Commonwealth-State agreement (the Offshore Constitutional Settlement)
3.(1) The Commonwealth and the States have agreed that:
(a) Commonwealth offshore mining legislation should be limited to the area that is outside State coastal waters; and
(b) the States should share, in the manner provided by this Act, in the administration of the Commonwealth offshore mining legislation; and
(c) State offshore mining legislation should apply to State coastal waters beyond the baseline for the territorial sea (that is, the first 3 nautical miles of the territorial sea); and
(d) the Commonwealth and the States should try to maintain, as far as practicable, common principles, rules and practices in regulating and controlling offshore mining beyond the baseline of Australia’s territorial sea.
Note: So far as the agreement relates to petroleum, it is reflected in Commonwealth legislation by the Petroleum (Submerged Lands) Act 1967.
(2) Other Acts that provide background to the agreement (commonly referred to as the “Offshore Constitutional Settlement”) are:
(a) the Seas and Submerged Lands Act 1973; and
(b) the Coastal Waters (State Powers) Act 1980; and
(c) the Coastal Waters (State Title) Act 1980; and
(d) the Petroleum (Submerged Lands) Act 1967; and
(e) the Coastal Waters (Northern Territory Powers) Act 1980; and
(f) the Coastal Waters (Northern Territory Title) Act 1980.
Note 1: The Seas and Submerged Lands Act 1973:
• declared and enacted that the sovereignty in respect of the territorial sea and the associated airspace, seabed and subsoil is vested in and exercisable by the Crown in right of the Commonwealth;
• gave the Governor-General power to declare, by Proclamation, the limits of the territorial sea;
• declared and enacted that the sovereignty in respect of waters of the sea that are on the landward side of the baseline of the territorial sea (but not within the limits of a State) and in respect of the associated airspace, seabed and subsoil is vested in and exercisable by the Crown in right of the Commonwealth;
• declared and enacted that the sovereign rights of Australia as a coastal State in respect of the Continental Shelf of Australia (for the purpose of exploring it and exploiting its natural resources) are vested in and exercisable by the Crown in right of the Commonwealth;
• gave the Governor-General power to declare, by Proclamation, the limits of the Continental Shelf of Australia.
Note 2: The Coastal Waters (State Powers) Act 1980 was enacted following a request from the Parliaments of all the States under paragraph 51 (xxxviii) of the Constitution of the Commonwealth and provided that the legislative powers exercisable under the Constitution of each State extended to the making of certain laws that would operate offshore.
Note 3: The Coastal Waters (State Title) Act 1980 vested in each State certain property rights in the seabed beneath the coastal waters of the State.
Note 4: The Petroleum (Submerged Lands) Act 1967 makes provision, based on the agreement referred to in subsection (1), for the licensing regime that applies to the exploration for and recovery of petroleum in offshore areas.
Note 5: The Coastal Waters (Northern Territory Powers) Act 1980 makes similar provision to the State Powers Act in relation to the Northern Territory.
Note 6: The Coastal Waters (Northern Territory Title) Act 1980 makes similar provision to the State Title Act in relation to the Northern Territory.
PART 1.2—INTERPRETATION
Division 1—General
Interpretation
4. In this Act, unless the contrary intention appears:
“approved” means approved by the Designated Authority under section 41;
“associate” has the meaning given by subsection 26(1);
“associated agent of a holder” has the meaning given by subsection 26(3);
“associated agent of an associated contractor” has the meaning given by subsection 26(4);
“associated contractor” has the meaning given by subsection 26(2);
“associated document file” means an associated document file kept for the purposes of Part 3.1;
“associated employee of an associated contractor” has the meaning given by subsection 26(6);
“associated employee of a holder” has the meaning given by subsection 26(5);
“associated revenue Act” means:
(a) the Exploration Licence Fees Act; or
(b) the Mining Licence Fees Act; or
(c) the Retention Licence Fees Act; or
(d) the Works Licence Fees Act; or
(e) the Registration Fees Act; or
(f) the Royalty Act; or
(g) the Exploration Licence User Charge Act; or
(h) the Retention Licence User Charge Act;
“block” means a portion of an offshore area constituted according to section 17;
“caveat” on a licence means a caveat against:
(a) the registration of dealings in relation to the licence; or
(b) the registration of a person as a holder of the licence under section 340;
“coastal waters” of a State has the meaning given by section 16;
“Commonwealth Minister” means a Minister of State for the Commonwealth;
“Commonwealth-State offshore area” has the meaning given by section 13;
“compliance direction” means a direction under section 387 or 392;
“compliance inspection” has the meaning given by section 377;
“confidential information” has the meaning given by section 27;
“confidential sample” has the meaning given by section 28;
“consent area” means the block or blocks specified in a special purpose consent;
“Continental Shelf” means the continental shelf of Australia within the meaning of the Seas and Submerged Lands Act 1973;
“dealing” in a licence means a transaction that creates, transfers, affects or otherwise deals with an interest in the licence and includes:
(a) a transfer of the licence; and
(b) a transfer of a share in a licence;
“Designated Authority” has the meaning given by section 29;
Note: If this Act confers a power or function on a Designated Authority generally, that power can be exercised, and that function can be performed, as provided by section 30.
“discrete area” has the meaning given by section 21;
“exploration” has the meaning given by section 23;
“Exploration Licence Fees Act” means the Offshore Minerals (Exploration Licence Fees) Act 1981;
“Exploration Licence User Charge Act” means the Offshore Minerals (Exploration Licence User Charge) Act 1994;
“external territory” means an external territory to which this Act extends under section 36;
“external territory offshore area” has the meaning given by section 14;
“Fees Act” means:
(a) when used in relation to an exploration licence—the Offshore Minerals (Exploration Licence Fees) Act 1981; and
(b) when used in relation to a retention licence—the Offshore Minerals (Retention Licence Fees) Act 1994; and
(c) when used in relation to a mining licence—the Offshore Minerals (Mining Licence Fees) Act 1981; and
(d) when used in relation to a works licence—the Offshore Minerals (Works Licence Fees) Act 1981;
and includes regulations made under those Acts;
“Gazette” means:
(a) in relation to a Commonwealth-State offshore area—the Government Gazette of the State; or
(b) in relation to an external territory offshore area—the Commonwealth of Australia Gazette;
“holder” of a licence has the meaning given by subsection 25(1);
“hydrocarbon” means a hydrocarbon whether in a gaseous, liquid or solid state;
“inspector” means an inspector appointed under section 421;
“interest”, in relation to a licence, includes:
(a) an equitable interest in the licence; and
(b) a security interest in the licence;
“Joint Authority” has the meaning given by section 32;
Note: If this Act confers a power or function on a Joint Authority generally, that power can be exercised, and that function can be performed, as provided by section 33.
“licence” means:
(a) an exploration licence; or
(b) a retention licence; or
(c) a mining licence; or
(d) a works licence;
“licence area” means the block or blocks covered by a licence;
“mineral” has the meaning given by section 22;
“Mining Licence Fees Act” means the Offshore Minerals (Mining Licence Fees) Act 1981;
“native title” and “native title rights and interests” have the same meaning as in the Native Title Act 1993;
“offshore area” means a Commonwealth-State offshore area or an external territory offshore area;
“offshore exploration or mining activity” means:
(a) the exploration for minerals in an offshore area; or
(b) the recovery of minerals from an offshore area; or
(c) activities carried out in an offshore area under a works licence;
“offshore mining register” means a register kept for the purposes of Part 3.1;
“petroleum” means:
(a) a hydrocarbon or a mixture of hydrocarbons; or
(b) a mixture of one or more hydrocarbons and one or more of the following:
(i) hydrogen sulphide;
(ii) nitrogen;
(iii) helium;
(iv) carbon dioxide;
“primary payment period” for the provisional grant or provisional renewal of a licence means the period of 30 days after the day on which the applicant is given a written notice:
(a) in the case of the grant of an exploration licence—under section 66 or 83; and
(b) in the case of the renewal of an exploration licence—under section 110; and
(c) in the case of the grant of a retention licence—under section 147; and
(d) in the case of the renewal of a retention licence—under section 169; and
(e) in the case of the grant of a mining licence—under section 210 or 227; and
(f) in the case of the renewal of a mining licence—under section 246; and
(g) in the case of the grant of a works licence—under section 279; and
(h) in the case of the renewal of a works licence—under section 296;
“provisional holder” means a person who has been provisionally granted a licence;
“recovery” has the meaning given by section 24;
“registered” means registered in an offshore mining register;
“Registration Fees Act” means the Offshore Minerals (Registration Fees) Act 1981;
“reserved block” is a block that is declared to be reserved under section 18;
“responsible Commonwealth Minister” means the Commonwealth Minister who is responsible for the administration of this Act;
“responsible State Minister”, for a State means the State Minister who is authorised under a law of the State to perform the functions of a Designated Authority under this Act;
“Retention Licence Fees Act” means the Offshore Minerals (Retention Licence Fees) Act 1994;
“Retention Licence User Charge Act” means the Offshore Minerals (Retention Licence User Charge) Act 1994;
“Royalty Act” means the Offshore Minerals (Royalty) Act 1981;
“sample” of the seabed or subsoil in an offshore area includes a core or cutting from the seabed or subsoil in that area;
“secondary payment period” for the provisional grant or provisional renewal of a licence means the period of 30 days after the day on which an extension of the primary payment period for the grant or renewal concerned ends;
“share” in a licence has the meaning given by subsections 6(1), (2) and (3);
“special purpose consent” means a consent granted under Part 2.6;
“standard block” has the meaning given by section 19;
“State” has a meaning that is affected by the operation of section 5;
“State Minister” means:
(a) a Minister of State for a State; or
(b) a Minister of State for the Northern Territory;
“successor licence” to a licence has the meaning given by section 8;
Note: See section 15.
“surrender day” for an exploration licence means:
(a) the day on which the initial term of the licence ends; or
(b) a day on which the term of a renewal of the licence ends;
“tender block” has the meaning given by section 20;
“the 1981 Act” means the Minerals (Submerged Lands) Act 1981;
“transfer”:
(a) when used in relation to a licence—has the meaning given by subsection 7(1); and
(b) when used in relation to a share in a licence—has the meaning given by subsections 7(2) and (3);
“vary” a licence condition includes revoke or suspend;
“Works Licence Fees Act” means the Offshore Minerals (Works Licence Fees) Act 1981.
Treatment of the Northern Territory
5. For the purposes of this Act:
(a) the Northern Territory is to be treated as though it were a State; and
(b) the Legislative Assembly of the Northern Territory is to be treated as though it were the Parliament of a State; and
(c) Ministers of the Northern Territory are to be treated as though they were Ministers of a State; and
(d) the laws of the Northern Territory are to be treated as though they were State laws; and
(e) the Northern Territory’s courts, tribunals, authorities and officers are to be treated as though they were State courts, tribunals, authorities and officers.
Note: For the significance of paragraphs (d) and (e) see Part 5.1 (application of State laws to Commonwealth-State offshore areas).
Shares in a licence
6.(1) A person has a share in a licence if the person is the holder, or one of the holders, of the licence.
(2) If a holder is entitled to a particular percentage of the value of the rights conferred by a licence, that percentage is the holder’s share in the licence.
Note: A sole holder has a 100% share in the licence.
(3) If:
(a) a person is a registered holder of a licence; and
(b) the person is shown in an offshore mining register as being entitled to a specified percentage of the value of the rights conferred by the licence;
the person’s share in the licence is taken to be the percentage specified in the register.
Transfer of a licence
7.(1) For the purposes of this Act, a licence is transferred if:
(a) the licence has only one holder and the holder transfers the whole of his or her interest in the licence to another person or other persons; or
(b) the licence has 2 or more holders and the holders all transfer the whole of their interests in the licence to another person or other persons.
(2) For the purposes of this Act, a share in a licence is transferred if:
(a) the licence has only one holder and the holder transfers a part of the holder’s share in the licence to another person or other persons; or
(b) the licence has 2 or more holders and:
(i) some, but not all, of the holders transfer the whole of their shares in the licence to another person; or
(ii) some or all of the holders transfer a part of their shares in the licence to another person.
(3) The other person referred to in paragraph (2)(b) may be an existing licence holder.
Successor licences
8.(1) If:
(a) a mining licence takes effect immediately after an exploration licence expires; and
(b) the holder of the mining licence immediately after it takes effect was the holder of the exploration licence immediately before it expired;
the mining licence is a successor licence to the exploration licence.
(2) If:
(a) a retention licence takes effect immediately after an exploration licence expires; and
(b) the holder of the retention licence immediately after it takes effect was the holder of the exploration licence immediately before it expired;
the retention licence is a successor licence to the exploration licence.
(3) If:
(a) a mining licence takes effect immediately after a retention licence expires; and
(b) the retention licence took effect immediately after an exploration licence expired; and
(c) the holder of the mining licence immediately after it takes effect was the holder of the retention licence immediately before it expired; and
(d) the holder of the retention licence immediately after it took effect was the holder of the exploration licence immediately before it expired;
the mining licence is a successor licence to the exploration licence and the retention licence.
Notes, diagrams etc. form part of section etc.
9.(1) For the purposes of this Act, a diagram is taken to be part of:
(a) if the diagram occurs in a section containing subsections—the subsection immediately preceding the diagram; or
(b) if the diagram occurs in a section without subsections—the section.
(2) For the purposes of this Act, a Note is taken to be part of:
(a) if the Note immediately follows a section without subsections—the section; or
(b) if the Note immediately follows a subsection—the subsection; or
(c) if the Note immediately follows a definition and is aligned with the text of the definition—the definition.
Position on the Earth’s surface
10.(1) Subject to subsection (2), this is how the position of a point, line or area on the Earth’s surface is to be worked out for the purposes of this Act and subordinate instruments:
(a) the position is to be worked out by reference to a spheroid that:
(i) has a major (equatorial) radius of 6,378,160 metres; and
(ii) has a flattening of 100/29825; and
(b) the Johnston Geodetic Station in the Northern Territory is taken to be located 571.2 metres above the point on the surface of the spheroid that is at:
(i) 133°12’30.0771” East Longitude; and
(ii) 25°56’54.5515” South Latitude.
(2) The position on the Earth’s surface of a point or line specified in an International Seabed Agreement is to be worked out for the purposes of this Act and subordinate instruments in accordance with the Agreement.
(3) In this section:
“International Seabed Agreement” means:
(a) the Agreement between Australia and Indonesia that was signed at Canberra on 18 May 1971 and established certain seabed boundaries; and
(b) the Agreement between Australia and Indonesia that was signed at Jakarta on 9 October 1972 and established certain seabed boundaries in the area of the Timor and Arafura Seas; and
(c) the Agreement between Australia and Indonesia that was signed at Jakarta on 12 February 1973 and that related to certain boundaries between Papua New Guinea and Indonesia; and
(d) the treaty between Australia and the Independent State of Papua New Guinea concerning sovereignty and maritime boundaries in the area between the 2 countries, including the area known as the Torres Strait, and related matters that was signed at Sydney on 18 December 1978; and
(e) the Agreement on Maritime Delimitation between the Government of Australia and the Government of the French Republic that was signed at Melbourne on 4 January 1982; and
(f) the agreement between the Government of Australia and the Government of the Solomon Islands Establishing Certain Sea and Seabed Boundaries that was signed at Honiara on 13 September 1988;
and includes those agreements as varied from time to time;
“subordinate instrument” means:
(a) the regulations; and
(b) instruments made under this Act and the regulations.
Effect of maximum penalty at foot of section or subsection 11.(1) A maximum penalty that is specified:
(a) at the foot of a section of this Act (other than a section that is divided into subsections); or
(b) at the foot of a subsection of this Act;
indicates that a person who intentionally or recklessly contravenes the section or subsection is guilty of an offence against the section or subsection that is punishable, on conviction, by a penalty up to that maximum.
Note: See also subsection 405(2).
(2) Subsection (1) does not apply to section 44.
Power to vary and revoke instruments
12.(1) Under subsection 33(3) of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901, any provision of this Act that confers a power to do something in writing is also taken to confer the power to repeal, rescind, revoke, amend or vary the written document by which that thing is done.
(2) The power to repeal, rescind, revoke, amend or vary:
(a) must also be exercised in writing; and
(b) is subject to the same procedural requirements as the original power; and
(c) is subject to the same conditions as those that governed the exercise of the original power.
Division 2—Basic concepts
Commonwealth-State offshore areas
13.(1) The Commonwealth-State offshore area for a State is the area that is the adjacent area for the State for the purposes of the Petroleum (Submerged Lands) Act 1967.
Note: The “adjacent area” for the purposes of the Petroleum (Submerged Lands) Act 1967 is worked out by taking an area off the coast of the State that is described in Schedule 2 to that Act and then excluding all waters within a line 3 nautical miles seaward of the territorial sea baseline and also excluding any areas that are beyond the outer limits of the Continental Shelf. The map in Schedule 2 to this Act illustrates the Commonwealth-State offshore areas. The map is intended to show roughly the boundaries between the various Commonwealth-State offshore areas and the outer limits of those areas (sometimes the limits of the Continental Shelf, sometimes a bilaterally negotiated boundary and sometimes an arbitrary median boundary adopted pending bilateral negotiations).
(2) The following diagram illustrates how a Commonwealth-State offshore area relates to:
(a) the territorial sea baseline; and
(b) the 3 nautical mile limit (the outer limit of the State’s coastal waters); and
(c) the 12 nautical mile limit (the outer limit of the territorial sea); and
(d) the outer limits of the Continental Shelf.
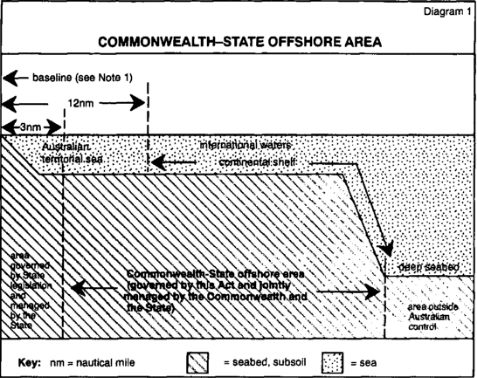
Note 1: For the “baseline” see Australia’s territorial sea baseline (AGPS) 1988: generally the baseline is the lowest astronomical tide along the coast but it also includes lines enclosing bays and indentations that are not bays and straight baselines that depart from the coast.
Note 2: The “Continental Shelf” in a legal sense starts not from the coast but from the outer limits of the territorial sea. In a geophysical sense, of course, the continental shelf starts at the coast. The diagram shows the outer edge of the continental margin as the limit of the Continental Shelf but sometimes the 200 nautical mile limit defines the limit of the Continental Shelf.
Note 3: Sometimes the outer limit of the Commonwealth-State offshore area is a bilaterally negotiated boundary or a median line adopted pending bilateral negotiations.
External territory offshore areas
14.(1) The external territory offshore area for the Territory of Ashmore and Cartier Islands is the area that is the adjacent area for that Territory for the purposes of the Petroleum (Submerged Lands) Act 1967.
Note 1: The “adjacent area” for the Territory of Ashmore and Cartier Islands for the purposes of the Petroleum (Submerged Lands) Act 1967 is worked out by taking the area off the coast of the territory that is described in Schedule 2 to that Act and then excluding any areas that are beyond the Continental Shelf.
Note 2: Under the Petroleum (Submerged Lands) Act 1967, any land that is in the adjacent area for the Territory of Ashmore and Cartier Islands is treated as submerged land and as part of the seabed and subsoil of that adjacent area.
(2) The external territory offshore area for Norfolk Island, the Territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands, Christmas Island and Cocos (Keeling) Islands is the area which starts at the coastline of the Islands at mean low water and ends at the outer limit of the superjacent waters of the Continental Shelf adjacent to the coast of the islands.
Note: Under the Petroleum (Submerged Lands) Act 1967, the adjacent area for the Coral Sea Islands Territory is treated as being part of the adjacent area for Queensland. Therefore, in this Act, the Coral Sea offshore area is part of the Commonwealth-Queensland offshore area.
Effect of change in baseline
15.(1) If:
(a) an area is covered by a licence; and
(b) there is a change to the baseline of Australia’s territorial sea; and
(c) as a result of the change to the baseline, the area ceases to be within an offshore area;
this Act applies as if the area were still within the offshore area.
(2) Subsection (1) continues to apply to the area only while the licence (and any successor licence) remains in force.
(3) If:
(a) an area in a State’s coastal waters is covered by a State offshore mining licence; and
(b) there is a change to the baseline of Australia’s territorial sea; and
(c) as a result of the change to the baseline, the area:
(i) ceases to be within the State’s coastal waters; and
(ii) falls within an offshore area;
this Act does not apply to the area.
(4) Subsection (3) continues to apply to the area only while the State offshore mining licence (and any successor licence) remains in force.
(5) In this section:
“State offshore mining licence” means a licence granted under State law that authorises the holder to:
(a) explore for or recover minerals (other than petroleum) in the seabed or subsoil under the State’s coastal waters; or
(b) carry out related activities;
“successor licence” to a State offshore mining licence is a licence that is a successor licence to that licence for the purposes of State law.
Coastal waters of a State
16.(1) The coastal waters of a State are so much of the area off the coast of the State that is described in Schedule 2 to the Petroleum (Submerged Lands) Act 1967 as is constituted by:
(a) the first 3 nautical miles of the Australian territorial sea from the baseline; and
(b) any waters that are inside the baseline and not within the limits of the State.
(2) The following diagram illustrates the coastal waters of a State:
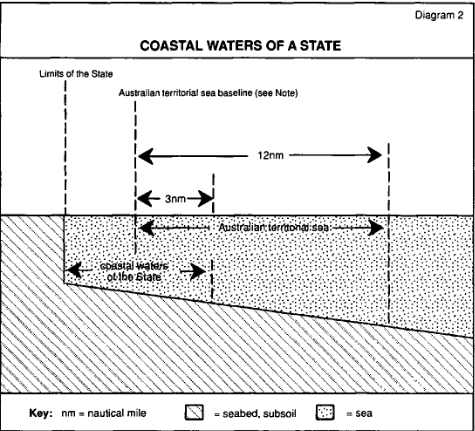
Note: For the “baseline” see Australia’s territorial sea baseline (AGPS) 1988: generally the baseline is the lowest astronomical tide along the coast but it also includes lines enclosing bays and indentations that are not bays and straight baselines that depart from the coast.
Blocks
17.(1) This is how a block is constituted in an offshore area:
(a) assume that there is laid over the offshore area a grid constituted by:
(i) lines running along meridians drawn through each degree of longitude and the minutes between those degrees; and
(ii) lines running along parallels drawn through each degree of latitude and the minutes between those degrees;
(b) take a bounded space defined by the grid;
(c) the seabed and subsoil within the offshore area that is under that space is a block in the offshore area.
