particulars of the decision that the person wishes to be reconsidered; or
(b) in any other form that is acceptable to CSC.
(3) CSC must refer the decision to which an application relates to a Committee.
(4) CSC may also, on its own motion, refer a decision of a delegate to a Committee.
(5) After taking into account, in relation to a decision referred to a Committee:
(a) the recommendations of the Committee; and
(b) any other matter that CSC considers relevant;
CSC must, by instrument in writing setting out the reasons for so doing, affirm or vary the decision or set it aside and substitute another decision for it.
(6) CSC must make a copy of an instrument referred to in subrule (5) available to the applicant.
Reconsideration of decision made by CSC
77. (1) A person affected by a decision made by CSC (including a decision under subrule 76 (5)) may apply to CSC for a reconsideration of that decision.
(2) An application must:
(a) be in writing addressed to CSC; and
(b) set out particulars of the decision that the person wishes to be reconsidered; and
(c) specify the grounds for reconsideration of those particulars; and
(d) be accompanied by the prescribed fee.
(3) A decision is to be reconsidered only if there is evidence relevant to the decision that was not previously taken into account by CSC in making the decision.
(4) If an application is not supported by evidence in accordance with subrule (3), CSC must dismiss the application.
(5) The dismissal of an application in respect of a decision does not preclude the applicant from subsequently submitting another application in respect of the decision.
(6) If CSC does not dismiss an application under subrule (4), CSC must refer the decision to which the application relates to a Committee.
(7) CSC may also, on its own motion, refer any of its decisions to a Committee.
(8) After taking into account, in relation to a decision referred to a Committee:
(a) the recommendation of the Committee; and
(b) any other matter that CSC considers relevant;
CSC must, by instrument in writing setting out the reasons for so doing, affirm or vary the decision or set it aside and substitute another decision for it.
(9) CSC must make a copy of an instrument referred to in subrule (8) available to the applicant.
Content of statements of reasons for decisions
78. Where CSC is required by a provision of this Part to give written reasons for a decision made by it, the instrument giving the reasons must also set out the findings on material questions of fact and refer to the evidence or other material on which those findings were based.
Interpretation
79. For the purposes of this Part, a determination or a decision of the Incapacity Classification Committee under Subdivision A of Division 2 of Part 3 is taken to be the decision of a delegate of CSC.
Schedule 1—Glossary
Rule 2
Part 1—Definitions
1. In these Rules, unless the contrary intention appears:
“actuary” means a Fellow or an Accredited Member of the Institute of Actuaries of Australia;
“Board” means the Military Superannuation and Benefits Board of Trustees established by section 13 of the Act;
“calendar month” means a period commencing at the beginning of a day of one of the 12 months of the year and ending immediately before the beginning of the corresponding day of the next month or, if there is no such corresponding day, ending at the expiration of the next month;
“child”, in relation to a person who has died, means a child (including an adopted child, an ex‑nuptial child, a stepchild, a ward or a foster child) of the person or of a spouse of the person;
“classification” means a classification referred to in rule 22;
“Committee”, in Part 3 of these Rules, means the Incapacity Classification Committee established under rule 17;
“Committee”, in Part 9 of these Rules, means a Reconsideration Advisory Committee established under rule 72;
“contribution” means contribution to the Fund;
“Department” means the Department of State for Defence;
“eligible child”, in relation to a person who has died and was, at the time of his or her death, a member or a retirement pensioner, means a person who:
(a) is a child in relation to the deceased person other than (where the deceased person was a retirement pensioner at the time of his or her death) a child who is declared by CSC not to be an eligible child for the purposes of these Rules; and
(b) is a person who has not attained the age of 16 years or:
(i) who has attained the age of 16 years but has not attained the age of 25 years; and
(ii) is receiving full‑time education at a school, college or university or other full‑time education approved by CSC for the purposes of this subparagraph; and
(iii) is not ordinarily in employment or engaged in work on his or her own account; and