(2) The following diagram shows how a block is constituted:
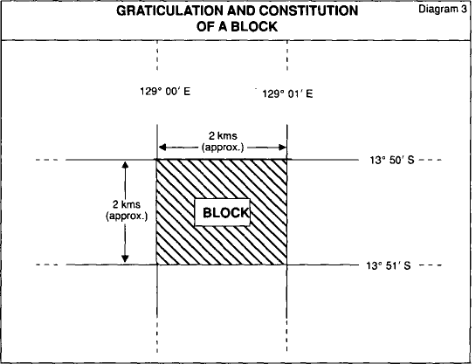
Note: Each block is identified by giving the name of the plan in the 1:1,000,000 map series, an identifying number of the 5 minute primary block and a letter identifying the 1 minute block. The block in the diagram is 1621(a) on the Darwin sheet.
Reserved block
18.(1) Subject to subsection (3), the Joint Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area may declare that a block in the offshore area is a reserved block.
Note 1: A reserved block may be put up for tender by a Joint Authority publishing in the Gazette a tender block licence notice (see sections 74 and 218).
Note 2: Paragraph 23(b) of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901 allows a single declaration under this subsection to be made in respect of 2 or more blocks.
(2) Subject to subsection (3), the responsible Commonwealth Minister may declare that a block in an external territory offshore area is a reserved block.
Note 1: A reserved block may be put up for tender by the responsible Commonwealth Minister publishing in the Gazette a tender block licence notice (see sections 74 and 218).
Note 2: Paragraph 23(b) of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901 allows a single declaration under this subsection to be made in respect of 2 or more blocks.
(3) A declaration under subsection (1) or (2) must not be made in relation to a block if:
(a) a licence over that block is in force; or
(b) an application for a licence over that block has been made and has not been determined.
(4) A declaration under subsection (1) or (2) must be made by notice published in the Gazette.
Standard block
19. A standard block is a block that is not the subject of a declaration under subsection 18(1) or (2).
Tender block
20. A tender block is a block that is the subject of a tender block licence notice published by the Joint Authority under section 74 or section 218.
Discrete area
21. A group of blocks forms a discrete area if the area formed by the blocks is continuous.
Mineral
22.(1) A mineral is a naturally occurring substance or a naturally occurring mixture of substances.
Note: This Act does not apply to petroleum (see section 35).
(2) Without limiting subsection (1), a mineral may be in the form of sand, gravel, clay, limestone, rock, evaporites, shale, oil-shale or coal.
Exploration
23.(1) For the purposes of this Act, exploration for minerals includes any activity that is directly related to the exploration for minerals.
(2) For the purposes of this Act, exploration does not include the exploration for minerals of the subsoil of a Commonwealth-State offshore area that is carried out by means of underground mining from State land in accordance with any law of the State governing mineral exploration.
Recovery
24.(1) For the purposes of this Act, recovery of minerals includes any activity that is directly related to the recovery of minerals.
(2) For the purposes of this Act, recovery does not include the recovery of minerals from the subsoil of a Commonwealth-State offshore area that is carried out by means of underground mining from State land in accordance with any law of the State governing mineral recovery.
Licence holder
25.(1) For the purposes of this Act, the holder of a licence is the person whose name is on the relevant offshore mining register as the person who holds the licence.
Note 1: This Act is based upon the grant and registration of licences.
Note 2: If a licence is granted to a person, that person’s name is entered on the register (see section 333).
Note 3: The entry on the register in relation to a licence will be varied if there is a change in the licence holder (see subsection 338(5)).
(2) A licence may be held by more than one person.
Associates
26.(1) For the purposes of this Act, the following are the associates of a licence holder:
(a) associated contractors of the holder;
(b) associated agents of the holder;
(c) associated agents of associated contractors;
(d) associated employees of the holder;
(e) associated employees of associated contractors.
(2) A person is an associated contractor of the holder if:
(a) the person enters an agreement with the holder for carrying out activities under the licence; or
(b) the person enters an agreement with a person who is an associated contractor under paragraph (a) or this paragraph for carrying out activities under the licence.
(3) A person is an associated agent of the holder if the person is the agent of, or acts on behalf of, the holder in relation to carrying out activities under the licence.
(4) A person is an associated agent of an associated contractor if the person is the agent of, or acts on behalf of, the associated contractor in relation to carrying out activities under the licence.
(5) A person is an associated employee of the holder if the person is employed by the holder and, in the course of that employment, carries out activities under the licence.
(6) A person is an associated employee of an associated contractor if the person is employed by the associated contractor and, in the course of that employment, carries out activities under the licence.
Confidential information
27.(1) For the purposes of this Act, information is confidential information if:
(a) a licence holder has given it to the Designated Authority; and
(b) it is in a record, return, report or document; and
(c) it relates to activities authorised by the licence; and
(d) it relates to an area of the seabed or subsoil of an offshore area that is covered by the licence or a successor licence to the licence.
(2) However, if:
(a) a person is required to give the Designated Authority a report in relation to particular blocks; and
(b) the person gives the Designated Authority a report that relates not only to those blocks but also to other blocks; and
(c) the Designated Authority is required to make the report available under section 376;
the information that relates to those other blocks is not confidential information.
Confidential sample
28. For the purposes of this Act, a core, cutting or sample is a confidential sample if:
(a) a licence holder has given it to the Designated Authority; and
(b) it was recovered in the course of activities authorised by the licence; and
(c) it was recovered from an area of the seabed or subsoil of an offshore area that is covered by the licence or a successor licence to the licence.
PART 1.3—DESIGNATED AUTHORITIES AND JOINT
AUTHORITIES
Designated Authorities
29.(1) For the purposes of this Act, there is a Designated Authority for each offshore area.
(2) The Designated Authority for the Commonwealth-State offshore area of a State is the responsible State Minister.
(3) The Designated Authority for an external territory offshore area is the responsible Commonwealth Minister.
Functions and powers of Designated Authorities
30.(1) A Designated Authority for a State has, in relation to the Commonwealth-State offshore area for that State, the functions and powers that this Act confers on a Designated Authority.
(2) A State Minister acting on behalf of the responsible State Minister may perform the functions and exercise the powers that the responsible State Minister has in the capacity of Designated Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area.
(3) The Designated Authority for an external territory offshore area has, in relation to the external territory offshore area, the functions and powers that this Act confers on a Designated Authority.
(4) A Commonwealth Minister acting on behalf of the responsible Commonwealth Minister may perform the functions and exercise the powers that the responsible Commonwealth Minister has in the capacity of Designated Authority of an external territory offshore area.
Judicial notice of signature of Designated Authority
31.(1) All courts must take judicial notice of:
(a) the signature of a person who is, or has been:
(i) the Designated Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area; or
(ii) a delegate of the Designated Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area; or
(iii) a State Minister acting on behalf of the responsible State Minister under subsection 30(2); and
(b) the fact that that person is, or was:
(i) the Designated Authority for that offshore area; or
(ii) acting on behalf of the responsible State Minister under subsection 30(2).
(2) All courts must take judicial notice of:
(a) the signature of a person who is, or has been:
(i) the Designated Authority for an external offshore area; or
(ii) a delegate of the Designated Authority for an external territory offshore area; or
(iii) a Commonwealth Minister acting on behalf of the responsible Commonwealth Minister under subsection 30(4); and
(b) the fact that that person is, or was:
(i) the Designated Authority for that offshore area; or
(ii) acting on behalf of the responsible Commonwealth Minister under subsection 30(4).
Joint Authorities
32.(1) For the purposes of this Act, there is a Joint Authority for each offshore area.
(2) The Joint Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area is constituted by the responsible State Minister and the responsible Commonwealth Minister.
Note: The procedures which are to be followed by Joint Authorities are set out in sections 408 to 418.
(3) The Joint Authority for an external territory offshore area is the responsible Commonwealth Minister.
Functions and powers of Joint Authorities
33.(1) A Joint Authority for a State has, in relation to the Commonwealth-State offshore area for that State, the functions and powers that this Act confers on a Joint Authority.
(2) The responsible Commonwealth Minister has, in relation to an external territory offshore area, the functions and powers that this Act confers on a Joint Authority.
Service of documents on a Joint Authority
34. A document that is to be given to the Joint Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area may be given to the Joint Authority by giving it to the Designated Authority for that offshore area.
PART 1.4—APPLICATION OF THIS ACT
Act does not apply to exploration for or recovery of petroleum
35. This Act does not apply to the exploration for or recovery of petroleum.
Note 1: For “petroleum” see section 4.
Note 2: Offshore petroleum exploration and mining are regulated by the Petroleum (Submerged Lands) Act 1967.
Act extends to certain external territories
36. This Act extends to the following external territories:
(a) the Territory of Ashmore and Cartier Islands;
(b) Norfolk Island;
(c) the Territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands;
(d) Christmas Island;
(e) the Territory of Cocos (Keeling) Islands;
(f) the Coral Sea Islands Territory.
Note 1: This Act treats the Coral Sea Islands Territory offshore area as part of Queensland’s offshore area.
Note 2: This Act operates in a Commonwealth-State offshore area on the basis of shared administration between the Commonwealth and the State and this involves sharing powers between Designated Authorities and Joint Authorities. In external territory offshore areas, the responsible Commonwealth Minister exercises all the powers and therefore has both Designated Authority powers and Joint Authority powers. When the Commonwealth-State offshore area regime requires communication and consultation between Designated Authorities and Joint Authorities, this Act contains special provisions dealing with external territory offshore areas (see, for example, section 64).
Note 3: This Act provides for review of the decisions of the Designated Authority in relation to external territory offshore areas (see Part 4.3).
Act applies to all individuals and corporations
37.(1) This Act applies to all individuals, including:
(a) individuals who are not Australian citizens; and
(b) individuals who are not resident in Australia or an external territory.
(2) This Act applies to all corporations, including:
(a) corporations that are not incorporated in Australia; and
(b) corporations that do not carry on business in Australia or an external territory.
CHAPTER 2—REGULATION OF OFFSHORE EXPLORATION
AND MINING
PART 2.1—GENERAL
General prohibition on exploring and mining in offshore areas without appropriate authorisation under this Act
38. A person must not:
(a) explore for minerals in an offshore area; or
(b) recover minerals from an offshore area;
unless the exploration or recovery is authorised by a licence or special purpose consent granted under this Act.
Note: A works licence may be necessary because “exploration” includes activities that are directly related to exploration (see subsection 23(1)) and “recovery” includes activities that are directly related to recovery (see subsection 24(1)).
Maximum penalty: 300 penalty units.
Licences and consents available under this Act
39. This Act provides for the grant of:
(a) exploration licences (see Part 2.2); and
(b) retention licences (see Part 2.3); and
(c) mining licences (see Part 2.4); and
(d) works licences (see Part 2.5); and
(e) special purpose consents (see Part 2.6).
Note 1: An exploration licence is designed to cover the exploration phase of a project and authorises:
• exploration; and
• the recovery of mineral samples.
Note 2: A retention licence is designed to ensure the retention of rights pending the transition of a project from the exploration phase to the commercial mining phase and authorises:
• exploration; and
• the recovery of minerals but not as part of a commercial mining operation.
Note 3: A mining licence is designed to cover the commercial mining phase of a project and authorises:
• exploration; and
• full commercial recovery.
Note 4: A project might make use of any of the following 3 licence arrangements:
• an exploration licence leading to a mining licence;
• an exploration licence leading to a retention licence and then a mining licence;
• a mining licence (without progressing through an exploration/retention licence stage).
Note 5: A licence is granted over a particular area (constituted by blocks). The licence holder may need to carry out engineering or other activities outside the licence area. If so, the licence holder or someone else must obtain a works licence to carry out those activities.
Note 6: If a person wants to carry out:
• a scientific investigation; or
• a reconnaissance survey; or
• the collection of only small amounts of minerals;
in an offshore area, the person must obtain a special purpose consent under Part 2.6 to carry out the activity.
Note 7: Even though a person has a licence or special purpose consent, the person must not interfere unnecessarily with navigation, native title, fishing, resource conservation or other activities in the area (see section 44).
Steps involved in the grant of a fully effective licence
40.(1) The following 3 steps must occur before a licence comes into force:
(a) provisional grant of the licence;
(b) proper acceptance of the grant;
(c) registration of the grant.
Note: See sections 88, 154, 232 and 286.
(2) If a licence is provisionally granted to a person, the person must do the following to properly accept the grant:
(a) give the Designated Authority a written acceptance;
(b) lodge any security that the Joint Authority has required;
(c) pay the fees that are payable under the Fees Act.
Note: See sections 70, 84, 151, 214, 228 and 283.
(3) The following 3 steps must occur before a renewal of a licence comes into force:
(a) provisional renewal of the licence;
(b) proper acceptance of the renewal;
(c) registration of the renewal.
Note: See sections 89, 155, 233 and 287.
(4) If a licence is provisionally renewed, the holder must do the following to properly accept the renewal:
(a) give the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the renewal;
(b) lodge any security that the Joint Authority has required;
(c) pay the fees that are payable under the Fees Act.
Note: See sections 114, 173, 250 and 300.
Approval of form and manner of applications etc.
41.(1) The Designated Authority for an offshore area may approve the form and the manner in which the following are to be made:
(a) applications for licences over blocks in the offshore area;
(b) applications for the renewal of licences over blocks in the offshore area.
(2) The Designated Authority for an offshore area may determine guidelines for the maps to accompany applications for licences over blocks in the offshore area.
(3) An approval under subsection (1) or a determination under subsection (2) is to be made in writing.
Rights to minerals recovered
42.(1) Any minerals recovered by a licence holder or special purpose consent holder from a block covered by the licence or consent become the property of the holder when they are recovered.
(2) If the licence or consent authorises the exploration for and the recovery of minerals only of a particular kind, subsection (1) only applies to the recovery of minerals of that kind.
(3) Subsection (1) does not apply to the recovery of minerals by a works licence holder.
(4) The minerals recovered are not subject to the rights of any other person.
(5) Subsection (4) does not apply to rights that the licence or consent holder transfers to the other person.
Effect of grant of licence or special purpose consent on native title
43.(1) The grant of a licence or special purpose consent under this Act does not extinguish native title in the licence or consent area.
(2) While a licence or consent under this Act is in force over an area, native title in the area is subject to the rights conferred by the licence or consent.
Licence etc. does not authorise unnecessary interference with other activities in the licence area
44. A person contravenes this section if:
(a) the person carries out activities in an offshore area under a licence or special purpose consent granted under this Act; and
(b) the person intentionally or recklessly carries out those activities in a way that interferes with:
(i) navigation; or
(ii) the exercise of native title rights and interests; or
(iii) fishing; or
(iv) the conservation of the resources of the sea or the seabed; or
(v) any activities that someone else is lawfully carrying out; and
(c) the interference is greater than is necessary for:
(i) the reasonable exercise of the person’s rights under the licence or consent; or
(ii) the performance of the person’s duties under the licence or consent.
Note 1: The person referred to here might be the licence or consent holder or might be an associated person.
Note 2: See section 4D of the Crimes Act 1914.
Penalty: 100 penalty units.
PART 2.2—EXPLORATION LICENCES
Division 1—General
Exploration licences
45.(1) This Part provides for the grant of exploration licences over blocks in an offshore area.
(2) An exploration licence may be granted over a standard block (see Division 2) or over a tender block (see Division 3).
Note: A tender block is a block that has been declared available for tender. A standard block is any block that is not a reserved block (see sections 19 and 20).
Activities authorised by an exploration licence
46.(1) Subject to subsection (2), an exploration licence holder may:
(a) explore for minerals in the licence area; and
(b) take samples of minerals in the licence area.
Note 1: Under subsection 23(1) the concept of “exploration” extends to activities that are directly related to exploration.
Note 2: Under subsection 24(1) the concept of “recovery” extends to activities that are directly related to the recovery of minerals.
(2) If the licence is expressed to restrict the kind of minerals covered by the licence, the holder is not permitted to explore for, or to take samples of, minerals not covered by the licence.
(3) A restriction on the kind of minerals covered by the licence may be inclusive (for example, only minerals A, B and C) or exclusive (for example, all minerals except A, B and C).
(4) For the purposes of subsection (2), the holder does not take samples of an excluded mineral if, in the course of exploring for, or taking samples of, another mineral, the holder recovers some excluded mineral.
Joint Authority may cancel or not renew exploration licence without compensation
47. No compensation is payable because of the cancellation or non-renewal of an exploration licence by the Joint Authority.
Note 1: The Joint Authority may cancel the licence under section 130.
Note 2: The Joint Authority may refuse under section 108 or 109 to renew the licence.
Licence rights may be suspended
48.(1) The Joint Authority must suspend particular rights conferred by an exploration licence if the Joint Authority is satisfied that it is necessary in the national interest to do so.
(2) The Joint Authority may suspend rights under subsection (1) for a specified period or for an indefinite period.
(3) The Joint Authority may end a suspension at any time.
(4) A suspension or the ending of a suspension must be in writing.
(5) If the Joint Authority:
(a) suspends rights conferred by an exploration licence; or
(b) ends a suspension;
the Joint Authority must give the licence holder a written notice that informs the holder of the suspension or the ending of the suspension.
Note: See section 122 for the effect of the suspension on the obligations associated with the licence.
(6) A suspension takes effect when:
(a) the holder has been given notice of the suspension under subsection (5); and
(b) the suspension has been registered under section 337.
Compensation for acquisition of property due to suspension of rights
49.(1) If:
(a) the Joint Authority suspends licence rights under section 48; and
(b) the suspension results in the acquisition of property from a person; and
(c) the Commonwealth and the person agree on an amount of compensation for the acquisition;
the Commonwealth must pay the person the agreed amount of compensation.
(2) If:
(a) the Joint Authority suspends licence rights under section 48; and
(b) the suspension results in the acquisition of property from a person; and
(c) the Commonwealth and the person do not agree on an amount of compensation for the acquisition; and
(d) the person brings an action for compensation against the Commonwealth in the High Court or an appropriate Supreme Court;
the Commonwealth must pay the person the amount of compensation (if any) that is determined by the court.
(3) In this section:
“acquisition of property” means an acquisition of property within the meaning of paragraph 51(xxxi) of the Constitution;
“appropriate Supreme Court” means the Supreme Court of, or having jurisdiction in, the State or Territory for which the Joint Authority is established.
Division 2—Application for and grant of exploration licence over
standard blocks
Application for exploration licence over standard block
50.(1) A person may apply to the Joint Authority for an exploration licence over a standard block if:
(a) the block is vacant; and
(b) the block is not excluded.
Note: For “excluded blocks” see section 51.
(2) A standard block is vacant if no exploration, retention or mining licence is in force over the block.
(3) A person may apply for an exploration licence over a group of standard blocks if:
(a) the group forms a discrete area; and
(b) there are not more than 500 blocks in the group.
Note: The Designated Authority may, in certain circumstances, allow an application to be made for an exploration licence covering up to 3 discrete areas (see section 53).
Which blocks are excluded?
51.(1) A block is excluded if:
(a) an exploration licence over the block has been surrendered or cancelled; and
(b) a period of 30 days after the day on which the licence was surrendered or cancelled has not ended.
(2) A block is excluded for a particular applicant if:
(a) the applicant previously applied for an exploration licence over the block; and
(b) the application was refused; and
(c) a period of 6 months after the day on which the previous application was refused has not ended.
(3) A block is excluded for a particular applicant if:
(a) the applicant was previously the holder of an exploration, retention or mining licence over the block; and
(b) the previous licence was surrendered or cancelled; and
(c) a period of 6 months after the day on which the previous licence was surrendered or cancelled has not ended.
(4) A block is excluded for a particular applicant if:
(a) the applicant was previously the holder of an exploration, retention or mining licence over the block; and
(b) the holder was:
(i) required by the licence conditions; or
(ii) given a compliance direction;
to provide the Designated Authority with information; and
(c) the holder provided the information; and
(d) the holder surrendered the licence; and
(e) a period of 6 months from the day on which the holder provided the information has not ended.
Designated Authority may determine that excluded block is available
52.(1) A person who wants to apply for an exploration licence over a block that is excluded may apply to the Designated Authority for a determination under subsection (2).
(2) The Designated Authority may determine that the person may apply for the licence over the block despite section 51.
(3) The determination is to be made in writing.
(4) The Designated Authority may make the determination only with the approval of the Joint Authority.
(5) Subsection (4) does not apply to a block in an external territory offshore area.
Note: The responsible Commonwealth Minister is both the Designated Authority (see subsection 29(3)) and the Joint Authority (see subsection 32(3)) for an external territory offshore area.
Designated Authority may allow application for more than one discrete area
53.(1) If:
(a) a person (the “first applicant”) applies for an exploration licence; and
(b) another person (the “second applicant”) subsequently applies for an exploration licence for a group of blocks that includes a block covered by the application made by the first applicant; and
(c) an exploration licence is then granted to the first applicant; and
(d) as a result of the grant, the blocks for which the second applicant can be granted an exploration licence no longer form a discrete area;
the second applicant may apply to the Designated Authority for approval for the application to proceed even though the blocks it covers no longer form a discrete area.
Note: See also section 59.
(2) Subject to subsections (3) and (4), the Designated Authority may approve the application proceeding even though the blocks that the application covers do not form a discrete area.
(3) The Designated Authority may give an approval under subsection (2) only if the blocks covered by the application form not more than 3 discrete areas.
(4) The Designated Authority may give an approval under subsection (1) only with the approval of the Joint Authority.
(5) Subsection (4) does not apply to a block in an external territory offshore area.
Note: The responsible Commonwealth Minister is both the Designated Authority (see subsection 29(3)) and the Joint Authority (see subsection 32(3)) for an external territory offshore area.
How to apply
54.(1) The application must:
(a) be made in accordance with the approved form; and
(b) be made in the approved manner; and
(c) specify the blocks for which the application is made; and
(d) include details of:
(i) the activities that the applicant intends to carry out on the block or blocks covered by the application; and
(ii) the amount of money that the applicant intends to spend on those activities; and
(iii) the technical qualifications of the applicant and of the applicant’s employees who are likely to be involved in activities authorised by the licence; and
(iv) the technical advice available to the applicant; and
(v) the financial resources available to the applicant; and
(vi) if the licence is to be held by more than one person—the share of the licence that each prospective holder will hold; and
(e) be accompanied by maps that:
(i) relate to the blocks; and
(ii) comply with guidelines issued by the Designated Authority under subsection 41(2); and
(f) specify an address for service of notices under this Act and the regulations.
Note 1: For paragraphs (a) and (b) see section 41.
Note 2: Paragraph (c): the Designated Authority may, after consulting the applicant, vary the blocks applied for (see section 59).
(2) The applicant may include in the application any other information that the applicant thinks is relevant.
(3) The application must be lodged with the Designated Authority.
Effect of inclusion of unavailable block in application
55. If:
(a) a person applies for a licence over a group of standard blocks; and
(b) because of section 18, 50 or 51:
(i) an exploration licence cannot be granted over one or more of the blocks in the group; or
(ii) the Joint Authority cannot grant the licence over one or more of the blocks in the group;
the Designated Authority and the Joint Authority may still deal with the application to the extent to which the application covers blocks:
(c) for which an exploration licence can be granted; or
(d) for which the Joint Authority does have power to grant the licence applied for.
Note 1: An exploration licence cannot be granted over a block that is not vacant or is excluded (see sections 50 and 51) or over a reserved block (see section 18).
Note 2: The Joint Authority for a State may grant a licence only over blocks in that State’s Commonwealth-State offshore area.
Payment of fee
56.(1) The applicant must pay the application fee prescribed by the regulations.
(2) The fee must be paid when the application is made.
(3) The Joint Authority may refund any fee paid under subsection (1) but only if it is satisfied that special circumstances exist that justify the refund of the fee.
Application must be advertised
57.(1) The applicant must advertise the application in a newspaper circulating throughout the State or external territory concerned.
(2) The advertisement must contain:
(a) the applicant’s name and address; and
(b) a map and description of the blocks applied for that are sufficient for the blocks to be identified; and
(c) the address of the Designated Authority; and
(d) a statement:
(i) that the applicant has applied for an exploration licence over the blocks described in the notice; and
(ii) that invites comment from the public on the application; and
(iii) that requests that comments be sent to the applicant and the Designated Authority within 30 days after the day on which the advertisement is published.
(3) The advertisement must be published as soon as possible after the applicant applies for an exploration licence.
(4) Subject to subsection (5), the advertisement must be published within 14 days after the day on which the applicant lodges the application.
(5) If:
(a) the applicant applies to the Designated Authority within the 14 day period referred to in subsection (4) for an extension of the period; and
(b) the Designated Authority extends the period;
the advertisement must be published within the period as extended by the Designated Authority.
How multiple applications are dealt with
58.(1) Subject to subsection (2), if a block is covered by 2 or more applications for an exploration or mining licence, the Designated Authority must deal with the applications in the order in which they are made.
Note: See also section 203.
(2) If:
(a) the applications are lodged within a particular time of each other; and
(b) the time is less than the time prescribed by the regulations;
the Designated Authority must determine the order in which the applications are to be dealt with by drawing lots in the way prescribed by the regulations.
Discussions about blocks applied for
59.(1) The Designated Authority may ask the applicant to discuss with the Designated Authority the blocks covered by the application.
(2) The request under subsection (1) must be:
(a) made in writing; and
(b) given to the applicant.
(3) The Designated Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area must ask the applicant to participate in discussions under subsection (1) if the responsible Commonwealth Minister asks the Designated Authority to do so.
(4) If, after discussions, the Designated Authority and the applicant agree on the blocks to be covered by the application, the applicant is taken to have applied for an exploration licence over the blocks agreed on.
(5) The Designated Authority must give the applicant written confirmation of the agreement as soon as possible after the agreement is reached.
(6) The Designated Authority may include in the written confirmation a direction that the applicant must advertise the revised application under section 60.
(7) If the Designated Authority and the applicant do not agree on the blocks to be covered by the application:
(a) the Joint Authority may make a written determination specifying the blocks to be covered by the application; and
(b) the applicant is taken to have applied for an exploration licence over the blocks specified in the determination.
(8) The Designated Authority may include in the written determination a direction that the applicant must advertise the revised application under section 60.
(9) If the Joint Authority makes a determination under subsection (7), the Designated Authority must give a copy of the determination to the applicant as soon as possible after the determination is made.
Advertising revised application
60.(1) If:
(a) the application has been revised under section 59; and
(b) the applicant has been given a direction under subsection 59(6) or (8);
the applicant must advertise the revised application in a newspaper circulating throughout the State or external territory concerned.
(2) The advertisement must contain:
(a) the applicant’s name and address; and
(b) a map and description of the blocks covered by the revised application that are sufficient for the blocks to be identified; and
(c) the address of the Designated Authority; and
(d) a statement:
(i) that the applicant has applied for an exploration licence over the blocks described in the notice; and
(ii) that invites comment from the public on the application; and
(iii) that requests that comments be sent to the applicant and the Designated Authority within 30 days after the day on which the advertisement is published.
(3) The advertisement must be published:
(a) if the Designated Authority and the applicant agree on the blocks applied for under subsection 59(4)—as soon as possible after the applicant is given written confirmation of the agreement under subsection 59(5); or
(b) if the Joint Authority makes a determination of the blocks applied for under subsection 59(7)—as soon as possible after the applicant is given a copy of the determination under subsection 59(9).
(4) Subject to subsection (5), the advertisement must be published within 14 days after the applicant is given the confirmation or copy.
(5) If:
(a) the applicant applies to the Designated Authority within the 14 day period referred to in subsection (4) for an extension of the period; and
(b) the Designated Authority extends the period;
the advertisement must be published within the period as extended by the Designated Authority.
Request for further information
61.(1) The Designated Authority may ask the applicant for further information about the application.
(2) The request must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) be given to the applicant; and
(c) specify the time within which the information must be provided.
(3) Information requested under subsection (1) must be provided:
(a) in writing; and
(b) within the time specified in the request.
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Designated Authority must refer application to Joint Authority if certain requirements met
62.(1) This section applies if the application covers blocks in a Commonwealth-State offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does what is required by sections 54 to 61, the Designated Authority must refer the application to the Joint Authority.
(3) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 54 to 61, the Designated Authority:
(a) must not refer the application to the Joint Authority; and
(b) must give the applicant written notice that the application has been refused.
(4) The application lapses if a notice is given under subsection (3).
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Joint Authority may provisionally grant exploration licence
63. If the Designated Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area refers the application to the Joint Authority under section 62, the Joint Authority may:
(a) provisionally grant an exploration licence to the applicant; or
(b) refuse the application.
Note: Under section 88, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration). The grant will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 70 for “proper acceptance”).
External territory offshore area—how application for exploration licence dealt with
64.(1) This section applies if the application covers blocks in an external territory offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 50 to 61, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for that offshore area) must refuse the application.
(3) If the applicant does what is required by sections 50 to 61, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for that offshore area) may:
(a) provisionally grant an exploration licence to the applicant; or
(b) refuse the application.
Note: Under section 88, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration). The grant will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 70 for “proper acceptance”).
Matters to be specified in the licence
65. The licence must specify:
(a) the blocks covered by the licence; and
(b) the term of the licence; and
(c) the licence conditions.
Note: For the term of a licence see section 88.
Applicant must be notified
66.(1) The Designated Authority must give the applicant written notice of the Joint Authority’s decision under section 63 or 64.
(2) If the Joint Authority provisionally grants an exploration licence:
(a) the Designated Authority must give the licence to the provisional holder; and
(b) the notice under subsection (1) must contain the following information:
(i) notification of any determination under section 399 that the provisional holder must lodge a security;
(ii) notification that the provisional grant will lapse unless the provisional holder, before the end of the primary payment period:
(A) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(B) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(C) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Exploration Licence Fees Act.
Amendment of conditions
67.(1) If the provisional holder is dissatisfied with a licence condition, the provisional holder may ask the Joint Authority to amend the condition.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the provisional holder is given the licence under section 66; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority is given a request under subsection (1), the Joint Authority may amend the licence conditions.
(4) The Joint Authority must give the provisional holder written notice of the amendment.
Amendment of security requirements
68.(1) If the provisional holder:
(a) is notified of a security requirement; and
(b) is dissatisfied with the amount of the security required;
the provisional holder may ask the Joint Authority to make a new determination under section 399.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the provisional holder is given notice under section 66; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority is given a request under subsection (1), the Joint Authority may make a new determination under section 399.
(4) The Joint Authority must give the provisional holder written notice of the new determination.
Extension of primary payment period
69.(1) If the provisional holder makes a request under section 67 or 68, the provisional holder may ask the Designated Authority to extend the primary payment period.
(2) The request must be made within 30 days after the day on which the provisional holder is given notice under section 66.
(3) If the Designated Authority agrees to the request, the Designated Authority must:
(a) determine the period of the extension; and
(b) give the provisional holder a written notice informing the applicant of the period of the extension.
Acceptance of grant of exploration licence for standard block
70.(1) The provisional grant of the exploration licence is properly accepted by the provisional holder if, before the end of the primary payment period, the provisional holder:
(a) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(b) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(c) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Exploration Licence Fees Act.
(2) The provisional grant of the exploration licence is properly accepted by the provisional holder if the provisional holder:
(a) has been granted an extension of the primary payment period under section 69; and
(b) before the end of the secondary payment period:
(i) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(ii) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(iii) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Exploration Licence Fees Act.
Note: Under section 88, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration).
Conditions applicable to licence on grant
71. If the provisional grant of the licence is properly accepted, it is subject to:
(a) the conditions specified in the licence given to the applicant under section 65; or
(b) if the Joint Authority amended those conditions under section 67—those conditions as amended.
Lapse of provisional grant of exploration licence
72. If the provisional grant of the licence is not properly accepted under section 70, the provisional grant lapses.
Division 3—Application for and grant of exploration licence over tender block
Matters to be determined before applications for exploration licence over tender blocks invited
73. If the Joint Authority proposes to invite applications for the grant of an exploration licence over reserved blocks, the Joint Authority must, before inviting the applications, determine:
(a) the procedure and criteria that the Joint Authority will adopt to allocate the licence; and
(b) the amount of security that will be required for the licence under section 399; and
(c) the licence conditions.
Joint Authority may invite applications for exploration licence over tender blocks
74.(1) Subject to subsection (2), the Joint Authority may invite applications for the grant of an exploration licence over reserved blocks.
(2) Applications may be invited for a licence covering a group of reserved blocks only if the group forms a discrete area.
(3) The Joint Authority is to invite applications by publishing a tender block licence notice for the licence in the Gazette.
Tender block licence notice—exploration licence
75.(1) A tender block licence notice for an exploration licence must:
(a) specify the blocks to be covered by the licence; and
(b) specify the period within which applications may be made; and
(c) specify the procedure and criteria that the Joint Authority will adopt to allocate the licence; and
(d) specify the amount of security that the successful applicant will be required to lodge; and
(e) include a statement to the effect that information about:
(i) the security that the successful applicant will be required to lodge; and
(ii) the licence conditions;
may be obtained from the Designated Authority.
(2) The tender block notice may specify not more than 500 blocks for the exploration licence.
Application for exploration licence over tender blocks
76. If a tender block licence notice has been published inviting applications for an exploration licence, a person may apply for the licence.
How to apply
77.(1) The application must:
(a) be made in accordance with the approved form; and
(b) be made in the approved manner; and
(c) be made before the end of the period specified in the tender block licence notice; and
(d) include details of:
(i) the technical qualifications of the applicant and of the applicant’s employees who are likely to be involved in activities authorised by the licence; and
(ii) the technical advice available to the applicant; and
(iii) the financial resources available to the applicant; and
(iv) if the licence is to be held by more than one person—the share of the licence that each prospective holder will hold; and
(e) specify an address for service of notices under this Act and the regulations.
Note: For paragraphs (a) and (b) see section 41.
(2) If the Joint Authority has specified in the tender block licence notice that it will select the successful applicant on the basis of exploration proposals submitted for the blocks to be covered by the licence, the application must include details of the applicant’s exploration proposals for the blocks.
(3) If the Joint Authority has specified in the tender block licence notice that it will select the successful applicant on the basis of the amounts of money offered for the licence, the application must state the amount offered by the applicant for the licence.
(4) The applicant may include in the application any other information that the applicant thinks is relevant.
(5) The application must be lodged with the Designated Authority.
Payment of fee
78.(1) The applicant must pay the application fee prescribed by the regulations.
(2) The fee must be paid when the application is made.
(3) The Joint Authority may refund any fee paid under subsection (1) but only if it is satisfied that special circumstances exist that justify the refund of the fee.
Request for further information
79.(1) The Designated Authority may ask the applicant for further information about the application.
(2) The request must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) be given to the applicant; and
(c) specify the time within which the information must be provided.
(3) Information requested under subsection (1) must be provided:
(a) in writing; and
(b) within the time specified in the request.
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Designated Authority must refer application to Joint Authority if certain requirements met
80.(1) This section applies if the tender block notice relates to blocks in a Commonwealth-State offshore area.
(2) If an applicant does what is required by sections 77 to 79, the Designated Authority must refer the application to the Joint Authority.
(3) If an applicant does not do what is required by sections 77 to 79, the Designated Authority:
(a) must not refer the application to the Joint Authority; and
(b) must give the applicant written notice that the application has been refused.
(4) The application lapses if a notice is given under subsection (3).
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Joint Authority may provisionally grant tender block exploration licence
81.(1) If the Designated Authority refers applications to the Joint Authority under section 80, the Joint Authority may provisionally grant an exploration licence to one of the applicants.
Note: Under section 88, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration). The grant will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 84 for “proper acceptance”).
(2) The Joint Authority may provisionally grant a licence under subsection (1) even if only one application is referred to the Joint Authority by the Designated Authority.
(3) When provisionally granting a licence under subsection (1), the Joint Authority must follow the procedure and apply the criteria specified in the tender block licence notice published for the licence under section 74.
External territory offshore area—how applications dealt with
82.(1) This section applies if the tender block licence notice relates to blocks in an external territory offshore area.
(2) The responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for that offshore area):
(a) must refuse an application if the applicant does not do what is required by sections 77 to 79; and
(b) may provisionally grant an exploration licence to an applicant whose application has not been refused under paragraph (a).
Note: Under section 88, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration). The grant will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 84 for “proper acceptance”).
(3) The responsible Commonwealth Minister may provisionally grant a licence under subsection (2) even if there is only one application that is not refused under paragraph (2)(a).
(4) When provisionally granting a licence under subsection (2), the responsible Commonwealth Minister must follow the procedure and apply the criteria specified in the tender block licence notice published for the licence under section 74.
Successful applicant must be notified
83.(1) If the Joint Authority provisionally grants an exploration licence under section 81, 82 or 87, the Designated Authority must give the provisional holder:
(a) the licence; and
(b) written notice that the provisional grant will lapse unless the provisional holder, before the end of the primary payment period:
(i) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(ii) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(iii) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Exploration Licence Fees Act; and
(iv) if the tender is determined on the basis of the amounts of money offered for the licence—pays the Commonwealth the amount that the provisional holder offered for the licence under subsection 77(3).
(2) The licence must specify:
(a) the blocks covered by the licence; and
(b) the term of the licence; and
(c) the licence conditions.
Note: For the term of a licence see section 88.
Acceptance of grant of exploration licence over tender blocks
84. The provisional grant of an exploration licence is properly accepted by the provisional holder if, within 30 days after the day on which the provisional holder is given notice under section 83, the provisional holder:
(a) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(b) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399;and
(c) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Exploration Licence Fees Act; and
(d) if the tender is determined on the basis of the amount of money offered for the licence—pays the Commonwealth the amount that the provisional holder offered for the licence under subsection 77(3).
Note: Under section 88, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration).
Conditions applicable to licence on grant
85. If the provisional grant of the licence is properly accepted, the licence is subject to the conditions determined under section 73.
Lapse of provisional grant of exploration licence
86. If the provisional grant of the licence is not properly accepted under section 85, the provisional grant lapses.
Provisional grant to next applicant if grant lapses
87.(1) If the provisional grant of the licence lapses under section 86, the Joint Authority may provisionally grant the licence to another of the applicants for the licence.
(2) When provisionally granting a licence under subsection (1), the Joint Authority must follow the procedure and apply the criteria specified in the tender block licence notice published for the licence under section 74.
Division 4—Duration of exploration licence
Initial term of exploration licence
88.(1) An exploration licence comes into force on:
(a) the day on which the grant of the licence is registered; or
(b) if a day later than the day on which the grant of the licence is registered is specified in the licence as its commencement day—that specified day.
(2) The initial term of an exploration licence ends 4 years after:
(a) the day on which the licence is provisionally granted; or
(b) if a day later than the day on which the licence is provisionally granted is specified in the licence as its commencement day—that specified day.
Note: The licence may be surrendered at any time (see section 127).
Term of renewal of exploration licence
89.(1) A renewal of an exploration licence comes into force on:
(a) the day on which the renewal is registered; or
(b) the day on which the previous term of the licence expires;
whichever is the later.
Note: See Division 6 for renewal.
(2) The term of a renewal of a licence ends 2 years after the day on which the previous term of the licence expires.
Note: The licence may be surrendered at any time (see section 127).
(3) Ignore section 90 in working out the period of 2 years referred to in subsection (2).
(4) An exploration licence is not to be renewed more than 3 times.
Effect of suspension of rights on term of exploration licence
90.(1) If the Joint Authority suspends rights conferred by an exploration licence for a specified period under section 48, the Joint Authority may extend the term of the licence.
(2) An extension of a licence term under subsection (1):
(a) must not be for a period that is longer than the period for which the licence rights were suspended; and
(b) must be in writing.
(3) If the Joint Authority extends the term of a licence under subsection (1), the Joint Authority must give the licence holder a written notice that informs the holder:
(a) that the licence has been extended; and
(b) of the period of the extension.
Effect of application for renewal on term of exploration licence
91. If:
(a) an exploration licence holder applies to renew the licence under section 101; and
(b) the current term of the licence expires; and
(c) a renewal of the licence does not take effect immediately after the current term expires;
the licence remains in force after the current term expires until:
(d) a renewal of the licence takes effect; or
(e) a provisional renewal of the licence lapses; or
(f) the application for renewal is withdrawn or refused.
Effect of application for retention licence or mining licence on term of exploration licence
92. If:
(a) an exploration licence holder applies for:
(i) a retention licence (see section 137); or
(ii) a mining licence (see section 198);
over the licence area, or part of the licence area, of the exploration licence; and
(b) the current term of the exploration licence expires; and
(c) a grant of the retention licence or mining licence does not take effect before the current term of the exploration licence expires;
the exploration licence remains in force until:
(d) the grant of the retention licence or mining licence takes effect; or
(e) a provisional grant of the retention licence or mining licence lapses; or
(f) the application for the retention licence or mining licence is withdrawn or refused.
Effect of application for extension on term of licence
93. If:
(a) an exploration licence holder applies for an extension of the licence under section 94 or 96; and
(b) the holder has also applied to renew the licence under section 101; and
(c) the extension application is not decided before the licence is due to expire;
then:
(d) the renewal application lapses; and
(e) the licence remains in force:
(i) until:
(A) if the Joint Authority extends the term of the licence under section 95 for a specified period—30 days after the day on which that period ends; or
(B) if the Joint Authority refuses to extend the term of the licence under section 95—30 days after the day on which the holder is given notice of the refusal under section 98; or
(ii) until a further application is made under section 101 to renew the licence;
whichever is the later.
Extension of licence—activities disrupted
94.(1) If:
(a) an exploration licence authorises the licence holder to carry out an activity; and
(b) circumstances beyond the control of the holder prevent the holder from carrying out the activity;
the holder may apply to the Joint Authority for an extension of the licence.
(2) The application must be made:
(a) within 30 days after the day on which the holder first became aware of the circumstances; and
(b) before the licence expires.
(3) The application must be lodged with the Designated Authority.
Grant of licence extension—activities disrupted
95.(1) Subject to subsection (2), if an exploration licence holder applies for an extension under section 94, the Joint Authority:
(a) must grant an extension of the licence if the Joint Authority is satisfied that:
(i) the holder is unable to carry out the activities authorised by the licence; and
(ii) the holder is unable to do so because of circumstances beyond the holder’s control; and
(iii) the period during which the holder is unable to do so:
(A) occurs while the licence is in force; and
(B) does not occur during any excluded time; and
(b) must refuse the application for extension if the Joint Authority is not satisfied of the matters referred to in paragraph (a).
(2) The period for which the extension is granted must not be longer than the disruption period for the licence less any excluded time for the licence.
(3) The extension may be granted subject to whatever conditions the Joint Authority thinks appropriate.
(4) In this section:
“disruption period” for a licence means the period during which the licence holder is unable to carry out activities authorised by the licence because of circumstances beyond the holder’s control;
“excluded time” for a licence means any period during which the licence was in force because of section 90, 91, 92 or 93.
Note: Under section 90, the Designated Authority can extend the term of a licence if there has been a suspension of rights under section 48. Under section 91, the term of a licence is automatically extended if there is an application for the renewal of a licence undecided when the licence is due to expire. Under section 92, the term of a licence is automatically extended if the holder applies for a retention or mining licence over the licence area. Under section 93, the term of a licence is automatically extended if there is an application for an extension of the licence undecided when the licence is due to expire.
Extension of licence—other circumstances
96.(1) An exploration licence holder may apply to the Joint Authority for an extension of the licence if, under section 121, the Joint Authority:
(a) suspends a licence condition; or
(b) exempts the holder from complying with a licence condition.
(2) The application:
(a) must be made not later than 30 days before the licence expires; and
(b) must be lodged with the Designated Authority.
Grant of licence extension—other circumstances
97.(1) Subject to subsection (2), if an exploration licence holder applies for an extension under section 96, the Joint Authority:
(a) may grant an extension of the licence; or
(b) may refuse to grant an extension of the licence.
(2) The extension must not be for a period that is longer than the period of the suspension or exemption.
(3) The extension may be granted subject to whatever conditions the Joint Authority thinks appropriate.
Notification of decision
98.(1) Ifthe Joint Authority grants an extension of an exploration licence under section 95 or 97, the Joint Authority must give the licence holder a written notice that informs the holder of:
(a) the grant of extension; and
(b) the period of the extension; and
(c) if the extension is subject to conditions—the conditions.
(2) If the Joint Authority refuses an application for a licence extension, the Joint Authority must give the licence holder a written notice that informs the holder of:
(a) the refusal; and
(b) the reasons for the refusal.
Division 5—Voluntary surrender of part of exploration licence area
Voluntary surrender of blocks if discrete area remains
99.(1) An exploration licence holder may surrender a block or some of the blocks covered by the licence if the remaining blocks in the licence area form a discrete area.
Note: See section 127 for the surrender of the whole licence.
(2) A surrender under subsection (1) must:
(a) be made in writing; and
(b) identify the blocks surrendered; and
(c) be given to the Designated Authority.