(c) immediately before the deceased person’s death:
(i) ordinarily lived with the deceased person; or
(ii) was, in the opinion of CSC, wholly or substantially dependent upon the deceased person; or
(iii) where the person is a child born after the deceased person’s death, ordinarily would have been, in the opinion of CSC, living with the deceased person or so dependent if the person had been born before the death of the deceased person;
“eligible service”, in relation to a person, means service calculated in accordance with Schedule 6;
“Emergency Forces” has the same meaning as in the Defence Act 1903;
“employer benefit”, in relation to a person, means the amount of employer benefit calculated in relation to that person in accordance with Schedule 8;
“final average salary”, in relation to a person, means an amount calculated in accordance with Schedule 7;
“financial year” means a period of 12 months commencing on 1 July;
“foreign service member” means a person (not being a person who has been an eligible member of the Defence Force within the meaning of the 1973 Act):
(a) who, before he or she became a member, had been a member of the armed forces of a country other than Australia; and
(b) who rendered with those forces a period of service (in this definition called “full‑time service”) of a kind similar to continuous full‑time service in the Defence Force for a period of or exceeding 12 months; and
(c) with regard to whom CSC has, after consultation with the appropriate authority of the Defence Force, formed the opinion that the full‑time service or a part of that service of that person with those forces should be regarded as eligible service;
“Fund” means the fund established, and vested in CSC, by the Trust Deed;
“funded employer benefit”, in relation to a person, means the sum of:
(a) the amount of employer contributions paid by the Department, in relation to the person, under rule 10 less the amount of income tax paid or payable by the Fund in respect of those contributions; and
(b) the interest (if any) in respect of the amount in paragraph (a) in accordance with a determination or determinations by CSC as to rates of interest and the method of allocation of interest to such amounts;
“higher duties allowance” means the allowance of that name determined under Part IIIA of the Defence Act 1903;
“invalidity”, in relation to a person, includes physical or mental incapacity of the person to perform his or her duties;
“invalidity pension” means a pension payable under rule 27 or 28;
“invalidity pensioner” means a person who is entitled to invalidity pension or would be so entitled if payment of that pension had not been suspended under subrule 25(3);
“invalidity retiree” means a person who is about to be, or has been, retired from the Defence Force on the ground of invalidity and includes a person who, in accordance with rule 30, is to be treated as if he or she had been retired on that ground;
“lump sum maximum benefit limit”, in relation to a person, means an amount calculated in accordance with paragraph 1 of Schedule 3;
“MBL member” means a member who has ceased to pay contributions in accordance with rule 5;
“member” means a person who, in accordance with section 6 of the Act, is a member of the Scheme;
“member benefit”, in relation to a member, means an amount calculated in accordance with Schedule 9;
“membership” means membership of the Scheme;
“month” means calendar month;
“Parliamentary Candidates Act” means the Defence (Parliamentary Candidates) Act 1969;
“pension” means a pension payable under these Rules;
“pension maximum benefit limit”, in relation to a person, means an amount calculated in accordance with paragraph 3 of Schedule 3;
“Permanent Forces” has the same meaning as in the Defence Act 1903;
“prescribed fee” means a fee prescribed in regulations made in pursuance of section 52 of the Act;
“prescribed year” means the year commencing on 1 July 1991 or a subsequent year;
“previous contributions”, in relation to a person, means contributions made by him or her under the previous legislation, less any such contributions refunded to him or her under that legislation;
“previous legislation” means the 1948 Act and the 1973 Act;
“relevant percentage”, in relation to a spouse or eligible child of a deceased person, means the percentage applicable to that spouse or child in accordance with Schedule 4;
“relevant period”, in relation to a person to whom Part 7 of these Rules applies, means the period referred to in a relevant provision in the application of that provision to that person;
“relevant provision”, in relation to the Parliamentary Candidates Act, means subsection 10 (2), 11 (2) or 12 (2), as the case requires;
“Reserve Forces” has the same meaning as in the Defence Act 1903.
“retirement pensioner” means a former member to whom a pension is payable but does not include a person to whom a pension is payable only because he or she is the spouse or the child of a deceased member;
“salary”, in relation to a person:
(a) includes, in relation to the person’s service as a member, service allowance and higher duties allowance payable to that person; and
(b) means, in relation to the person’s service on a particular day as an eligible member of the Defence Force within the meaning of the 1973 Act, the amount that, for the purposes of that Act, was the annual rate of pay applicable to the person on that day;
“Scheme” means the Military Superannuation and Benefits Scheme established by the Trust Deed;
“service” means service as a member of the Defence Force;
“service allowance” means the allowance of that name determined under Part IIIA of the Defence Act 1903;
“service offence” has the same meaning as in the Defence Force Discipline Act 1982;
“spouse’s pension” means pension payable to a spouse under Part 4 of these Rules;
“Statistician” means the Australian Statistician;
“total benefit”, in relation to a person, means the sum of the person’s member benefit and employer benefit;
“transferred person” means a person who became a member in consequence of his or her having made an election to do so under section 132 of the 1973 Act;
“transfer value”, in relation to a transferred person, means an amount calculated in accordance with Schedule 10;
“unfunded preserved benefit”, in relation to a person, means so much of the employer benefit included in the preserved benefit applicable to the person as is not funded;
“1948 Act” means the Defence Forces Retirement Benefits Act 1948;
“1973 Act” means the Defence Force Retirement and Death Benefits Act 1973;
“1973 Scheme” means the retirement and death benefits scheme provided for in the 1973 Act;
“1973 Scheme recipient member” means a member who:
(a) began to render continuous full‑time service on or after the date of commencement of the Scheme; and
(b) immediately before beginning to render that service was a 1973 Scheme retirement pensioner;
“1973 Scheme re‑entrant” means a person who became a member because he or she made an election to do so under section 61B of the 1973 Act immediately before he or she began to render the period of continuous full‑time service which he or she is rendering;
“1973 Scheme retirement pensioner” means a person to whom retirement pay is payable under the 1973 Act;
“1991 Scheme” means the Scheme;
“1991 Scheme re‑entrant” means a member who, having been a member and retired, again became a member after a break in the continuity of his or her service.
Part 2—Resign to contest an election
2. A reference in these Rules to a person who resigns to contest an election is a reference to a member:
(a) who is transferred to a Reserve (being a Reserve within the meaning of the Parliamentary Candidates Act); or
(b) who is discharged from the Defence Force; or
(c) has his or her continuous full‑time service terminated;
under the Parliamentary Candidates Act.
Part 3—Retirement
3. A reference in these Rules to the retirement of a person is a reference to his or her retirement from the Defence Force and includes:
(a) any voluntary or involuntary termination of the person’s services as a member of that force; or
(b) in the case of a person who is an officer of the Permanent Forces—the transfer of the officer to the Emergency Forces or the Reserve Forces if, on that transfer, the person ceases to render continuous full‑time service; or
(c) in the case of a person who is a member of the Emergency Forces or the Reserve Forces and is rendering continuous full‑time service—the cessation of that service.
4. Where a person retires and, without a break in the continuity of his or her service, again becomes a member of the Defence Force serving on continuous full‑time service, the person is to be treated, for the purposes of these Rules, as not having retired by reason only of that retirement.
Part 4—Retiring age
5. A reference in these Rules to the retiring age of a member is:
(a) in the case of a member who is a member of the Permanent Forces—the age for the compulsory retirement of the member ascertained in accordance with, or in accordance with regulations under, the Defence Act 1903, the Naval Defence Act 1910 or the Air Force Act 1923; or
(b) in the case of a member who is not a member of the Permanent Forces—the age that would be the age for the compulsory retirement of the person if the person were a member of the Permanent Forces.
6. Where the age for the compulsory retirement of a member is, in accordance with a law referred to in paragraph 5, extended, the member is treated for the purposes of these Rules, on his or her subsequent retirement, as if:
(a) where he or she is subsequently retired on the ground of invalidity—he or she had been retired on that ground; or
(b) where he or she retires or is retired on any other ground—he or she retired on reaching the age for his or her compulsory retirement.
7. In paragraph 5:
“Permanent Forces” does not include the Regular Army Supplement.
Part 5—Spouse
8. In this Part:
“deceased person” means a person who:
(a) has died; and
(b) was, at the time of his or her death, a member or a former member.