Note: The surrender takes effect when it is registered under section 337 (see subsection 337(5)).
Voluntary surrender of blocks if up to 3 discrete areas remain
100.(1) If:
(a) an exploration licence holder wants to surrender some of the blocks covered by the licence; and
(b) the blocks remaining in the licence area after the proposed surrender would form not more than 3 discrete areas;
the holder may apply to the Designated Authority for approval of the proposed surrender.
(2) The application:
(a) must be in writing; and
(b) must include a surrender proposal that identifies the blocks in the licence area that the holder proposes to surrender; and
(c) may include any other information that the holder thinks is relevant; and
(d) must be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) Subject to subsection (6), if the Designated Authority agrees with the surrender proposal the Designated Authority may approve the surrender of the blocks specified in the proposal by giving the holder written notice of the approval.
Note: The surrender takes effect when it is registered under section 337 (see subsection 337(5)).
(4) If the Designated Authority does not agree with the surrender proposal, the Designated Authority may ask the holder to discuss the proposal.
(5) Subject to subsection (6), if the Designated Authority and the holder agree, after discussions, on the blocks to be surrendered the Designated Authority may approve the surrender of the blocks agreed on by giving the holder written confirmation of the agreement.
Note: The surrender takes effect when it is registered under section 337 (see subsection 337(5)).
(6) The Designated Authority may give approval under subsection (3) or (5) only with the approval of the Joint Authority.
(7) Subsection (6) does not apply to a block in an external territory offshore area.
Note: The responsible Commonwealth Minister is both the Designated Authority (see subsection 29(3)) and the Joint Authority (see subsection 32(3)) for an external territory offshore area.
(8) If, after discussions, the Designated Authority and the holder do not agree on the surrender proposal, no blocks are surrendered.
Division 6—Application for and grant of renewal of exploration licence
Application for renewal of exploration licence
101.An exploration licence holder may apply to the Joint Authority to renew the licence.
Note 1: Part of the licence area must be surrendered on each renewal (see section 104).
Note 2: At each renewal, the licence conditions are reviewed (see section 118).
When must an application to renew be made?
102.(1) Subject to subsection (2), the application must be made at least 30 days before the day on which the licence is to expire.
Note: If an application for extension of a licence is made, the expiry of the licence is postponed (see section 91).
(2) The Designated Authority may accept an application that is made later than 30 days before the day on which the licence is to expire if:
(a) the application is made before the day on which the licence expires; and
(b) the Designated Authority believes that there are reasonable grounds for accepting the application.
How to apply for renewal
103.(1) The application must:
(a) be made in accordance with the approved form; and
(b) be made in the approved manner; and
(c) include details of:
(i) the activities carried out by the applicant under the licence during its current term; and
(ii) the amount of money spent by the applicant in relation to the blocks covered by the licence during its current term; and
(iii) the activities that the applicant intends to carry out under the licence during the term applied for; and
(iv) the amount of money that the applicant intends to spend on those activities during the term applied for; and
(d) specify the blocks that the applicant nominates for surrender in accordance with section 104.
Note: For paragraphs (a) and (b) see section 41.
(2) The applicant may include in the application any other information that the applicant thinks is relevant.
(3) The application must be lodged with the Designated Authority.
Mandatory reduction of licence area on renewal of exploration licence
104.(1) This section deals with the mandatory reduction of the licence area covered by an exploration licence when the licence is renewed.
(2) Subject to paragraph (4)(b), on each surrender day of an exploration licence, the licence holder must surrender:
(a) 50% of the number of blocks in the licence area; or
(b) if 50% of that number is a whole number and a fraction—the next higher whole number.
(3) Subject to paragraph (4)(a), the blocks that remain in the licence area after a surrender under subsection (2) must form a discrete area.
(4) Subject to subsection (5), the Designated Authority may:
(a) give permission for the surrender of blocks in a licence area if the licence area remaining after the proposed surrender would consist of not more than 3 discrete areas; or
(b) give permission for a licence area to be reduced by less than 50% if the Designated Authority considers that there are special circumstances present in relation to the renewal application.
(5) The Designated Authority may give permission under subsection (4) only with the approval of the Joint Authority.
(6) Subsection (5) does not apply to a block in an external territory offshore area.
Note: The responsible Commonwealth Minister is both the Designated Authority (see subsection 29(3)) and the Joint Authority (see subsection 32(3)) for an external territory offshore area.
Request for further information
105.(1) The Designated Authority may ask the applicant to provide further information about the application.
(2) The request must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) be given to the applicant; and
(c) specify the time within which the information must be provided.
(3) Information requested under subsection (1) must be provided:
(a) in writing; and
(b) within the time specified in the request.
Payment of fee
106.(1) The applicant must pay the application fee prescribed by the regulations.
(2) The fee must be paid when the application is made.
(3) The Joint Authority may refund any fee paid under subsection (1) but only if it is satisfied that special circumstances exist that justify the refund of the fee.
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Designated Authority must refer renewal application to Joint Authority if certain requirements met
107.(1) This section applies if the renewal application covers blocks in a Commonwealth-State offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does what is required by sections 101 to 106, the Designated Authority must refer the application to the Joint Authority.
(3) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 101 to 106, the Designated Authority:
(a) must not refer the application to the Joint Authority; and
(b) must give the applicant written notice that the application has been refused.
(4) The application lapses if a notice is given under subsection (3).
Commonwealth-State offshore area—provisional renewal of an exploration licence
108.(1) The Joint Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area must provisionally renew an exploration licence if:
(a) the Designated Authority refers the renewal application to the Joint Authority under section 107; and
(b) the applicant has complied with:
(i) this Act; and
(ii) the regulations; and
(iii) the licence conditions.
Note 1: Under section 89, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration). The renewal will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 114 for “proper acceptance”).
Note 2: Under section 118, new conditions may be imposed on renewal.
(2) If subsection (1) does not require the Joint Authority to provisionally renew the licence, the Joint Authority may:
(a) provisionally renew the licence; or
(b) refuse to renew the licence.
External territory offshore area—how application for renewal dealt with
109.(1) This section applies if the renewal application covers blocks in an external territory offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 101 to 106, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for the offshore area) must refuse to renew the licence.
(3) If:
(a) the applicant does what is required by sections 101 to 106; and
(b) the applicant has complied with:
(i) this Act; and
(ii) the regulations; and
(iii) the licence conditions.
the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for that offshore area) must provisionally renew the exploration licence.
Note 1: Under section 89, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration). The renewal will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 114 for “proper acceptance”).
Note 2: Under section 118, new conditions may be imposed on renewal.
(4) If:
(a) subsection (2) does not require the responsible Commonwealth Minister to refuse to renew the licence; and
(b) subsection (3) does not require the responsible Commonwealth Minister to provisionally renew the licence;
the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for that offshore area) may:
(c) provisionally renew the licence; or
(d) refuse to renew the licence.
Note: Under section 89, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration). The renewal will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 114 for “proper acceptance”).
Applicant must be notified
110.(1) The Designated Authority must give the applicant written notice of the Joint Authority’s decision under section 108 or 109.
(2) If the Joint Authority provisionally renews the exploration licence under section 108 or 109, the notice must contain the following information:
(a) notification of the conditions of the renewed licence;
(b) notification of any determination under section 399 that the applicant must lodge a security or a further security;
(c) notification that the provisional renewal will lapse unless the applicant, before the end of the primary payment period:
(i) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the renewal; and
(ii) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(iii) pays the fees that must be paid under the Exploration Licence Fees Act.
Note: Section 118 provides for renewals to be granted subject to conditions.
Amendment of conditions
111.(1) If the licence holder:
(a) has been provisionally granted a renewal of the licence under section 108 or 109; and
(b) is notified of the licence conditions; and
(c) is dissatisfied with a condition;
the holder may ask the Joint Authority to amend the condition.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the holder is given notice under section 110; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority is given a request under subsection (1), the Joint Authority may amend the licence conditions.
(4) The Joint Authority must give the holder written notice of the amendment.
Amendment of security requirements
112.(1) If the licence holder:
(a) has been provisionally granted a renewal of the licence under section 108 or 109; and
(b) is notified of a security requirement; and
(c) is dissatisfied with the amount of the security required;
the holder may ask the Joint Authority to make a new determination under section 399.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the holder is given notice under section 110; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority is given a request under subsection (1), the Authority may make a new determination under section 399.
(4) The Joint Authority must give the holder written notice of the new determination.
Extension of primary payment period
113.(1) If the licence holder makes a request under section 111 or 112, the holder may ask the Designated Authority to extend the primary payment period.
(2) The request must be made within 30 days after the day on which the holder is given notice under section 110.
(3) If the Designated Authority agrees to the request, the Designated Authority must:
(a) determine the period of the extension in writing; and
(b) give the holder a written notice informing the holder of the period of the extension.
Acceptance of renewal of exploration licence
114.(1) The provisional renewal of an exploration licence is properly accepted by the licence holder if, before the end of the primary payment period, the holder:
(a) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the renewal; and
(b) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(c) pays the fees that must be paid under the Exploration Licence Fees Act.
Note: Under section 89, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration).
(2) The provisional renewal of an exploration licence is properly accepted by the licence holder if the holder:
(a) has been granted an extension of the primary payment period under section 113; and
(b) before the end of the secondary payment period:
(i) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the renewal; and
(ii) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(iii) pays the fees that must be paid under the Exploration Licence Fees Act.
Note: Under section 89, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration).
Conditions applicable to licence on renewal
115. If the provisional renewal is properly accepted, the renewed licence is subject to:
(a) the conditions specified in the notice given to the licence holder under section 110; or
(b) if the Joint Authority amended those conditions under section 111—those conditions as amended.
Lapse of provisional renewal of exploration licence
116. If the provisional renewal of an exploration licence is not properly accepted under section 114, the provisional renewal lapses.
Division 7—Obligations associated with exploration licence
General
117.(1) The sources of obligations associated with an exploration licence are:
(a) the licence conditions; and
(b) obligations arising from compliance directions given by the Designated Authority; and
(c) obligations imposed by this Act and the regulations.
Note: For paragraph (a) see sections 118 to 120. For paragraph (b) see sections 387 and 392. For paragraph (c) see sections 123 to 125 and section 372.
(2) If an exploration licence has 2 or more holders, all the holders are jointly and severally bound by the obligations that attach to the licence.
Conditions of exploration licence
118.(1) The Joint Authority may grant or renew an exploration licence subject to whatever conditions the Joint Authority thinks appropriate.
(2) If the Joint Authority grants or renews an exploration licence subject to conditions, the conditions must be specified in the licence.
(3) Without limiting subsection (1), the Joint Authority may attach the following kinds of conditions to the grant or renewal of an exploration licence:
(a) a condition requiring the licence holder to take out insurance as required by the Designated Authority;
(b) a condition requiring the holder to carry out certain work in or in relation to the licence area during the term of the licence, and to comply with directions concerning that work given under section 387;
(c) a condition requiring the holder to spend a specified amount of money in carrying out the work referred to in paragraph (b), and to comply with directions concerning that expenditure given under section 387;
(d) a condition requiring the holder to lodge a security with the Designated Authority;
(e) a condition requiring the holder to keep specified information;
(f) a condition requiring the holder to give the Designated Authority, on request, specified information;
(g) a condition requiring the holder to take steps to protect the environment of the licence area, including conditions relating to:
(i) protecting wildlife; or
(ii) minimising the effect on the environment of the licence area and the area surrounding the licence area of activities carried out in the licence area;
(h) a condition requiring the holder to repair any damage to the environment caused by activities in the licence area;
(i) a condition requiring the holder to pay a specified penalty to the Commonwealth if the holder does not comply with a licence condition.
(4) A condition under paragraph (3)(d) must specify:
(a) the amount of the security required; and
(b) the kind of security required; and
(c) the manner and form in which the security is to be lodged.
(5) Without limiting paragraph (3)(d), a condition under that paragraph may require the lodgment of a security in the form of a guarantee and if a guarantee is required the condition may specify:
(a) the kind of person who is to give the guarantee; and
(b) the terms of the guarantee.
No conditions requiring payment of money
119.Except for a condition requiring the payment of a penalty or lodgment of security, a licence condition must not require the payment of money to:
(a) the Designated Authority; or
(b) the Joint Authority; or
(c) the Commonwealth.
Variation of conditions
120.(1) If:
(a) an exploration licence holder requests the Designated Authority in writing to vary a licence condition; or
(b) an exploration licence continues in force because of section 93; or
(c) an extension of an exploration licence is granted under section 95; or
(d) part of the licence area of an exploration licence is surrendered under section 99 or 100;
the Joint Authority may vary a licence condition.
(2) If a Designated Authority gives:
(a) a direction under section 387; or
(b) an approval, consent or exemption under the regulations;
to an exploration licence holder, the Joint Authority may vary a licence condition to the extent necessary to avoid inconsistency between the licence conditions and the direction, approval, consent or exemption.
(3) The Joint Authority may vary a licence condition subject to whatever conditions the Joint Authority thinks appropriate.
(4) If the Joint Authority varies a licence condition, the Designated Authority must give the licence holder a written notice that:
(a) informs the holder of the variation; and
(b) specifies the conditions which have been varied; and
(c) specifies any conditions to which the variation is subject.
Exemption from or suspension of conditions
121.(1) If:
(a) an exploration licence holder requests the Designated Authority in writing to:
(i) suspend a licence condition; or
(ii) exempt the holder from complying with a licence condition; or
(b) an exploration licence continues in force because of section 93; or
(c) an extension of an exploration licence is granted under section 95; or
(d) part of the licence area of an exploration licence is surrendered under section 99 or 100;
the Joint Authority may:
(e) suspend a licence condition; or
(f) exempt the holder from complying with a licence condition.
(2) If a Designated Authority gives:
(a) a direction under section 387; or
(b) an approval, consent or exemption under the regulations;
to an exploration licence holder, the Joint Authority may suspend a licence condition, or exempt the holder from compliance with a licence condition, to the extent necessary to avoid inconsistency between the licence conditions and the direction, approval, consent or exemption.
(3) The Joint Authority may:
(a) suspend a licence condition; or
(b) exempt the licence holder from complying with a licence condition;
subject to whatever conditions the Joint Authority thinks appropriate.
(4) If the Joint Authority:
(a) suspends a licence condition; or
(b) exempts the licence holder from complying with a licence condition;
the Designated Authority must give the holder a written notice that:
(c) informs the holder of the exemption or suspension; and
(d) specifies the conditions which have been suspended or affected by the exemption; and
(e) specifies any conditions to which the suspension or exemption is subject.
Note: A suspension or exemption of a condition cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 337).
Automatic suspension of conditions if licence rights are suspended
122. If:
(a) the Joint Authority suspends particular rights conferred by an exploration licence under section 48; and
(b) a licence condition is affected by the suspension;
the licence condition is suspended for the period of the suspension of the rights.
Work practices
123. If a person who is:
(a) an exploration licence holder; or
(b) an associate of the holder;
carries out activities in the licence area that are authorised by the licence, the person must take all reasonable steps:
(c) to ensure that the activities are carried out at a standard that is accepted as reasonable and proper in the mining industry; and
(d) to protect the health, safety and welfare of people engaged in the activities in and about the licence area; and
(e) to maintain in good repair all structures and equipment brought into the licence area by the person; and
(f) to remove from the licence area any structure, equipment or other property that:
(i) belongs to the person, or is under the person’s control; and
(ii) is not being used, or is not going to be used, in connection with the activities.
Maximum penalty: 200 penalty units.
Licence holder must keep specified records etc.
124. An exploration licence holder must:
(a) keep whatever records, cores and samples; and
(b) give whatever records, cores and samples to the Designated Authority for inspection; and
(c) make whatever returns;
are necessary to comply with:
(d) the regulations; or
(e) the licence conditions; or
(f) a direction given by the Designated Authority under section 387.
Note: Under section 387 the Designated Authority may direct a person to keep records and cores, to collect and retain samples, and to make returns.
Maximum penalty: 100 penalty units.
Licence holder must assist inspectors
125. An exploration licence holder must provide an inspector with reasonable facilities and assistance so that the inspector is able to carry out compliance inspections.
Note: See sections 377 to 384 for compliance inspections.
Maximum penalty: 50 penalty units.
Division 8—Expiry of exploration licence
General
126. An exploration licence expires if:
(a) the term of the licence ends without the licence being renewed; or
(b) the licence holder surrenders the licence; or
(c) a retention licence is granted over the blocks in the licence area of the exploration licence; or
(d) a mining licence is granted over the blocks in the licence area of the exploration licence; or
(e) the licence is cancelled.
Note: For paragraph (a) see Division 6. For paragraph (b) see section 127. For paragraph (c) see section 128. For paragraph (d) see section 129. For paragraph (e) see section 130.
Voluntary surrender of exploration licence
127. An exploration licence holder may surrender the licence.
Note 1: See Division 5 for voluntary surrender of part of a licence area.
Note 2: The surrender takes effect when it is registered under section 337 (see subsection 337(5)).
Automatic expiry of exploration licence when retention licence takes effect
128. If:
(a) an exploration licence is in force under this Act; and
(b) the Joint Authority provisionally grants a retention licence over all or some of the blocks in the exploration licence area; and
(c) the provisional grant of the retention licence is properly accepted; and
(d) the retention licence comes into force;
the exploration licence expires in relation to the blocks covered by the retention licence.
Automatic expiry of exploration licence when mining licence takes effect
129. If:
(a) an exploration licence is in force under this Act; and
(b) the Joint Authority provisionally grants a mining licence over all or some of the blocks in the exploration licence area; and
(c) the provisional grant of the mining licence is properly accepted; and
(d) the mining licence comes into force;
the exploration licence expires in relation to the blocks covered by the mining licence.
Cancellation of exploration licence
130.(1) Subject to subsection (5), the Joint Authority may cancel an exploration licence if the licence holder:
(a) breaches a licence condition; or
(b) contravenes a provision of this Act or the regulations; or
(c) breaches a condition attached to an approval under subsection 365(2); or
(d) fails to pay user charge that is payable for the licence under the Exploration Licence User Charge Act.
(2) If the Joint Authority proposes to cancel a licence under subsection (1), the Designated Authority must give the licence holder a written notice that informs the holder of the proposed cancellation.
(3) The notice must:
(a) specify the reason for the proposed cancellation; and
(b) invite the holder to make submissions in relation to the proposed cancellation; and
(c) specify the day by which submissions should be given to the Joint Authority; and
(d) specify an address where submissions are to be lodged.
(4) The day specified under paragraph (3)(c) must be not less than 60 days after the day on which the notice is given.
(5) The Joint Authority may cancel the licence only if:
(a) the holder has been given a notice under subsection (2); and
(b) the Joint Authority has considered:
(i) any submission made by the holder; and
(ii) any steps taken by the holder to remedy the circumstances that led to the proposal to cancel the licence and to prevent those circumstances from happening again; and
(c) the Joint Authority is satisfied that no special circumstances exist that justify the licence not being cancelled.
Obligations of former exploration licence holders and former associates
131.(1) Subject to subsection (4), if:
(a) a person was:
(i) an exploration licence holder; or
(ii) an associate of an exploration licence holder; and
(b) the licence:
(i) expires; or
(ii) is cancelled; or
(iii) is surrendered; and
(c) an obligation associated with the licence arising out of:
(i) a licence condition; or
(ii) a direction given under section 387; or
(iii) this Act or the regulations;
has not been discharged; and
(d) the person was bound by that obligation when the person was the licence holder or an associate;
the person remains bound by the obligation until the obligation is discharged.
(2) Subsection (1) does not continue an obligation to carry out exploration or recovery activities.
(3) Subsection (1) continues an obligation that a person had to carry out exploration or recovery activities in a particular manner if the person carries them out.
(4) The Joint Authority may determine that the person is not subject to:
(a) a particular obligation under this section; or
(b) all the person’s remaining obligations under this section.
(5) A determination under subsection (4) is to be in writing.
PART 2.3—RETENTION LICENCES
Division 1—General
Retention licences
132. This Part provides for the grant of retention licences over blocks in an offshore area.
Note: A retention licence is designed to allow an exploration licence holder to retain rights over an area if:
• the holder has identified and evaluated a significant mineral deposit in the exploration licence area; and
• mining the deposit is not commercially viable in the short term for some reason (for example, the political situation, the prevailing situation in the commodity market for particular minerals, the need to arrange finance or build up capital reserves, the need to develop new technologies or the impending development of new technologies); and
• there is a reasonable prospect of development of the deposit in the longer term.
See section 145 for the grounds on which a retention licence may be granted.
Activities authorised by a retention licence
133.(1) Subject to subsections (2) and (3), a retention licence holder may:
(a) explore for minerals in the licence area; and
(b) recover minerals in the licence area.
Note 1: The retention licence may specify a restricted range of activities that are the only ones authorised by the licence (see subsection 146(3)).
Note 2: Under subsection 23(1) the concept of “exploration” extends to activities that are directly related to exploration.
Note 3: Under subsection 24(1) the concept of “recovery” extends to activities that are directly related to the recovery of minerals.
(2) A retention licence does not authorise the recovery of minerals as part of a commercial mining operation.
(3) If the licence is expressed to restrict the kind of minerals covered by the licence, the holder is not permitted to explore for, or to recover, minerals not covered by the licence.
(4) A restriction on the kind of minerals covered by the licence may be inclusive (for example, only minerals A, B and C) or exclusive (for example, all minerals except A, B and C).
(5) For the purposes of subsection (3), the holder does not recover an excluded mineral if, in the course of exploring for, or recovering, another mineral, the holder recovers some excluded mineral.
Joint Authority may cancel or not renew retention licence without compensation
134.No compensation is payable because of the cancellation or non-renewal of a retention licence by the Joint Authority.
Note 1: The Joint Authority may cancel the licence under section 189 or 190.
Note 2: The Joint Authority may refuse under section 165 or 166 to renew the licence.
Licence rights may be suspended
135.(1) The Joint Authority must suspend particular rights conferred by a retention licence if the Joint Authority is satisfied that it is necessary in the national interest to do so.
(2) The Joint Authority may suspend rights under subsection (1) for a specified period or for an indefinite period.
(3) The Joint Authority may end a suspension at any time.
(4) A suspension or the ending of a suspension must be in writing.
(5) If the Joint Authority:
(a) suspends rights conferred by a retention licence; or
(b) ends a suspension;
the Joint Authority must give the licence holder a written notice that informs the holder of the suspension or the ending of a suspension.
Note: See section 181 for the effect of the suspension on the obligations associated with the licence.
(6) A suspension takes effect when:
(a) the holder has been given notice of the suspension under subsection (5); and
(b) the suspension has been registered under section 337.