9. Subject to this Part, a reference in these Rules to a spouse of a deceased person is a reference to:
(a) a person who was legally married to the deceased person at the time of his or her death and who, at that time, was ordinarily living with the deceased person on a permanent and bona fide domestic basis; and
(b) a person who was legally married to the deceased person at the time of his or her death but who was not ordinarily living with the deceased person on a permanent and bona fide domestic basis at that time and who, in the opinion of CSC, was wholly or substantially dependent upon the deceased person at that time; and
(c) a person who was not legally married to the deceased person at the time of his or her death but who, for a continuous period of not less than 3 years immediately before the deceased person’s death, had ordinarily lived with the deceased person as his or her husband or wife, as the case may be, on a permanent and bona fide domestic basis; and
(d) a person who was not legally married to the deceased person at the time of his or her death but who, for a continuous period of less than 3 years immediately before the deceased person’s death, had ordinarily lived with the deceased person as his or her husband or wife, as the case may be, on a permanent and bona fide domestic basis and who, in the opinion of CSC, was wholly or substantially dependent upon the deceased person at the time of his or her death.
10. Where:
(a) a deceased person was, at the time of his or her death, a retirement pensioner (in this paragraph called the “pensioner”); and
(b) the marriage of the pensioner to the person to whom the pensioner was legally married at the time of his or her death took place after the pensioner had become a pensioner and had attained the age of 60 years;
a reference in these Rules to a spouse of a deceased person is, in relation to the pensioner, a reference to the person to whom the pensioner was so married if:
(c) the marriage took place not less than 5 years before the pensioner’s death; or
(d) the marriage took place less than 5 years before the pensioner’s death but:
(i) the person had, immediately before the marriage, for a continuous period that commenced not later than 5 years before the pensioner’s death but after the pensioner became a pensioner and attained the age of 60 years, ordinarily lived with the pensioner as his or her husband or wife, as the case may be, on a permanent and bona fide domestic basis; or
(ii) the person had, immediately before the marriage, for a continuous period that commenced not later than 3 years before the pensioner’s death but before the pensioner became a pensioner or attained the age of 60 years, whichever last occurred, ordinarily lived with the pensioner as his or her husband or wife, as the case may be, on a permanent and bona fide domestic basis; or
(iii) the person had, immediately before the marriage, for a continuous period that commenced later than 3 years before the pensioner’s death but before the pensioner became a pensioner or attained the age of 60 years, whichever last occurred, ordinarily lived with the pensioner as his or her husband or wife, as the case may be, on a permanent and bona fide domestic basis and was, in the opinion of CSC, wholly or substantially dependent upon the pensioner at the time of his or her death;
but not otherwise.
11. Where:
(a) a deceased person was, at the time of his or her death, a retirement pensioner (in this subrule called the “pensioner”); and
(b) a person who was not legally married to the pensioner at the time of his or her death commenced living with the pensioner as his or her husband or wife, as the case may be, on a permanent and bona fide domestic basis after the pensioner had become a pensioner and had attained the age of 60 years;
a reference in these Rules to a spouse of a deceased person is, in relation to the pensioner, a reference to the person with whom the pensioner had so lived if the person had ordinarily lived with the pensioner for a continuous period of not less than 5 years immediately before the pensioner’s death, but not otherwise.
12. In spite of anything in this Part, a person is not, for the purposes of these Rules, a spouse in relation to another person if he or she is of the same sex as that other person.
Part 6—Parts of speech and grammatical forms
13. In these Rules, unless the contrary intention appears, where a word or phrase is given a particular meaning, other parts of speech and grammatical forms of that word or phrase have corresponding meanings.
Part 7—Number
14. In these Rules, unless the contrary intention appears, words in the singular number include the plural and words in the plural number include the singular.
Part 8—Reckoning of time
15. Where, in these Rules, any period of time, dating from a given day, act or event, is required or allowed for any purpose, the time is, unless the contrary intention appears, to be reckoned exclusive of that day or the day of that act or event.
16. Where the last day of any period required or allowed by a provision of these Rules for the doing of anything falls on a Saturday, on a Sunday or on a day which is a public holiday or a bank holiday in the place in which the thing is to be or may be done, the thing may be done on the first day following which is not a Saturday, a Sunday or a public holiday or bank holiday in the place.
Part 9—Attainment of particular age
17. For the purposes of these Rules, unless the contrary intention appears, the time at which a person attains a particular age expressed in years is the commencement of the relevant anniversary of the date of the birth of that person.