Compensation for acquisition of property due to suspension of rights
136.(1) If:
(a) the Joint Authority suspends licence rights under section 135; and
(b) the suspension results in the acquisition of property from a person; and
(c) the Commonwealth and the person agree on an amount of compensation for the acquisition;
the Commonwealth must pay the person the agreed amount of compensation.
(2) If:
(a) the Joint Authority suspends licence rights under section 135; and
(b) the suspension results in the acquisition of property from a person; and
(c) the Commonwealth and the person do not agree on an amount of compensation for the acquisition; and
(d) the person brings an action for compensation against the Commonwealth in the High Court or an appropriate Supreme Court;
the Commonwealth must pay the person the amount of compensation (if any) that is determined by the court.
(3) In this section:
“acquisition of property” means an acquisition of property within the meaning of paragraph 51(xxxi) of the Constitution;
“appropriate Supreme Court” means the Supreme Court of, or having jurisdiction in, the State or Territory for which the Joint Authority is established.
Division 2—Application for and grant of retention licence
Application for retention licence
137.(1) An exploration licence holder may apply to the Joint Authority for a retention licence over blocks within the exploration licence area.
(2) A person may apply for a retention licence over a group of blocks only if:
(a) the group forms a discrete area; and
(b) there are not more than 20 blocks in the group.
(3) The exploration licence holder may apply for 2 or more retention licences over different parts of the exploration licence area.
How to apply
138.(1) The application must:
(a) be made in accordance with the approved form; and
(b) be made in the approved manner; and
(c) specify the blocks for which the application is made; and
(d) include details of:
(i) the reasons why the applicant is applying for a retention licence rather than a mining licence; and
(ii) the mineral deposit that the applicant has identified and evaluated and that the applicant believes is commercially viable in the longer term; and
(iii) the applicant’s assessment of the present and potential commercial viability of the mineral deposit; and
(iv) the overall work program that the applicant has already carried out under the exploration licence on the blocks covered by the application; and
(v) the amount of money that the applicant has already spent under the exploration licence on and in connection with the blocks covered by the application; and
(vi) the activities that the applicant intends to carry out on the blocks covered by the application; and
(vii) the amount of money that the applicant intends to spend on and in connection with those activities; and
(viii) the technical qualifications of the applicant and of the applicant’s employees who are likely to be involved in activities authorised by the licence; and
(ix) the technical advice available to the applicant; and
(x) the financial resources available to the applicant; and
(e) be accompanied by maps that:
(i) relate to the blocks; and
(ii) comply with guidelines issued by the Designated Authority under subsection 41(2); and
(f) specify an address for service of notices under this Act and the regulations.
Note: For paragraphs (a) and (b) see section 41.
(2) The mineral deposit details given under subparagraph (1)(d)(ii) must include:
(a) a full description of the mineral deposit; and
(b) both factual information about the deposit and the applicant’s interpretation of the factual information.
(3) The applicant may include in the application any other information that the applicant thinks is relevant.
(4) The application must be lodged with the Designated Authority.
Payment of fee
139.(1) The applicant must pay the application fee prescribed by the regulations.
(2) The fee must be paid when the application is made.
(3) The Joint Authority may refund any fee paid under subsection (1) but only if it is satisfied that special circumstances exist that justify the refund of the fee.
Application must be advertised
140.(1) The applicant must advertise the application in a newspaper circulating throughout the State or external territory concerned.
(2) The advertisement must contain:
(a) the applicant’s name and address; and
(b) a map and description of the blocks applied for that are sufficient for the blocks to be identified; and
(c) the address of the Designated Authority; and
(d) a statement:
(i) that the applicant has applied for a retention licence for the blocks described in the notice; and
(ii) that invites comment from the public on the application; and
(iii) that requests that comments be sent to the applicant and the Designated Authority within 30 days after the day on which the advertisement is published.
(3) The advertisement must be published as soon as possible after the applicant applies for a retention licence.
(4) Subject to subsection (5), the advertisement must be published within 14 days after the day on which the applicant lodges the application.
(5) If:
(a) the applicant applies to the Designated Authority within the 14 day period referred to in subsection (4) for an extension of the period; and
(b) the Designated Authority extends the period;
the advertisement must be published within the period as extended by the Designated Authority.
Request for further information
141.(1) The Designated Authority may ask the applicant for further information about the application.
(2) The request must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) be given to the applicant; and
(c) specify the time within which the information must be provided.
(3) Information requested under subsection (1) must be provided:
(a) in writing; and
(b) within the time specified in the request.
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Designated Authority must refer application to Joint Authority if certain requirements met
142.(1) This section applies if the application covers blocks in a Commonwealth-State offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does what is required by sections 138 to 141, the Designated Authority must refer the application to the Joint Authority.
(3) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 138 to 141, the Designated Authority:
(a) must not refer the application to the Joint Authority; and
(b) must give the applicant written notice that the application has been refused.
(4) The application lapses if a notice is given under subsection (3).
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Joint Authority may provisionally grant retention licence
143. If the Designated Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area refers the application to the Joint Authority under section 142, the Joint Authority may:
(a) subject to section 145, provisionally grant a retention licence to the applicant; or
(b) refuse the application.
Note: Under section 154, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration). The grant will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 151 for “proper acceptance”).
External territory offshore area—how application for retention licence dealt with
144.(1) This section applies if the application covers blocks in an external territory offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 137 to 141, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for the offshore area) must refuse the application.
(3) If the applicant does what is required by sections 137 to 141, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for the offshore area) may:
(a) subject to section 145, provisionally grant a retention licence to the applicant; or
(b) refuse the application.
Note: Under section 154, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration). The grant will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 151 for “proper acceptance”).
Grounds for granting retention licence
145.(1) The Joint Authority may provisionally grant the retention licence only if it is satisfied that:
(a) the exploration licence holder has identified and evaluated a significant mineral deposit in the exploration licence area; and
(b) there are reasonable grounds for the holder not applying immediately for a mining licence.
(2) Without limiting subsection (1), reasonable grounds for not applying immediately for a mining licence include the following:
(a) the need to obtain government approvals (for example, relating to environmental protection) before mining activities can commence;
(b) the need to carry out further exploration or evaluation in order to establish the commercial viability of a mineral deposit found in the licence area;
(c) the need to develop technologies before mining activities can commence;
(d) the need to arrange finance, or to secure additional capital reserves, before mining activities can commence;
(e) the existence of economic considerations (for example, the prevailing condition of the commodity market for the minerals concerned) that effectively preclude mining activities in the immediate future;
(f) the existence of political considerations that effectively preclude mining activities in the immediate future.
Matters to be specified in the licence
146.(1) The licence must specify:
(a) the blocks covered by the licence; and
(b) the term of the licence; and
(c) the licence conditions.
(2) The term specified under paragraph (1)(b) is not to exceed 5 years.
(3) The licence may specify the activities that may be carried out under the licence.
(4) If the licence includes a specification under subsection (3), the licence authorises only the specified activities.
Applicant must be notified
147.(1) The Designated Authority must give the applicant written notice of the Joint Authority’s decision under section 143 or 144.
(2) If the Joint Authority provisionally grants a retention licence:
(a) the Designated Authority must give the licence to the provisional holder; and
(b) the notice under subsection (1) must contain the following information:
(i) notification of any determination under section 399 that the provisional holder must lodge a security;
(ii) notification that the provisional grant will lapse unless the provisional holder, before the end of the primary payment period:
(A) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(B) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(C) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Retention Licence Fees Act.
Amendment of conditions
148.(1) If the provisional holder is dissatisfied with a licence condition, the provisional holder may ask the Joint Authority to amend the condition.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the provisional holder is given the licence under section 147; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority receives a request under subsection (1), the Joint Authority may amend the licence conditions.
(4) The Joint Authority must give the provisional holder written notice of the amendment.
Amendment of security requirements
149.(1) If the provisional holder:
(a) is notified of a security requirement; and
(b) is dissatisfied with the amount of the security required;
the provisional holder may ask the Joint Authority to make a new determination under section 399.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the provisional holder is given notice under section 147; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority receives a request under subsection (1), the Joint Authority may make a new determination under section 399.
(4) The Joint Authority must give the provisional holder written notice of the new determination.
Extension of primary payment period
150.(1) If the provisional holder makes a request under section 148 or 149, the provisional holder may ask the Designated Authority to extend the primary payment period.
(2) The request must be made within 30 days after the day on which the provisional holder is given notice under section 147.
(3) If the Designated Authority agrees to the request, the Designated Authority must:
(a) determine the period of the extension; and
(b) give the provisional holder a written notice informing the applicant of the period of the extension.
Acceptance of grant of retention licence
151.(1) The provisional grant of a retention licence is properly accepted by the provisional holder if, before the end of the primary payment period, the provisional holder:
(a) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(b) lodges any security for the licence required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(c) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Retention Licence Fees Act.
(2) A retention licence provisionally granted under section 143 or 144 is properly accepted by the provisional holder if the provisional holder:
(a) has been granted an extension of the primary payment period under section 150; and
(b) before the end of the secondary payment period:
(i) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(ii) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(iii) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Retention Licence Fees Act.
Note: Under section 154, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before the grant is registered (see section 333 for registration).
Conditions applicable to licence on grant
152. If the provisional grant of the licence is properly accepted, it is subject to:
(a) the conditions specified in the licence given to the applicant under section 147; or
(b) if the Joint Authority amended those conditions under section 148—those conditions as amended.
Lapse of provisional grant of retention licence
153. If the provisional grant of the licence is not properly accepted under section 151, the provisional grant lapses.
Division 3—Duration of retention licence
Initial term of retention licence
154.(1) A retention licence comes into force on:
(a) the day on which the grant of the licence is registered; or
(b) if a day later than the day on which the grant of the licence is registered is specified in the licence as its commencement day—that specified day.
(2) The initial term of a retention licence expires at the end of the period specified in the licence under subsection 146(1).
Note 1: For the maximum initial term see subsection 146(2).
Note 2: The licence may be surrendered at any time (see section 187).
(3) The period runs from:
(a) the day on which the licence is provisionally granted; or
(b) if a day later than the day on which the licence is provisionally granted is specified in the licence as its commencement day—that specified day.
Term of renewal of licence
155.(1) A renewal of a retention licence comes into force on:
(a) the day on which the renewal is registered; or
(b) the day on which the previous term of the licence expires;
whichever is the later.
Note: See Division 5 for renewal.
(2) The term of a renewal of a licence expires at the end of the period specified in the notice under section 169.
Note 1: For the maximum term of renewal see subsection 169(3).
Note 2: The licence may be surrendered at any time (see section 187).
(3) The period runs from the expiry of the previous term of the licence.
(4) Ignore section 156 in working out the period referred to in subsection (3).
Effect of application for renewal on term of retention licence
156. If:
(a) a retention licence holder applies to renew the licence under section 159; and
(b) the current term of the licence expires; and
(c) a renewal of the licence does not take effect immediately after the current term expires;
the licence remains in force after the current term expires until:
(d) a renewal of the licence takes effect; or
(e) a provisional renewal of the licence lapses; or
(f) the application for renewal is withdrawn or refused.
Effect of application for mining licence on term of retention licence
157. If:
(a) a retention licence holder applies for a mining licence over the licence area, or part of the licence area, of the retention licence; and
(b) the current term of the retention licence expires; and
(c) a grant of the mining licence does not take effect before the current term of the retention licence expires;
the retention licence remains in force until:
(d) the grant of the mining licence takes effect; or
(e) a provisional grant of the mining licence lapses; or
(f) the application for the mining licence is withdrawn or refused.
Division 4—Voluntary surrender of part of retention licence area
Voluntary surrender of blocks if discrete area remains
158.(1) A retention licence holder may surrender a block or some of the blocks covered by the licence if the remaining blocks in the licence area form a discrete area.
Note: See section 187 for the surrender of the whole licence.
(2) A surrender under subsection (1):
(a) must be made in a written notice; and
(b) must identify the blocks surrendered; and
(c) must be given to the Designated Authority.
Note: The surrender takes effect when it is registered under section 337 (see subsection 337(5)).
Division 5—Application for and grant of renewal of retention licence
Application for renewal of retention licence
159. A retention licence holder may apply to the Joint Authority to renew the licence.
Note: At each renewal, the licence conditions are reviewed (see section 177).
When must an application to renew be made?
160.(1) Subject to subsection (2), the application must be made at least 6 months before the day on which the licence is to expire.
(2) The Designated Authority may accept an application that is made later than 6 months before the day on which the licence is to expire if:
(a) the application is made before the day on which the licence expires; and
(b) the Designated Authority believes that there are reasonable grounds for accepting the application.
How to apply for renewal
161.(1) The application must:
(a) be made in accordance with the approved form; and
(b) be made in the approved manner; and
(c) include details of:
(i) the reasons why the applicant is applying to renew the retention licence rather than applying for a mining licence; and
(ii) the activities carried out by the applicant under the licence during its current term; and
(iii) the amount of money spent by the applicant in relation to the blocks covered by the licence during its current term; and
(iv) the results obtained by the applicant from carrying out the activities referred to in subparagraph (ii); and
(v) the activities that the applicant intends to carry out under the licence during the term applied for; and
(vi) the amount of money that the applicant intends to spend in relation to activities authorised by the licence during the term applied for.
Note: For paragraphs (a) and (b) see section 41.
(2) The applicant may include in the application any other information that the applicant thinks is relevant.
(3) The application must be lodged with the Designated Authority.
Request for further information
162.(1) The Designated Authority may ask the applicant to provide further information relating to the application.
(2) The request must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) be given to the applicant; and
(c) specify the time within which the information must be provided.
(3) Information requested under subsection (1) must be provided:
(a) in writing; and
(b) within the time specified in the request.
Payment of fee
163.(1) The applicant must pay the application fee prescribed by the regulations.
(2) The fee must be paid when the application is made.
(3) The Joint Authority may refund any fee paid under subsection (1) but only if it is satisfied that special circumstances exist that justify the refund of the fee.
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Designated Authority must refer renewal application to Joint Authority if certain requirements met
164.(1) This section applies if the renewal application covers blocks in a Commonwealth-State offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does what is required by sections 161 to 163, the Designated Authority must refer the application to the Joint Authority.
(3) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 161 to 163, the Designated Authority:
(a) must not refer the application to the Joint Authority; and
(b) must give the applicant written notice that the application has been refused.
(4) The application lapses if a notice is given under subsection (3).
Commonwealth-State offshore area—provisional renewal of retention licence
165. If the Designated Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area refers the application to the Joint Authority under section 164, the Joint Authority may:
(a) provisionally renew the licence; or
(b) subject to section 168, refuse to renew the licence.
Note 1: Under section 155, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration). The renewal will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 173 for “proper acceptance”).
Note 2: Under section 177, new conditions may be imposed on renewal.
External territory offshore area—how application for renewal dealt with
166.(1) This section applies if the renewal application covers blocks in an external territory offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 161 to 163, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for the offshore area) must refuse to renew the licence.
(3) If the applicant does what is required by sections 161 to 163, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for that offshore area) may:
(a) provisionally renew the licence; or
(b) subject to section 168, refuse to renew the licence.
Note 1: Under section 155, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration). The renewal will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 173 for “proper acceptance”).
Note 2: Under section 177, new conditions may be imposed on renewal.
Matters to be taken into account in deciding whether to renew retention licence
167. In determining whether to renew the licence, the Joint Authority may have regard to:
(a) whether mining activities are commercially viable in the retention licence area; and
(b) whether the applicant has complied with:
(i) this Act; and
(ii) the regulations; and
(iii) any licence conditions.
Refusal of application for renewal
168.(1) If the Joint Authority proposes to refuse to renew the licence, the Designated Authority must give the applicant notice of the proposed refusal.
Note: The retention licence remains in force until the application for renewal has been finally determined (i.e. until the Joint Authority decides whether or not to renew the licence) (see section 156).
(2) The notice must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) give details of the Joint Authority’s reasons for its proposal not to renew the licence; and
(c) invite the applicant to make written submissions on the proposed non-renewal to the Designated Authority; and
(d) specify the day by which submissions should be made to the Designated Authority.
(3) The day specified under paragraph (2)(d) is to be at least 30 days after the day on which the notice under subsection (1) is given to the applicant.
(4) The Joint Authority, in deciding whether to refuse to renew the licence, must have regard to any submissions made by the applicant in response to the notice under subsection (1).
Applicant must be notified
169.(1) The Designated Authority must give the applicant written notice of the Joint Authority’s decision under section 165 or 166.
(2) If the Joint Authority provisionally renews the licence under section 165 or 166, the notice must contain the following information:
(a) notification of the term of the renewal;
(b) notification of the conditions of the renewed licence;
(c) notification of any determination under section 399 that the applicant must lodge a security or a further security;
(d) notification that the provisional renewal will lapse unless the applicant, before the end of the primary payment period:
(i) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the renewal; and
(ii) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(iii) pays the fees that must be paid under the Retention Licence Fees Act.
Note: Paragraph (b): section 177 provides for renewals to be granted to conditions.
(3) The term specified under paragraph (2)(a) is not to be more than 5 years.
Amendment of conditions
170.(1) If the licence holder:
(a) has been provisionally granted a renewal of the licence under section 165 or 166; and
(b) is notified of the licence conditions; and
(c) is dissatisfied with a condition;
the holder may ask the Joint Authority to amend the condition.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the applicant is given notice under section 169; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority is given a request under subsection (1), the Joint Authority may amend the licence conditions.
(4) The Designated Authority must give the holder written notice of the amendment.
Amendment of security requirements
171.(1) If the licence holder:
(a) has been provisionally granted a renewal of the licence under section 165 or 166; and
(b) is notified of a security requirement; and
(c) is dissatisfied with the amount of the security required;
the holder may ask the Joint Authority to make a new determination under section 399.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the holder is given notice under section 169; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority is given a request under subsection (1), the Joint Authority may make a new determination under section 399.
(4) The Designated Authority must give the holder written notice of the new determination.
Extension of primary payment period
172.(1) If the licence holder makes a request under section 170 or 171, the holder may ask the Designated Authority to extend the primary payment period.
(2) The request must be made within 30 days after the day on which the holder is given notice under section 169.
(3) If the Designated Authority agrees to the request to extend the primary payment period, the Designated Authority must:
(a) determine the period of the extension in writing; and
(b) give the holder a written notice informing the holder of the period of the extension.
Acceptance of renewal of retention licence
173.(1) The provisional renewal of a retention licence is properly accepted by the licence holder if, before the end of the primary payment period, the holder:
(a) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the renewal; and
(b) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(c) pays the fees that must be under the Retention Licence Fees Act.
Note: Under section 155, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration).
(2) The provisional renewal of a retention licence is properly accepted by the licence holder if the holder:
(a) has been granted an extension of the primary payment period under section 172; and
(b) before the end of the secondary payment period:
(i) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the renewal; and
(ii) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(iii) pays the fees that must be paid under the Retention Licence Fees Act.
Note: Under section 155, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration).
Conditions applicable to licence on renewal
174. If the provisional renewal is properly accepted, the renewed licence is subject to:
(a) the conditions specified in the notice given to the licence holder under section 169; or
(b) if the Joint Authority amended those conditions under section 170—those conditions as amended.
Lapse of provisional renewal of retention licence
175. If the provisional renewal of a retention licence is not properly accepted under section 173, the provisional renewal lapses.
Division 6—Obligations associated with retention licence
General
176.(1) The sources of obligations associated with a retention licence are:
(a) the licence conditions; and
(b) obligations arising from compliance directions given by the Designated Authority; and
(c) obligations imposed by this Act and the regulations.
Note: For paragraph (a) see section 177. For paragraph (b) see section 387. For paragraph (c) see sections 177 to 185 and section 372.
(2) If a retention licence has 2 or more holders, all the holders are jointly and severally bound by the obligations that attach to the licence.
Conditions of retention licence
177.(1) The Joint Authority may grant or renew a retention licence subject to whatever conditions the Joint Authority thinks appropriate.
(2) If the Joint Authority grants or renews a retention licence subject to conditions, the conditions must be specified in the licence.
(3) Without limiting subsection (1), the Joint Authority may attach the following kinds of conditions to the grant or renewal of a retention licence:
(a) a condition requiring the licence holder to take out insurance as required by the Designated Authority;
(b) a condition requiring the holder to carry out certain activities in or in relation to the licence area during the term of the licence, and to comply with directions concerning those activities given under section 387;
(c) a condition requiring the holder to spend a specified amount of money in carrying out the activities referred to in paragraph (b), and to comply with directions concerning that expenditure given under section 387;
(d) a condition requiring the holder to lodge a security with the Designated Authority;
(e) a condition requiring the holder to keep specified information;
(f) a condition requiring the holder to give the Designated Authority, on request, specified information;
(g) a condition requiring the holder to take steps to protect the environment of the licence area, including conditions relating to:
(i) protecting wildlife; or
(ii) minimising the effect on the environment of the licence area and the area surrounding the licence area of activities carried out in the licence area;
(h) a condition requiring the holder to repair any damage to the environment caused by activities in the licence area;
(i) a condition requiring the holder to pay a specified penalty to the Commonwealth if the holder does not comply with a licence condition.
(4) A condition under paragraph (3)(d) must specify:
(a) the amount of the security required; and
(b) the kind of security required; and
(c) the manner and form in which the security is to be lodged.
(5) Without limiting paragraph (3)(d), a condition under that paragraph may require the lodgment of a security in the form of a guarantee and if a guarantee is required the condition may specify:
(a) the kind of person who is to give the guarantee; and
(b) the terms of the guarantee.
No conditions requiring payment of money
178. Except for a condition requiring the payment of a penalty or lodgment of a security, a licence condition must not require the payment of money to:
(a) the Designated Authority; or
(b) the Joint Authority; or
(c) the Commonwealth.
Variation of conditions
179.(1) If:
(a) a retention licence holder requests the Designated Authority in writing to vary a licence condition; or
(b) part of the licence area of a retention licence is surrendered under section 158;
the Joint Authority may vary a licence condition.
(2) If a Designated Authority gives:
(a) a direction under section 387; or
(b) an approval, consent or exemption under the regulations;
to a retention licence holder, the Joint Authority may vary a licence condition to the extent necessary to avoid inconsistency between the licence conditions and the direction, approval, consent or exemption.
(3) The Joint Authority may vary a licence condition subject to whatever conditions the Joint Authority thinks appropriate.
(4) If the Joint Authority varies a licence condition, the Designated Authority must give the licence holder a written notice that:
(a) informs the holder of the variation; and
(b) specifies the conditions which have been varied; and
(c) specifies any conditions to which the variation is subject.
Exemption from or suspension of conditions
180.(1) If:
(a) a retention licence holder requests the Designated Authority in writing to:
(i) suspend a licence condition; or
(ii) exempt the holder from complying with a licence condition; or
(b) part of the licence area of a retention licence is surrendered under section 158;
the Joint Authority may:
(c) suspend a licence condition; or
(d) exempt the holder from complying with a licence condition.
(2) If a Designated Authority gives:
(a) a direction under section 387; or
(b) an approval, consent or exemption under the regulations;
to a retention licence holder, the Joint Authority may suspend a licence condition, or exempt the holder from compliance with a licence condition, to the extent necessary to avoid inconsistency between the licence conditions and the direction, approval, consent or exemption.
(3) The Joint Authority may:
(a) suspend a licence condition; or
(b) exempt the licence holder from compliance with a licence condition;
subject to whatever conditions the Joint Authority thinks appropriate.
(4) If the Joint Authority:
(a) suspends a licence condition; or
(b) exempts the licence holder from complying with a licence condition;
the Designated Authority must give the holder a written notice that:
(c) informs the holder of the exemption or suspension; and
(d) specifies the conditions which have been suspended or affected by the exemption; and
(e) specifies any conditions to which the suspension or exemption is subject.
Note: A suspension or exemption of a condition does not take effect until registered (see section 337).
Automatic suspension of conditions if licence rights are suspended
181. If:
(a) the Joint Authority suspends particular rights conferred by a retention licence under section 135; and
(b) a licence condition is affected by the suspension;
the licence condition is suspended for the period of the suspension of the rights.
Significant changes in circumstances to be reported to Designated Authority
182.(1) A retention licence holder must notify the Designated Authority of any change of circumstances that significantly affects the long term viability of mining activities in the retention licence area.
Note: The Joint Authority may cancel the retention licence if it believes that circumstances have changed so that mining activities can now commence (see section 190).
(2) Subsection (1) applies to a change of circumstances whether favourable or unfavourable to the long term viability of mining activities in the retention licence area.
Work practices
183. If a person who is:
(a) a retention licence holder; or
(b) an associate of the holder;
carries out activities in the licence area that are authorised by the licence, the person must take all reasonable steps:
(c) to ensure that the activities are carried out at a standard that is accepted as reasonable and proper in the mining industry; and
(d) to protect the health, safety and welfare of people engaged in the activities in and about the licence area; and
(e) to maintain in good repair all structures and equipment in the licence area brought there by the person; and
(f) to remove from the licence area any structure, equipment or other property that:
(i) belongs to the person, or is under the person’s control; and
(ii) is not being used, or is not going to be used, in connection with the activities.
Maximum penalty: 200 penalty units.
Licence holder must keep specified records etc.
184. A retention licence holder must:
(a) keep whatever records, cores and samples; and
(b) give whatever records, cores and samples to the Designated Authority for inspection; and
(c) make whatever returns;
are necessary to comply with:
(d) the regulations; or
(e) the licence conditions; or
(f) a direction given by the Designated Authority under section 387.
Note: Under section 387 the Designated Authority may direct a person to keep records and cores, to collect and retain samples, and to make returns.
Maximum penalty: 100 penalty units.
Licence holder must assist inspectors
185. A retention licence holder must provide an inspector with reasonable facilities and assistance so that the inspector is able to carry out compliance inspections.
Note: See sections 377 to 384 for compliance inspections.
Maximum penalty: 50 penalty units.
Division 7—Expiry of retention licence
General
186. A retention licence expires if:
(a) the term of the licence expires without the licence being renewed; or
(b) the licence holder surrenders the licence; or
(c) a mining licence is granted over the blocks in the licence area of the retention licence; or
(d) the licence is cancelled.
Note: For paragraph (a) see Division 5. For paragraph (b) see section 187. For paragraph (c) see section 188. For paragraph (d) see sections 189 and 190.
Voluntary surrender of retention licence
187. A retention licence holder may surrender the licence.
Note 1: See Division 4 for voluntary surrender of part of a licence area.
Note 2: The surrender takes effect when it is registered under sction 337 (see subsection 337(5)).
Automatic expiry of retention licence when mining licence takes effect
188. If:
(a) a retention licence is in force under this Act; and
(b) the Joint Authority provisionally grants a mining licence over all or some of the blocks in the retention licence area; and
(c) the provisional grant of the mining licence is properly accepted; and
(d) the grant of the mining licence comes into force;
the retention licence expires in relation to the blocks covered by the mining licence.
Cancellation of retention licence—breach of condition etc.
189.(1) Subject to subsection (5), the Joint Authority may cancel a retention licence if the licence holder:
(a) breaches a licence condition; or
(b) contravenes a provision of this Act or the regulations; or
(c) breaches a condition attached to an approval under subsection 365(2); or
(d) fails to pay user charge that is payable for the licence under the Retention Licence User Charge Act.
(2) If the Joint Authority proposes to cancel a licence under subsection (1), the Designated Authority must give the holder a written notice that informs the holder of the proposed cancellation.
(3) The notice must:
(a) specify the reason for the proposed cancellation; and
(b) invite the holder to make submissions in relation to the proposed cancellation; and
(c) specify the day by which submissions should be given to the Joint Authority; and
(d) specify an address where submissions are to be lodged.
(4) The day specified under paragraph (3)(c) must be not less than 60 days after the day on which the notice is given.
(5) The Joint Authority may cancel the licence only if:
(a) the holder has been given a notice under subsection (2); and
(b) the Joint Authority has considered:
(i) any submission made by the holder; and
(ii) any steps taken by the holder to remedy the circumstances that led to the proposal to cancel the licence and to prevent those circumstances from happening again; and
(c) the Joint Authority is satisfied that no special circumstances exist that justify the licence not being cancelled.
Cancellation of retention licence—mining activities viable
190.(1) If the Joint Authority believes that mining activities should commence in a retention licence area, the Designated Authority must ask the licence holder to explain why the holder should not apply for a mining licence over the retention licence area.
(2) A request under subsection (1) must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) specify the day by which the holder should give the explanation to the Designated Authority.
(3) The day specified under paragraph (2)(b) is to be at least 30 days after the day on which the request is given to the holder.
(4) An explanation provided in response to a request under subsection (1) must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) be given to the Designated Authority.
(5) The Joint Authority may cancel the retention licence if:
(a) the holder is given a request under subsection (1); and
(b) either:
(i) the holder does not give the Designated Authority an explanation in response to the request by the day specified in the request; or
(ii) the holder gives the Designated Authority an explanation in response to the request but the Joint Authority does not consider the explanation to be satisfactory.
(6) If the Joint Authority cancels a retention licence under subsection (5), the Joint Authority may specify the day on which the cancellation takes effect.
(7) Without limiting subsection (6), the Joint Authority, in determining the day on which the cancellation is to take effect, may have regard to the time needed by the holder to obtain the grant of a mining licence over the retention licence area.
Obligations of former retention licence holders and former associates
191.(1) Subject to subsection (4), if:
(a) a person was:
(i) a retention licence holder; or
(ii) an associate of a retention licence holder; and
(b) the licence:
(i) expires; or
(ii) is cancelled; or
(iii) is surrendered; and
(c) an obligation associated with the licence arising out of:
(i) a licence condition; or
(ii) a direction given under section 387 by the Designated Authority in relation to the licence; or
(iii) this Act or the regulations;
has not been discharged; and
(d) the person was bound by that obligation when the person was the licence holder or an associate;
the person remains bound by the obligation until the obligation is discharged.
(2) Subsection (1) does not continue an obligation to carry out exploration or recovery activities.
(3) Subsection (1) continues an obligation that a person had to carry out exploration or recovery activities in a particular manner if the person carries them out.
(4) The Joint Authority may determine that the person is not subject to:
(a) a particular obligation under this section; or
(b) all the person’s remaining obligations under this section.
(5) A determination under subsection (4) is to be in writing.
PART 2.4—MINING LICENCES
Division 1—General
Mining licences
192.(1) This Part provides for the grant of mining licences over blocks in an offshore area.
(2) A mining licence may be granted over:
(a) a vacant standard block (see Division 2); or
(b) certain blocks that are not vacant (see Division 2); or
(c) a tender block (see Division 3).
Note 1: A tender block is a block that has been declared available for tender. A standard block is any other block (see sections 19 and 20).
Note 2: A retention or exploration licence holder may apply for a mining licence over the same area or part of the same area.
Activities authorised by a mining licence
193.(1) Subject to subsection (2), a mining licence holder may:
(a) recover minerals in the licence area; and
(b) explore for minerals in the licence area.
Note 1: Under subsection 23(1) the concept of “exploration” extends to activities that are directly related to exploration.
Note 2: Under subsection 24(1) the concept of “recovery” extends to activities that are directly related to the recovery of minerals.
(2) If the licence is expressed to restrict the kind of minerals covered by the licence, the holder is not permitted to recover, or to explore for, minerals not covered by the licence.
(3) A restriction on the kind of minerals covered by the licence may be inclusive (for example, only minerals A, B and C) or exclusive (for example, all minerals except A, B and C).
(4) For the purposes of subsection (2), the holder does not recover an excluded mineral if, in the course of recovering, or exploring for, another mineral, the holder recovers some excluded mineral.
Joint Authority may cancel or not renew mining licence without compensation
194. No compensation is payable because of the cancellation or non-renewal of a mining licence by the Joint Authority.
Note 1: The Joint Authority may cancel the licence under section 265.
Note 2: The Joint Authority may refuse under section 242 or 243 to renew the licence.
Licence rights may be suspended
195.(1) The Joint Authority must suspend particular rights conferred by a mining licence if the Joint Authority is satisfied that it is necessary in the national interest to do so.
(2) The Joint Authority may suspend rights conferred under subsection (1) for a specified period or for an indefinite period.
(3) The Joint Authority may end a suspension at any time.
(4) A suspension or the ending of a suspension must be in writing.
(5) If the Joint Authority:
(a) suspends rights conferred by a mining licence; or
(b) ends a suspension;
the Joint Authority must give the licence holder a written notice that informs the holder of the suspension or the ending of a suspension.
Note: See section 258 for the effect of the suspension on the obligations associated with the licence.
(6) A suspension takes effect when:
(a) the holder has been given notice of the suspension under subsection (5); and
(b) the suspension has been registered under section 337.
Compensation for acquisition of property due to suspension of rights
196.(1) If:
(a) the Joint Authority suspends licence rights under section 195; and
(b) the suspension results in the acquisition of property from a person; and
(c) the Commonwealth and the person agree on an amount of compensation for the acquisition;
the Commonwealth must pay the person the agreed amount of compensation.
(2) If:
(a) the Joint Authority suspends licence rights under section 195; and
(b) the suspension results in the acquisition of property from a person; and
(c) the Commonwealth and the person do not agree on an amount of compensation for the acquisition; and
(d) the person brings an action for compensation against the Commonwealth in the High Court or an appropriate Supreme Court;
the Commonwealth must pay the person the amount of compensation (if any) that is determined by the court.
(3) In this section:
“acquisition of property” means an acquisition of property within the meaning of paragraph 51(xxxi) of the Constitution;
“appropriate Supreme Court” means the Supreme Court of, or having jurisdiction in, the State or Territory for which the Joint Authority is established.
Division 2—Application for and grant of mining licence over
standard blocks
Application for mining licence over vacant standard block
197.(1) A person may apply to the Joint Authority for a mining licence over a standard block that is vacant.
(2) A standard block is vacant if no exploration, retention or mining licence is in force over the block.
(3) The application must not cover more than 20 blocks.
(4) If the application is for a licence over a group of blocks, the blocks must form a discrete area.
Holder of exploration licence or retention licence may apply for mining licence
198.(1) An exploration or retention licence holder may apply to the Joint Authority for a mining licence over all or some of the blocks in the licence area of the exploration or retention licence.
(2) A person may apply for a mining licence under subsection (1) over a group of blocks only if:
(a) the group forms a discrete area; and
(b) there are not more than 20 blocks in the group.
(3) The holder may apply for 2 or more mining licences over different parts of the licence area of the exploration or retention licence.
How to apply
199.(1) An application under section 197 or 198 must:
(a) be made in accordance with the approved form; and
(b) be made in the approved manner; and
(c) specify the blocks for which the application is made; and
(d) include details of:
(i) the activities that the applicant intends to carry out on the block or blocks covered by the application; and
(ii) the amount of money that the applicant intends to spend on those activities; and
(iii) the technical qualifications of the applicant and of the applicant’s employees who are likely to be involved in activities authorised by the licence; and
(iv) the technical advice available to the applicant; and
(v) the financial resources available to the applicant; and
(vi) if the licence is to be held by more than one person—the share of the licence that each prospective holder will hold; and
(e) be accompanied by maps that:
(i) relate to the blocks; and
(ii) comply with guidelines issued by the Designated Authority under subsection 41(2); and
(f) specify an address for service of notices under this Act and the regulations.
Note: For paragraphs (a) and (b) see section 41.
(2) The applicant may include in the application any other information that the applicant thinks is relevant.
(3) The application must be lodged with the Designated Authority.
Effect of inclusion of unavailable block in application
200. If:
(a) a person applies under section 197 or 198 for a licence over a group of blocks; and
(b) because of section 18, 197 or 198:
(i) a mining licence cannot be granted over one or more of the blocks in the group; or
(ii) the Joint Authority cannot grant the licence over one or more of the blocks in the group;
the Designated Authority and the Joint Authority may still deal with the application to the extent to which the application covers blocks:
(c) for which a mining licence can be granted; or
(d) for which the Joint Authority does have power to grant the licence applied for.
Note 1: A mining licence cannot be granted over a block that is not vacant or over a reserved block (see section 18).
Note 2: The Joint Authority for a State may grant a licence only over blocks in that State’s Commonwealth-State offshore area.
Payment of fee
201.(1) The applicant must pay the application fee prescribed by the regulations.
(2) The fee must be paid when the application is made.
(3) The Joint Authority may refund any fee paid under subsection (1) but only if it is satisfied that special circumstances exist that justify the refund of the fee.
Application must be advertised
202.(1) The applicant must advertise the application in a newspaper that circulates throughout the State or external territory concerned.
(2) The advertisement must contain:
(a) the applicant’s name and address; and
(b) a map and description of the blocks applied for that are sufficient for the blocks to be identified; and
(c) the address of the Designated Authority; and
(d) a statement:
(i) that the applicant has applied for a mining licence over the blocks described in the notice; and
(ii) that invites comment from the public on the application; and
(iii) that requests that comments be sent to the applicant and the Designated Authority within 30 days after the day on which the advertisement is published.
(3) The advertisement must be published as soon as possible after the applicant applies for a mining licence.
(4) Subject to subsection (5), the advertisement must be published within 14 days after the day on which the applicant lodges the application.
(5) If:
(a) the applicant applies to the Designated Authority within the 14 day period referred to in subsection (4) for an extension of the period; and
(b) the Designated Authority extends the period;
the advertisement must be published within the period as extended by the Designated Authority.
How multiple applications are dealt with
203.(1) Subject to subsection (2), if a block is covered by 2 or more applications for a mining or exploration licence, the Designated Authority must deal with the applications in the order in which they are made.
Note: See also section 58.
(2) If:
(a) the applications are lodged within a particular time of each other; and
(b) the time is less than the time prescribed by the regulations;
the Designated Authority must determine the order in which the applications are to be dealt with by drawing lots in the way prescribed by the regulations.
Request for further information
204.(1) The Designated Authority may ask the applicant for further information relating to the application.
(2) The request must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) be given to the applicant; and
(c) specify the time within which the information must be provided.
(3) Information requested under subsection (1) must be provided:
(a) in writing; and
(b) within the time specified in the request.
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Designated Authority must refer application to Joint Authority if certain requirements met
205.(1) This section applies if the application covers blocks in a Commonwealth-State offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does what is required by sections 199 to 204, the Designated Authority must refer the application to the Joint Authority.
(3) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 199 to 204, the Designated Authority:
(a) must not refer the application to the Joint Authority; and
(b) must give the applicant written notice that the application has been refused.
(4) The application lapses if a notice is given under subsection (3).
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Joint Authority may provisionally grant mining licence
206. If the Designated Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area refers the application to the Joint Authority under section 205, the Joint Authority may:
(a) provisionally grant a mining licence to the applicant; or
(b) subject to section 208, refuse the application.
Note: Under section 232, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration). The grant will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 214 for “proper acceptance”).
External territory offshore area—how application for mining licence dealt with
207.(1) This section applies if the application covers blocks in an external territory offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 199 to 204, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for that offshore area) must refuse the application.
(3) If the applicant does what is required by sections 199 to 204, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for that offshore area) may:
(a) provisionally grant a mining licence to the applicant; or
(b) subject to section 208, refuse the application.
Note: Under section 232, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration). The grant will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 214 for “proper acceptance”).
Refusal of application for mining licence made under section 198
208.(1) If the Joint Authority proposes to refuse an application for a mining licence made under section 198, the Designated Authority must notify the applicant of the proposed refusal.
(2) The notice must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) specify the reason for the proposed refusal; and
(c) invite the applicant to make written submissions in relation to the proposed refusal; and
(d) specify the day by which submissions should be given to the Designated Authority; and
(e) specify an address where submissions are to be lodged.
(3) The day specified under paragraph (2)(d) must be not less than 30 days after the day on which the notice is given.
(4) The Joint Authority may refuse to grant an application for a mining licence made under section 198 only if:
(a) the applicant has been given a notice under subsection (1); and
(b) the Joint Authority has considered any submission made by the applicant; and
(c) the Joint Authority is satisfied that no special circumstances exist that justify the licence being granted.
Matters to be specified in the licence
209.(1) The licence must specify:
(a) the blocks covered by the licence; and
(b) the term of the licence; and
(c) the licence conditions.
(2) The term specified under paragraph (1)(b) is not to exceed 21 years.
Applicant must be notified
210.(1) The Designated Authority must give the applicant written notice of the Joint Authority’s decision under section 206 or 207.
(2) If the Joint Authority provisionally grants a mining licence:
(a) the Designated Authority must give the licence to the provisional holder; and
(b) the notice under subsection (1) must contain the following information:
(i) notification of any determination under section 399 that the provisional holder must lodge a security;
(ii) notification that the provisional grant will lapse unless the provisional holder, before the end of the primary payment period:
(A) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(B) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(C) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Mining Licence Fees Act.
Amendment of conditions
211.(1) If the provisional holder is dissatisfied with a licence condition, the provisional holder may ask the Joint Authority to amend the condition.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the provisional holder is given the licence under section 210; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority is given a request under subsection (1), the Joint Authority may amend the licence conditions.
(4) The Designated Authority must give the provisional holder written notice of the amendment.
Amendment of security requirements
212.(1) If the provisional holder:
(a) is notified of a security requirement; and
(b) is dissatisfied with the amount of the security required;
the provisional holder may ask the Joint Authority to make a new determination under section 399.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the applicant is given notice under section 210; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority is given a request under subsection (1), the Joint Authority may make a new determination under section 399.
(4) The Designated Authority must give the provisional holder written notice of the new determination.
Extension of primary payment period
213.(1) If the provisional holder makes a request under section 211 or 212, the provisional holder may ask the Designated Authority to extend the primary payment period.
(2) The request must be made within 30 days after the day on which the provisional holder is given notice under section 210.
(3) If the Designated Authority agrees to the request, the Designated Authority must:
(a) determine the period of the extension; and
(b) give the provisional holder a written notice informing the applicant of the period of the extension.
Acceptance of grant of mining licence for standard block
214.(1) The provisional grant of a mining licence is properly accepted by the provisional holder if, before the end of the primary payment period, the provisional holder:
(a) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(b) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(c) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Mining Licence Fees Act.
(2) The provisional grant of a mining licence is properly accepted by the provisional holder if the provisional holder:
(a) has been granted an extension of the primary payment period under section 213; and
(b) before the end of the secondary payment period:
(i) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(ii) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(iii) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Mining Licence Fees Act.
Note: Under section 232, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration).
Conditions applicable to licence on grant
215. If the provisional grant of the licence is properly accepted, it is subject to:
(a) the conditions specified in the licence given to the applicant under section 210; or
(b) if the Joint Authority amended those conditions under section 211—those conditions as amended.
Lapse of provisional grant of mining licence
216. If the provisional grant of the licence is not properly accepted under section 214, the provisional grant lapses.
Division 3—Application for and grant of mining licence over tender block
Matters to be determined before applications for mining licence over tender blocks invited
217.(1) If the Joint Authority proposes to invite applications for the grant of a mining licence over reserved blocks, the Joint Authority must, before inviting the applications, determine:
(a) the procedure and criteria that the Joint Authority will adopt to allocate the licence; and
(b) the amount of security that will be required for the licence under section 399; and
(c) the initial term of the licence; and
(d) the licence conditions.
(2) The term determined under paragraph (1)(c) is not to exceed 21 years.
Joint Authority may invite applications for mining licence over tender blocks
218.(1) Subject to subsection (2), the Joint Authority may invite applications for the grant of a mining licence over reserved blocks.
(2) Applications may be invited for a licence covering a group of reserved blocks only if the group forms a discrete area.
(3) The Joint Authority is to invite applications by publishing a tender block licence notice for the licence in the Gazette.
Note 1: A mining licence may cover not more than 20 tender blocks (see section 219).
Note 2: A mining licence might be made available by a tender block notice if a mineral deposit in the area had already been identified and sufficient information was already available to justify the issue of a mining licence rather than an exploration licence.
Tender block licence notice—mining licence
219.(1) A tender block licence notice for a mining licence must:
(a) specify the blocks to be covered by the licence; and
(b) specify the period within which applications may be made; and
(c) specify the procedure and criteria that the Joint Authority will adopt to allocate the licence; and
(d) specify the amount of security that the successful applicant will be required to lodge; and
(e) specify the initial term of the licence; and
(f) include a statement to the effect that information about:
(i) the security that the successful applicant will be required to lodge; and
(ii) the licence conditions;
may be obtained from the Designated Authority.
(2) The tender block licence notice may specify not more than 20 blocks for the mining licence.
Application for mining licence over tender blocks
220. If a tender block licence notice has been published inviting applications for a mining licence, a person may apply for the licence.
How to apply
221.(1) The application must:
(a) be made in accordance with the approved form; and
(b) be made in the approved manner; and
(c) be made before the end of the period specified in the tender block licence notice; and
(d) include details of:
(i) the technical qualifications of the applicant and of the applicant’s employees who are likely to be involved in activities authorised by the licence; and
(ii) the technical advice available to the applicant; and
(iii) the financial resources available to the applicant; and
(iv) if the licence is to be held by more than one person—the share of the licence that each prospective holder will hold; and
(e) specify an address for service of notices under this Act and the regulations.
Note: For paragraphs (a) and (b) see section 41.
(2) If the Joint Authority has specified in the tender block licence notice that it will select the successful applicant on the basis of development proposals submitted for the blocks to be covered by the licence, the application must include details of the applicant’s development proposals for the blocks.
(3) If the Joint Authority has specified in the tender block licence notice that it will select the successful applicant on the basis of the amounts of money offered for the licence, the application must state the amount offered by the applicant for the licence.
(4) The applicant may include in the application any other information that the applicant thinks is relevant.
(5) The application must be lodged with the Designated Authority.
Payment of fee
222.(1) The applicant must pay the application fee prescribed by the regulations.
(2) The fee must be paid when the application is made.
(3) The Joint Authority may refund any fee paid under subsection (1) but only if it is satisfied that special circumstances exist that justify the refund of the fee.
Request for further information
223.(1) The Designated Authority may ask the applicant for further information relating to the application.
(2) The request must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) be given to the applicant; and
(c) specify the time within which the information must be provided.
(3) Information requested under subsection (1) must be provided:
(a) in writing; and
(b) within the time specified in the request.
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Designated Authority must refer application to Joint Authority if certain requirements met
224.(1) This section applies if the tender block notice relates to blocks in a Commonwealth-State offshore area.
(2) If an applicant does what is required by sections 221 to 223, the Designated Authority must refer the application to the Joint Authority.
(3) If an applicant does not do what is required by sections 221 to 223, the Designated Authority:
(a) must not refer the application to the Joint Authority; and
(b) must give the applicant written notice that the application has been refused.
(4) The application lapses if a notice is given under subsection (3).
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Joint Authority may provisionally grant tender block mining licence
225.(1) If the Designated Authority refers applications to the Joint Authority under section 224, the Joint Authority may provisionally grant a mining licence to one of the applicants.
Note: Under section 232, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration). The grant will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 228 for “proper acceptance”).
(2) The Joint Authority may provisionally grant a licence under subsection (1) even if only one application is referred to the Joint Authority by the Designated Authority.
(3) When provisionally granting a licence under subsection (1), the Joint Authority must follow the procedure and apply the criteria specified in the tender block licence notice published for the licence under section 218.
External territory offshore area—how applications dealt with
226.(1) This section applies if the tender block licence notice relates to blocks in an external territory offshore area.
(2) The responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for that offshore area):
(a) must refuse an application if the applicant does not do what is required by sections 221 to 223; and
(b) may provisionally grant a mining licence to an applicant whose application has not been refused under paragraph (a).
Note: Under section 232, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration). The grant will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 228 for “proper acceptance”).
(3) The responsible Commonwealth Minister may provisionally grant a licence under subsection (2) even if there is only one application that is not refused under paragraph (2)(a).
(4) When provisionally granting a licence under subsection (2), the responsible Commonwealth Minister must follow the procedure and apply the criteria specified in the tender block licence notice published for the licence under section 218.
Successful applicant must be notified
227.(1) If the Joint Authority provisionally grants a mining licence under section 225, 226 or 231, the Designated Authority must give the provisional holder:
(a) the licence; and
(b) written notice that the provisional grant will lapse unless the provisional holder, before the end of the primary payment period:
(i) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(ii) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(iii) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Mining Licence Fees Act; and
(iv) if the tender is determined on the basis of the amounts of money offered for the licence—pays the Commonwealth the amount that the provisional holder offered for the licence under subsection 221(3).
(2) The licence must specify:
(a) the blocks covered by the licence; and
(b) the term of the licence; and
(c) the licence conditions.
Note: For the term of a licence see subsection 217(2).
Acceptance of grant of mining licence over tender blocks
228. The provisional grant of a mining licence is properly accepted by the provisional holder if, within 30 days after the day on which the provisional holder is given notice under section 227, the provisional holder:
(a) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(b) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(c) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Mining Licence Fees Act; and
(d) if the tender is determined on the basis of the amounts of money offered for the licence—pays the Commonwealth the amount that the provisional holder offered for the licence under subsection 221(3).
Note: Under section 232, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration).
Conditions applicable to licence on grant
229. If the provisional grant of the licence is properly accepted, the licence is subject to the conditions determined under section 217.
Lapse of provisional grant of mining licence
230. If the provisional grant of the licence is not properly accepted under section 229, the provisional grant lapses.
Provisional grant to next applicant if grant lapses
231.(1) If the provisional grant of the licence lapses under section 230, the Joint Authority may provisionally grant the licence to another of the applicants for the licence.
(2) When provisionally granting a licence under subsection (1), the Joint Authority must follow the procedure and apply the criteria specified in the tender block licence notice published for the licence under section 218.
Division 4—Duration of mining licence
Initial term of mining licence
232.(1) A mining licence comes into force on:
(a) the day on which the grant of the licence is registered; or
(b) if a day later than the day on which the grant of the licence is registered is specified in the licence as its commencement day—that specified day.
(2) The initial term of a mining licence ends:
(a) if the licence is granted under Division 2—at the end of the period specified in the licence under subsection 209(1); or
(b) if the licence is granted under Division 3—at the end of the period specified under subsection 227(2).
Note 1: For the maximum initial term of renewal see subsections 209(2) and 217(2).
Note 2: The licence may be surrendered at any time (see section 264).
(3) The period runs from:
(a) the day on which the licence is provisionally granted; or
(b) if a day later than the day on which the licence is provisionally granted is specified in the licence as its commencement day—that specified day.
Term of renewal of licence
233.(1) A renewal of a mining licence comes into force on:
(a) the day on which the renewal is registered; or
(b) the day on which the previous term of the licence expires;
whichever is the later.
Note: See Division 6 for renewal.
(2) The term of a renewal of a licence ends at the end of the period specified in the notice under section 246.
Note 1: For the maximum term of renewal see subsection 246(3).
Note 2: The licence may be surrendered at any time (see section 264).
(3) The period runs from the day on which the previous term of the licence expires.
(4) Ignore section 234 in working out the period referred to in subsection (3).
Effect of application for renewal on term of mining licence
234. If:
(a) a mining licence holder applies to renew the licence under section 236; and
(b) the current term of the licence expires; and
(c) a renewal of the licence does not take effect immediately after the current term expires;
the licence remains in force after the current term expires until:
(d) a renewal of the licence takes effect; or
(e) a provisional renewal of the licence lapses; or
(f) the application for renewal is withdrawn or refused.
Division 5—Voluntary surrender of part of mining licence area
Voluntary surrender of blocks if discrete area remains
235.(1) A mining licence holder may surrender a block or some of the blocks covered by the licence if the remaining blocks in the licence area form a discrete area.
Note: See section 264 for the surrender of the whole licence.
(2) A surrender under subsection (1) must:
(a) be made in writing; and
(b) identify the blocks surrendered; and
(c) be given to the Designated Authority.
Note: The surrender takes effect when it is registered under section 337 (see subsection 337(5)).
Division 6—Application for and grant of renewal of mining licence
Application for renewal of mining licence
236. A mining licence holder may apply to the Joint Authority to renew the licence.
Note: At each renewal, the licence conditions are reviewed (see section 254).
When must an application to renew be made?
237.(1) Subject to this section, the application must be made at least 6 months before the day on which the licence is to expire.
(2) The Designated Authority may accept an application that is made later than 6 months before the day on which the licence is to expire if:
(a) the application is made before the day on which the licence expires; and
(b) the Designated Authority believes that there are reasonable grounds for accepting the application.
How to apply for renewal
238.(1) The application must:
(a) be made in accordance with the approved form; and
(b) be made in the approved manner; and
(c) include details of:
(i) the activities carried out by the applicant under the licence during its current term; and
(ii) the amount of money spent by the applicant in relation to the blocks covered by the licence during its current term; and
(iii) the activities that the applicant intends to carry out under the licence during the term applied for; and
(iv) the amount of money that the applicant intends to spend in relation to activities authorised by the licence during the term applied for.
Note: For paragraphs (a) and (b) see section 41.
(2) The applicant may include in the application any other information that the applicant thinks is relevant.
(3) The application must be lodged with the Designated Authority.
Request for further information
239.(1) The Designated Authority may ask the applicant to provide further information relating to the application.
(2) The request must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) be given to the applicant; and
(c) specify the time within which the information must be provided.
(3) Information requested under subsection (1) must be provided:
(a) in writing; and
(b) within the time specified in the request.
Payment of fee
240.(1) The applicant must pay the application fee prescribed by the regulations.
(2) The fee must be paid when the application is made.
(3) The Joint Authority may refund any fee paid under subsection (1) but only if it is satisfied that special circumstances exist that justify the refund of the fee.
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Designated Authority must refer renewal application to Joint Authority if certain requirements met
241.(1) This section applies if the renewal application covers blocks in a Commonwealth-State offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does what is required by sections 237 to 240, the Designated Authority must refer the application to the Joint Authority.
(3) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 237 to 240, the Designated Authority:
(a) must not refer the application to the Joint Authority; and
(b) must give the applicant written notice that the application has been refused.
(4) The application lapses if a notice is given under subsection (3).
Commonwealth-State offshore area—provisional renewal of mining licence
242. If the Designated Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area refers the renewal application to the Joint Authority under section 241, the Joint Authority may:
(a) provisionally renew the licence; or
(b) subject to section 245, refuse to renew the licence.
Note 1: Under section 233, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration). The renewal will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 250 for “proper acceptance”).
Note 2: Under section 254, new conditions may be imposed on renewal.
External territory offshore area—how application for renewal dealt with
243.(1) This section applies if the renewal application covers blocks in an external territory offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 237 to 240, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for the offshore area) must refuse to renew the licence.
(3) If the applicant does what is required by sections 237 to 240, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for that offshore area) may:
(a) provisionally renew the licence; or
(b) subject to section 245, refuse to renew the licence.
Note 1: Under section 233, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration). The renewal will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 250 for “proper acceptance”).
Note 2: Under section 254, new conditions may be imposed on renewal.
Matters to be taken into account in deciding whether to renew mining licence
244. In deciding whether to renew a mining licence, the Joint Authority may have regard to whether the applicant has complied with:
(a) this Act; and
(b) the regulations; and
(c) any licence conditions.
Refusal of application for renewal
245.(1) If the Joint Authority proposes to refuse to renew the licence, the Designated Authority must give the applicant notice of the proposed refusal.
(2) The notice must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) specify the reason for the proposed refusal; and
(c) invite the holder to make written submissions in relation to the proposed refusal; and
(d) specify the day by which submissions should be given to the Designated Authority; and
(e) specify an address where submissions are to be lodged.
(3) The day specified under paragraph (2)(d) must be not less than 30 days after the day on which the notice is given.
(4) The Joint Authority may refuse to grant the application only if:
(a) the holder has been given a notice under subsection (1); and
(b) the Joint Authority has considered any submission made by the applicant; and
(c) the Joint Authority is satisfied that no special circumstances exist that justify the renewal being granted.
Applicant must be notified
246.(1) The Designated Authority must give the applicant written notice of the Joint Authority’s decision under section 242 or 243.
(2) If the Joint Authority provisionally renews the licence under section 242 or 243, the notice must contain the following information:
(a) notification of the term of the renewal;
(b) notification of the conditions of the renewed licence;
(c) notification of any determination under section 399 that the applicant must lodge a security or a further security;
(d) notification that the provisional renewal will lapse unless the applicant, before the end of the primary payment period:
(i) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the renewal; and
(ii) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(iii) pays the fees that must be paid for the renewal under the Mining Licence Fees Act.
Note: Section 254 provides for renewals to be granted subject to conditions.
(3) The term specified under paragraph (2)(a) is not to be more than 21 years.
Amendment of conditions
247.(1) If the licence holder:
(a) has been provisionally granted a renewal of the licence under section 242 or 243; and
(b) is notified of the licence conditions; and
(c) is dissatisfied with a condition;
the holder may ask the Joint Authority to amend the condition.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the holder is given notice under section 246; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority is given a request under subsection (1), the Joint Authority may amend the licence conditions.
(4) The Designated Authority must give the holder written notice of the amendment.
Amendment of security requirements
248.(1) If the licence holder:
(a) has been provisionally granted a renewal of the licence under section 242 or 243; and
(b) is notified of a security requirement for the licence; and
(c) is dissatisfied with the amount of the security required;
the holder may ask the Joint Authority to make a new determination under section 399.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the holder is given notice under section 246; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority is given a request under subsection (1), the Authority may make a new determination under section 399.
(4) The Designated Authority must give the holder written notice of the new determination.
Extension of primary payment period
249.(1) If the licence holder makes a request under section 247 or 248, the holder may ask the Designated Authority to extend the primary payment period.
(2) The request must be made within 30 days after the day on which the holder is given notice under section 246.
(3) If the Designated Authority agrees to the request, the Designated Authority must:
(a) determine the period of the extension in writing; and
(b) give the holder a written notice informing the holder of the period of the extension.
Acceptance of renewal of mining licence
250.(1) The provisional renewal of a mining licence is properly accepted by the licence holder if, before the end of the primary payment period, the holder:
(a) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the renewal; and
(b) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(c) pays the fees that must be paid under the Mining Licence Fees Act.
Note: Under section 233, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration).
(2) The provisional renewal of a mining licence is properly accepted by the licence holder if the holder:
(a) has been granted an extension of the primary payment period under section 249; and
(b) before the end of the secondary payment period:
(i) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the renewal; and
(ii) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(iii) pays the fees that must be paid under the Mining Licence Fees Act.
Note: Under section 233, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration).
Conditions applicable to licence on renewal
251. If the provisional renewal is properly accepted, the renewed licence is subject to:
(a) the conditions specified in the notice given to the licence holder under section 246; or
(b) if the Joint Authority amended those conditions under section 247— those conditions as amended.
Lapse of provisional renewal of mining licence
252. If the provisional renewal of a mining licence is not properly accepted under section 250, the provisional renewal lapses.
Division 7—Obligations associated with mining licence
General
253.(1) The sources of obligations associated with a mining licence are:
(a) the licence conditions; and
(b) obligations arising from compliance directions given by the Designated Authority; and
(c) obligations imposed by this Act and the regulations.
Note: For paragraph (a) see sections 254 to 256. For paragraph (b) see section 387. For paragraph (c) see sections 259 to 262 and section 372.
(2) If a mining licence has 2 or more holders, all the holders are jointly and severally bound by the obligations that attach to the licence.
Conditions of mining licence
254.(1) The Joint Authority may grant or renew a mining licence subject to whatever conditions the Joint Authority thinks appropriate.
(2) If the Joint Authority grants or renews a mining licence subject to conditions, the conditions must be specified in the licence.
(3) Without limiting subsection (1), the Joint Authority may attach the following kinds of conditions to the grant or renewal of a mining licence:
(a) a condition requiring the licence holder to take out insurance as required by the Designated Authority;
(b) a condition requiring the holder to carry out certain work in or in relation to the licence area during the term of the licence, and to comply with directions concerning that work given under section 387;
(c) a condition requiring the holder to lodge a security with the Designated Authority;
(d) a condition requiring the holder to keep specified information;
(e) a condition requiring the holder to give to the Designated Authority, on request, specified information;
(f) a condition requiring the holder to take steps to protect the environment of the licence area, including conditions relating to:
(i) protecting wildlife; or
(ii) minimising the effect on the environment of the licence area and the area surrounding the licence area of activities carried out in the licence area;
(g) a condition requiring the holder to repair any damage to the environment caused by activities in the licence area;
(h) a condition requiring the holder to pay a specified penalty to the Commonwealth if the holder does not comply with a licence condition.
(4) A condition under paragraph (3)(c) must specify:
(a) the amount of the security required; and
(b) the kind of security required; and
(c) the manner and form in which the security is to be lodged.
(5) Without limiting paragraph (3)(c), a condition under that paragraph may require the lodgment of a security in the form of a guarantee and if a guarantee is required the condition may specify:
(a) the kind of person who is to give the guarantee; and
(b) the terms of the guarantee.
No conditions requiring payment of money
255. Except for a condition requiring the payment of a penalty or lodgment of security, a licence condition must not require the payment of money to:
(a) the Designated Authority; or
(b) the Joint Authority; or
(c) the Commonwealth.
Variation of conditions
256.(1) If:
(a) a mining licence holder requests the Designated Authority in writing to vary a licence condition; or
(b) part of the licence area of a mining licence is surrendered under section 235;
a Joint Authority may vary a licence condition.
(2) If a Designated Authority gives:
(a) a direction under section 387; or
(b) an approval, consent or exemption under the regulations;
to a mining licence holder, the Joint Authority may vary a licence condition to the extent necessary to avoid inconsistency between the licence conditions and the direction, approval, consent or exemption.
(3) The Joint Authority may vary a licence condition subject to whatever conditions the Joint Authority thinks appropriate.
(4) If the Joint Authority varies a licence condition, the Designated Authority must give the licence holder a written notice that:
(a) informs the holder of the variation; and
(b) specifies the conditions which have been varied; and
(c) specifies any conditions to which the variation is subject.
Exemption from or suspension of conditions
257.(1) If:
(a) a mining licence holder requests the Designated Authority in writing to:
(i) suspend a licence condition; or
(ii) exempt the holder from complying with a licence condition; or
(b) part of the licence area of a mining licence is surrendered under section 235;
the Joint Authority may:
(c) suspend a licence condition; or
(d) exempt the holder from complying with a licence condition.
(2) If a Designated Authority gives:
(a) a direction under section 387; or
(b) an approval, consent or exemption under the regulations;
to a mining licence holder, the Joint Authority may suspend a licence condition, or exempt the holder from compliance with a licence condition, to the extent necessary to avoid inconsistency between the licence conditions and the direction, approval, consent or exemption.
(3) The Joint Authority may:
(a) suspend a licence condition; or
(b) exempt the licence holder from complying with a licence condition;
subject to whatever conditions the Joint Authority thinks appropriate.
(4) If the Joint Authority:
(a) suspends a licence condition; or
(b) exempts the licence holder from complying with a licence condition;
the Designated Authority must give the holder a written notice that:
(c) informs the holder of the exemption or suspension; and
(d) specifies the conditions which have been suspended or affected by the exemption; and
(e) specifies any conditions to which the suspension or exemption is subject.
Note: A suspension or exemption of a condition does not take effect until registered (see section 337).
Automatic suspension of conditions if licence rights are suspended
258. If:
(a) the Joint Authority suspends particular rights conferred by a mining licence under section 195; and
(b) a licence condition is affected by the suspension;
the licence condition is suspended for the period of the suspension of the rights.
Work practices
259. If a person who is:
(a) a mining licence holder; or
(b) an associate of the holder;
carries out activities in the licence area that are authorised by the licence, the person must take all reasonable steps:
(c) to ensure that the activities are carried out at a standard that is accepted as reasonable and proper in the mining industry; and
(d) to protect the health, safety and welfare of people engaged in the activities in and about the licence area; and
(e) to maintain in good repair all structures and equipment in the licence area brought there by the person; and
(f) to remove from the licence area any structure, equipment or other property that:
(i) belongs to the person, or is under the person’s control; and
(ii) is not being used, or is not going to be used, in connection with the activities.
Maximum penalty: 200 penalty units.
Licence holder must comply with Royalty Act
260. A mining licence holder must comply with the Royalty Act.
Licence holder must keep specified records
261. A mining licence holder must:
(a) keep whatever records, cores and samples; and
(b) give whatever records, cores and samples to the Designated Authority for inspection; and
(c) make whatever returns;
are necessary to comply with:
(d) the regulations; or
(e) the licence conditions; or
(f) a direction given by the Designated Authority under section 387.
Note: Under section 387 the Designated Authority may direct a person to keep records and cores, to collect and retain samples, and to make returns.
Maximum penalty: 100 penalty units.
Licence holder must assist inspectors
262. A mining licence holder must provide an inspector with reasonable facilities and assistance so that the inspector is able to carry out compliance inspections.
Note: See sections 377 to 384 for compliance inspections.
Maximum penalty: 50 penalty units.
Division 8—Expiry of mining licence
General
263. A mining licence expires if:
(a) the term of the licence expires without the licence being renewed; or
(b) the licence holder surrenders the licence; or
(c) the licence is cancelled.
Note: For paragraph (a) see Division 6. For paragraph (b) see section 264. For paragraph (c) see section 265.
Voluntary surrender of mining licence
264. A mining licence holder may surrender the licence.
Note 1: See Division 5 for voluntary surrender of part of a licence area.
Note 2: The surrender takes effect when it is registered under section 337 (see subsection 337(5)).
Cancellation of mining licence
265.(1) Subject to subsection (5), the Joint Authority may cancel a mining licence if the licence holder:
(a) breaches a licence condition; or
(b) contravenes a provision of this Act or the regulations; or
(c) breaches a condition attached to an approval under subsection 365(2).
(2) If the Joint Authority proposes to cancel a licence under subsection (1), the Designated Authority must give the licence holder a written notice that informs the holder of the proposed cancellation.
(3) The notice must:
(a) specify the reason for the proposed cancellation; and
(b) invite the holder to make submissions in relation to the proposed cancellation; and
(c) specify the day by which submissions should be given to the Joint Authority; and
(d) specify an address where submissions are to be lodged.
(4) The day specified under paragraph (3)(c) must be not less than 60 days after the day on which the notice is given.
(5) The Joint Authority may cancel the licence only if:
(a) the holder has been given a notice under subsection (2); and
(b) the Joint Authority has considered:
(i) any submission made by the holder; and
(ii) any steps taken by the holder to remedy the circumstances that led to the proposal to cancel the licence and to prevent those circumstances from happening again; and
(c) the Joint Authority is satisfied that no special circumstances exist that justify the licence not being cancelled.
Obligations of former mining licence holders and former associates
266.(1) Subject to subsection (4), if:
(a) a person was:
(i) a mining licence holder; or
(ii) an associate of a mining licence holder; and
(b) the licence:
(i) expires; or
(ii) is cancelled; or
(iii) is surrendered; and
(c) an obligation associated with the licence arising out of:
(i) a licence condition; or
(ii) a direction given under section 387 by the Designated Authority in relation to the licence; or
(iii) this Act or the regulations;
has not been discharged; and
(d) the person was bound by that obligation when the person was the licence holder or an associate;
the person remains bound by the obligation until the obligation is discharged.
(2) Subsection (1) does not continue an obligation to carry out exploration or recovery activities.
(3) Subsection (1) continues an obligation that a person had to carry out exploration or recovery activities in a particular manner if the person carries them out.
(4) The Joint Authority may determine that the person is not subject to:
(a) a particular obligation under this section; or
(b) all the person’s remaining obligations under this section.
(5) A determination under subsection (4) is to be in writing.
PART 2.5—WORKS LICENCES
Division 1—General
Works licences
267.(1) This Part provides for the grant of works licences over blocks in an offshore area.
Note: A works licence allows licence-related activities to be carried out on blocks that are outside the licence area of the exploration, retention or mining licence concerned.
(2) A works licence can only authorise activities that:
(a) are directly connected with activities that are carried out, or are to be carried out, under an exploration, retention or mining licence; and
(b) are necessary or desirable for the exploration, retention or mining licence holder to:
(i) effectively exercise the licence rights; or
(ii) effectively perform the licence obligations.
(3) A works licence can be granted over a particular block even though the block is a reserved block or is in someone else’s licence area.
(4) More than one works licence can be granted over a particular block.
(5) A works licence may be granted so as to allow activities that are connected with 2 or more licences.
Activities authorised by a works licence
268. A works licence holder may carry out in the licence area the activities that are specified in the licence.
Joint Authority may cancel or not renew works licence without compensation
269. No compensation is payable because of the cancellation or non-renewal of a works licence by the Joint Authority.
Note 1: The Joint Authority may cancel the licence under section 313.
Note 2: The Joint Authority may refuse under section 294 or 295 to renew the licence.
Division 2—Application for and grant of works licence
Application for works licence
270. A person may apply to the Joint Authority for a works licence over a block.
How to apply
271.(1) The application must:
(a) be made in accordance with the approved form; and
(b) be made in the approved manner; and
(c) include details of the activities that the applicant proposes to carry out; and
(d) be accompanied by a map that shows the proposed location of the activities; and
(e) specify an address for service of notices under this Act and the regulations.
Note: For paragraphs (a) and (b) see section 41.
(2) The applicant may include in the application any other information that the applicant thinks is relevant.
(3) The application must be lodged with the Designated Authority.
Payment of fee
272.(1) The applicant must pay the application fee prescribed by the regulations.
(2) The fee must be paid when the application is made.
(3) The Joint Authority may refund any fee paid under subsection (1) but only if it is satisfied that special circumstances exist that justify the refund of the fee.
Applicant to notify licence holders affected by the application
273.(1) The applicant must notify interested licence holders of the application.
(2) The notification:
(a) must be given to the interested licence holder in writing; and
(b) must give details of the works licence applied for; and
(c) must invite the interested licence holder to give comments to the Designated Authority within 30 days after the day on which the notice is given.
(3) For the purposes of this section, a licence holder is interested if:
(a) a block covered by the application is inside the licence area; and
(b) the holder is not the applicant.
Application must be advertised
274.(1) The applicant must advertise the application in a newspaper circulating throughout the State or external territory concerned.
(2) The advertisement must contain:
(a) the applicant’s name and address; and
(b) a map and description of the blocks covered that are sufficient for the blocks to be identified; and
(c) details of the activities that the applicant proposes to carry out; and
(d) a map showing the proposed location of those activities; and
(e) the address of the Designated Authority; and
(f) a statement:
(i) that the applicant has applied for a works licence over the blocks described in the notice; and
(ii) that invites comment from the public on the application; and
(iii) that requests that comments be sent to the applicant and to the Designated Authority specified in the notice within 30 days of the day on which the advertisement is published.
(3) The advertisement must be published as soon as possible after the applicant applies for the works licence.
(4) Subject to subsection (5), the advertisement must be published within 14 days after the day on which the applicant lodges the application.
(5) If:
(a) the applicant applies to the Designated Authority within the 14 day period referred to in subsection (4) for an extension of the period; and
(b) the Designated Authority extends the period;
the advertisement must be published within the period as extended by the Designated Authority.
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Designated Authority must refer application to Joint Authority if certain requirements met
275.(1) This section applies if the application covers blocks in a Commonwealth-State offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does what is required by sections 271 to 274, the Designated Authority must refer the application to the Joint Authority.
(3) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 271 to 274, the Designated Authority:
(a) must not refer the application to the Joint Authority; and
(b) must give the applicant written notice that the application has been refused.
(4) The application lapses if a notice is given under subsection (3).
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Joint Authority may provisionally grant works licence
276. If the Designated Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area refers the application to the Joint Authority under section 275, the Joint Authority may:
(a) provisionally grant a works licence to the applicant; or
(b) refuse the application.
Note: Under section 286, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration). The grant will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 283 for “proper acceptance”).
External territory offshore area—how application for works licence dealt with
277.(1) This section applies if the application covers blocks in an external territory offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 271 to 274, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for that offshore area) must refuse the application.
(3) If the applicant does what is required by sections 271 to 274, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for that offshore area) may:
(a) provisionally grant a works licence to the applicant; or
(b) refuse the application.
Note: Under section 286, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration). The grant will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 283 for “proper acceptance”).
Matters to be specified in the licence
278.(1) The licence must specify:
(a) the blocks covered by the licence; and
(b) the activities authorised by the licence; and
(c) the area in which the activities are to be carried out; and
(d) the term of the licence; and
(e) the licence conditions.
(2) The term specified under paragraph (1)(d) is not to exceed 5 years.
Applicant must be notified
279.(1) The Designated Authority must give the applicant written notice of the Joint Authority’s decision under section 276 or 277.
(2) If the Joint Authority provisionally grants a works licence:
(a) the Designated Authority must give the licence to the provisional holder; and
(b) the notice under subsection (1) must contain the following information:
(i) notification of any determination under section 399 that the provisional holder must lodge a security;
(ii) notification that the provisional grant will lapse unless the provisional holder, before the end of the primary payment period:
(A) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(B) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(C) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Works Licence Fees Act.
Amendment of conditions
280.(1) If the provisional holder is dissatisfied with a licence condition, the provisional holder may ask the Joint Authority to amend the condition.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the provisional holder is given the licence under section 279; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority receives a request under subsection (1), the Joint Authority may amend the licence conditions.
(4) The Designated Authority must give the provisional holder written notice of the amendment.
Amendment of security requirements
281.(1) If the provisional holder:
(a) is notified of a security requirement; and
(b) is dissatisfied with the amount of the security required;
the provisional holder may ask the Joint Authority to make a new determination under section 399.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the applicant is given notice under section 279; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority receives a request under subsection (1), the Joint Authority may make a new determination under section 399.
(4) The Designated Authority must give the provisional holder written notice of the new determination.
Extension of primary payment period
282.(1) If the provisional holder makes a request under section 280 or 281, the provisional holder may ask the Designated Authority to extend the primary payment period.
(2) The request must be made within 30 days after the day on which the provisional holder is given notice under section 279.
(3) If the Designated Authority agrees to the request, the Designated Authority must:
(a) determine the period of the extension; and
(b) give the provisional holder a written notice informing the holder of the period of the extension.
Acceptance of grant of works licence
283.(1) The provisional grant of a works licence is properly accepted by the provisional holder if, before the end of the primary payment period, the provisional holder:
(a) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(b) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(c) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Works Licence Fees Act.
Note: Under section 286, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration).
(2) The provisional grant of a works licence is properly accepted by the provisional holder if the provisional holder:
(a) has been granted an extension of the primary payment period under section 282; and
(b) before the end of the secondary payment period:
(i) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the grant; and
(ii) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(iii) pays the fees that must be paid for the licence under the Works Licence Fees Act.
Note: Under section 286, the grant of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 333 for registration).
Conditions applicable to works licence on grant
284. If the provisional grant of the licence is properly accepted, it is subject to:
(a) the conditions specified in the licence given to the applicant under section 279; or
(b) if the Joint Authority amended those conditions under section 280—those conditions as amended.
Lapse of provisional grant of works licence
285. If the provisional grant of the licence is not properly accepted under section 283, the provisional grant lapses.
Division 3—Duration of works licence
Initial term of works licence
286.(1) A works licence comes into force on:
(a) the day on which the grant of the licence is registered; or
(b) if a day later than the day on which the grant of the licence is registered is specified in the licence as its commencement day—that specified day.
(2) The initial term of a works licence expires at the end of the period specified in the licence under subsection 278(1).
Note 1: For the maximum initial term see subsection 278(2).
Note 2: The licence may be surrendered at any time (see section 312).
(3) The period is to run from:
(a) the day on which the licence is provisionally granted; or
(b) if a day later than the day on which the licence is provisionally granted is specified in the licence as the licence’s commencement day—that specified day.
Term of renewal of works licence
287.(1) A renewal of a works licence comes into force on:
(a) the day on which the renewal is registered; or
(b) the day on which the previous term of the licence expires;
whichever is the later.
Note: See Division 4 for renewal.
(2) The term of a renewal of a licence expires at the end of the period specified in the notice under section 296.
Note 1: For the maximum term of renewal see subsection 296(3).
Note 2: The licence may be surrendered at any time (see section 312).
(3) The period runs from the day on which the previous term of the licence expires.
Effect of application for renewal on term of works licence
288. If:
(a) a works licence holder applies to renew the licence under section 289; and
(b) the current term of the licence expires; and
(c) a renewal of the licence does not take effect immediately after the current term expires;
the licence remains in force after the current term expires until:
(d) a renewal of the licence takes effect; or
(e) a provisional renewal of the licence lapses; or
(f) the application for renewal is withdrawn or refused;
whichever happens first.
Division 4—Application for and grant of renewal of works licence
Application for renewal of works licence
289. A works licence holder may apply to the Joint Authority to renew the licence.
Note: At each renewal, the works licence conditions are reviewed (see section 304).
When must an application to renew be made?
290.(1) Subject to subsection (2), the application must be made at least 30 days before the day on which the licence is to expire.
(2) The Designated Authority may accept an application that is made later than 30 days before the day on which the works licence is to expire if:
(a) the application is made before the day on which the licence expires; and
(b) the Designated Authority believes that there are reasonable grounds for accepting the application.
How to apply for renewal
291.(1) The application must:
(a) be made in accordance with the approved form; and
(b) be made in the approved manner; and
(c) include details of:
(i) the activities carried out by the applicant under the licence during its current term; and
(ii) the amount of money spent by the applicant in relation to the blocks covered by the licence during its current term; and
(iii) the activities that the applicant intends to carry out under the licence during the term applied for; and
(iv) the amount of money that the applicant intends to spend in relation to the activities authorised by the licence during the term applied for.
Note: For paragraphs (a) and (b) see section 41.
(2) The applicant may include in the application any other information that the applicant thinks is relevant.
(3) The application must be lodged with the Designated Authority.
Payment of fee
292.(1) The applicant must pay the application fee prescribed by the regulations.
(2) The fee must be paid when the application is made.
(3) The Joint Authority may refund any fee paid under subsection (1) but only if it is satisfied that special circumstances exist that justify the refund of the fee.
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Designated Authority must refer renewal application to Joint Authority if certain requirements met
293.(1) This section applies if the renewal application covers blocks in a Commonwealth-State offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does what is required by sections 290 to 292, the Designated Authority must refer the application to the Joint Authority.
(3) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 290 to 292, the Designated Authority:
(a) must not refer the application to the Joint Authority; and
(b) must give the applicant written notice that the application has been refused.
(4) The application lapses if a notice is given under subsection (3).
Commonwealth-State offshore area—provisional renewal of works licence
294. If the Designated Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area refers the application to the Joint Authority under section 293, the Joint Authority may:
(a) provisionally renew the licence; or
(b) refuse to renew the licence.
Note 1: Under section 287, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration). The renewal will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 300 for “proper acceptance”).
Note 2: Under section 304, new conditions may be imposed on renewal.
External territory offshore area—how application for renewal dealt with
295.(1) This section applies if the renewal application covers blocks in an external territory offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 290 to 292, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for the offshore area) must refuse to renew the licence.
(3) If the applicant does what is required by sections 290 to 292, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for that offshore area) may:
(a) provisionally renew the licence; or
(b) refuse to renew the licence.
Note 1: Under section 287, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration). The renewal will not be registered until it has been properly accepted (see section 300 for “proper acceptance”).
Note 2: Under section 304, new conditions may be imposed on renewal.
Applicant must be notified
296.(1) The Designated Authority must give the applicant written notice of the Joint Authority’s decision under section 294 or 295.
(2) If the Joint Authority provisionally renews the works licence under section 294 or 295, the notice must contain the following information:
(a) notification of the term of the renewal;
(b) notification of the conditions of the renewed licence;
(c) notification that the provisional renewal will lapse unless the applicant, before the end of the primary payment period:
(i) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the renewal; and
(ii) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(iii) pays the fees that must be paid under the Works Licence Fees Act.
Note: Paragraph (b): section 304 provides for renewals to be granted subject to conditions.
(3) The term specified under paragraph (2)(a) is not to be more than 5 years.
Amendment of conditions
297.(1) If the licence holder:
(a) has been provisionally granted a renewal of the licence under section 294 or 295; and
(b) is notified of the licence conditions; and
(c) is dissatisfied with a licence condition;
the holder may ask the Joint Authority to amend the condition.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the holder is given notice under section 296; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority is given a request under subsection (1), the Joint Authority may amend the licence conditions.
(4) The Designated Authority must give the holder written notice of the amendment.
Amendment of security requirements
298.(1) If the licence holder:
(a) has been provisionally granted a renewal of the licence under section 294 or 295; and
(b) is notified of a security requirement; and
(c) is dissatisfied with the amount of security required;
the holder may ask the Joint Authority to make a new determination under section 399.
(2) The request must:
(a) be made within 30 days after the day on which the holder is given notice under section 296; and
(b) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) If the Joint Authority is given a request under subsection (1), the Authority may make a new determination under section 399.
(4) The Designated Authority must give the holder written notice of the new determination.
Extension of primary payment period
299.(1) If the licence holder makes a request under section 297 or 298, the holder may ask the Designated Authority to extend the primary payment period.
(2) The request must be made within 30 days after the day on which the holder is given notice under section 296.
(3) If the Designated Authority agrees to the request, the Designated Authority must:
(a) determine the period of the extension in writing; and
(b) give the holder written notice informing the holder of the period of the extension.
Acceptance of renewal of works licence
300.(1) The provisional renewal of a works licence is properly accepted by the holder if, before the end of the primary payment period, the holder:
(a) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the renewal; and
(b) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(c) pays the fees that must be paid under the Works Licence Fees Act.
Note: Under section 287, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration).
(2) The provisional renewal of a works licence is properly accepted by the holder if the holder:
(a) has been granted an extension of the primary payment period under section 299; and
(b) before the end of the secondary payment period:
(i) gives the Designated Authority a written acceptance of the renewal; and
(ii) lodges any security required by the Joint Authority under section 399; and
(iii) pays the fees that must be paid under the Works Licence Fees Act.
Note: Under section 287, the renewal of the licence cannot be effective before it is registered (see section 334 for registration).
Conditions applicable to works licence on renewal
301. If the provisional renewal is properly accepted, the licence is subject to:
(a) the conditions specified in the notice given to the licence holder under section 296; or
(b) if the Joint Authority amended those conditions under section 297— those conditions as amended.
Lapse of provisional renewal of works licence
302. If the provisional renewal of the licence is not properly accepted under section 300, the provisional renewal lapses.
Division 5—Obligations associated with works licence
General
303.(1) The sources of obligations associated with a works licence are:
(a) the licence conditions; and
(b) obligations arising from compliance directions given by the Designated Authority; and
(c) obligations imposed by this Act and the regulations.
Note: For paragraph (a) see sections 304 and 305. For paragraph (b) see section 387. For paragraph (c) see sections 308 to 310 and section 372.
(2) If a works licence has 2 or more holders, all the holders are jointly and severally bound by the obligations that attach to the licence.
Conditions of works licence
304.(1) The Joint Authority may grant or renew a works licence subject to whatever conditions the Joint Authority thinks are appropriate.
(2) If the Joint Authority grants or renews a works licence subject to conditions, the conditions must be specified in the licence.
(3) Without limiting subsection (1), the Joint Authority may attach the following kinds of conditions to the grant or renewal of a works licence:
(a) a condition requiring the licence holder to take out insurance as required by the Designated Authority;
(b) a condition requiring the holder to carry out certain work in or in relation to the licence area during the term of the licence, and to comply with directions concerning that work given under section 387;
(c) a condition requiring the holder to lodge a security with the Joint Authority;
(d) a condition requiring the holder to keep specified information;
(e) a condition requiring the holder to give the Joint Authority, on request, specified information;
(f) a condition requiring the holder to take steps to protect the environment of the licence area, including conditions relating to:
(i) protecting wildlife; or
(ii) minimising the effect on the environment of the licence area and the area surrounding the licence of activities carried out in the licence area;
(g) a condition requiring the holder to repair any damage to the environment caused by activities in the licence area;
(h) a condition requiring the holder to pay a specified penalty to the Commonwealth if the holder does not comply with a licence condition.
(4) A condition under paragraph (3)(c) must specify:
(a) the amount of the security required; and
(b) the kind of security required; and
(c) the manner and form in which the security is to be lodged.
(5) Without limiting paragraph (3)(c), a condition under that paragraph may require the lodgment of a security in the form of a guarantee and if a guarantee is required the condition may specify:
(a) the kind of person who is to give the guarantee; and
(b) the terms of the guarantee.
No conditions requiring payment of money
305. Except for a condition requiring the payment of a penalty or lodgment of a security, a licence condition must not require the payment of money to:
(a) the Designated Authority; or
(b) the Joint Authority; or
(c) the Commonwealth.
Variation of conditions
306.(1) If a works licence holder requests the Designated Authority in writing to vary a licence condition, the Joint Authority may vary the condition.
(2) If a Designated Authority gives:
(a) a direction under section 387; or
(b) an approval, consent or exemption under the regulations;
to a works licence holder, the Joint Authority may vary a licence condition to the extent necessary to avoid inconsistency between the licence conditions and the direction, approval, consent or exemption.
(3) The Joint Authority may vary a licence condition subject to whatever conditions the Joint Authority thinks appropriate.
(4) If the Joint Authority varies a licence condition, the Designated Authority must give the licence holder a written notice that:
(a) informs the holder of the variation; and
(b) specifies the conditions which have been varied; and
(c) specifies any conditions to which the variation is subject.
Exemption from or suspension of conditions
307.(1) If a works licence holder requests the Designated Authority in writing to:
(a) suspend a licence condition; or
(b) exempt the holder from complying with a licence condition;
the Joint Authority may:
(c) suspend a licence condition; or
(d) exempt the holder from complying with a licence condition.
(2) If a Designated Authority gives:
(a) a direction under section 387; or
(b) an approval, consent or exemption under the regulations;
to a works licence holder, the Joint Authority may suspend a licence condition, or exempt the holder from compliance with a licence condition, to the extent necessary to avoid inconsistency between the licence conditions and the direction, approval, consent or exemption.
(3) The Joint Authority may:
(a) suspend a licence condition; or
(b) exempt the licence holder from complying with a licence condition;
subject to whatever conditions the Joint Authority thinks appropriate.
(4) If the Joint Authority:
(a) suspends a licence condition; or
(b) exempts the licence holder from complying with a licence condition;
the Designated Authority must give the holder a written notice that:
(c) informs the holder of the exemption or suspension; and
(d) specifies the conditions which have been suspended or affected by the exemption; and
(e) specifies any conditions to which the suspension or exemption is subject.
Note: A suspension or exemption of a condition does not take effect until registered (see section 337).
Work practices
308. If a person who is:
(a) a works licence holder; or
(b) an associate of the holder;
carries out activities in the licence area that are authorised by the licence, the holder or associate must take all reasonable steps:
(c) to ensure that the activities are carried out at a standard that is accepted as reasonable and proper in the mining industry; and
(d) to protect the health, safety and welfare of people engaged in the activities in and about the licence area; and
(e) to maintain in good repair all structures, equipment and other property in the licence area brought there by the person; and
(f) to remove from the licence area any structure, equipment or other property that:
(i) belongs to the person, or is under the person’s control; and
(ii) is not being used, or is not going to be used, in connection with the activities.
Maximum penalty: 200 penalty units.
Licence holder must keep specified records etc.
309. A works licence holder must:
(a) keep whatever records; and
(b) give whatever records to the Designated Authority for inspection; and
(c) make whatever returns;
are necessary to comply with:
(d) the regulations; or
(e) the licence conditions; or
(f) a direction given by the Designated Authority under section 387.
Note: Under section 387 the Designated Authority may direct a person to keep records and to make returns.
Maximum penalty: 100 penalty units.
Licence holder must assist inspectors
310. A works licence holder must provide an inspector with reasonable facilities and assistance so that the inspector is able to carry out compliance inspections.
Note: See sections 377 to 384 for compliance inspections.
Maximum penalty: 50 penalty units.
Division 6—Expiry of works licence
General
311. A works licence expires if:
(a) the term of the licence expires without the licence being renewed; or
(b) the licence holder surrenders the licence; or
(c) the licence is cancelled.
Note: For paragraph (a) see Division 4. For paragraph (b) see section 312. For paragraph (c) see section 313.
Voluntary surrender of works licence
312. The holder of a works licence may surrender the licence.
Note: The surrender takes effect when it is registered under section 337 (see subsection 337(5)).
Cancellation of works licence
313.(1) Subject to subsection (5), the Joint Authority may cancel a works licence if the licence holder:
(a) breaches a licence condition; or
(b) contravenes a provision of this Act or the regulations; or
(c) breaches a condition attached to an approval under subsection 365(2).
(2) If the Joint Authority proposes to cancel a works licence under subsection (1), the Designated Authority must give the licence holder a written notice that informs the holder of the proposed cancellation.
(3) The notice must:
(a) specify the reason for the proposed cancellation; and
(b) invite the holder to make submissions in relation to the proposed cancellation; and
(c) specify the day by which submissions should be given to the Joint Authority; and
(d) specify an address where submissions are to be lodged.
(4) The day specified under paragraph (3)(c) must be not less than 60 days after the day on which the notice is given.
(5) The Joint Authority may cancel a works licence only if:
(a) the holder has been given a notice under subsection (2); and
(b) the Joint Authority has considered:
(i) any submission made by the holder; and
(ii) any steps taken by the holder to remedy the circumstances that led to the proposal to cancel the licence and to prevent those circumstances from happening again; and
(c) the Joint Authority is satisfied that no special circumstances exist that justify the licence not being cancelled.
Obligations of former works licence holders and former associates
314.(1) Subject to subsection (2), if:
(a) a person was:
(i) a works licence holder; or
(ii) an associate of a works licence holder; and
(b) the licence:
(i) expires; or
(ii) is cancelled; or
(iii) is surrendered; and
(c) an obligation associated with the licence arising out of:
(i) a licence condition; or
(ii) a direction given under section 387 by the Designated Authority in relation to the licence; or
(iii) this Act or the regulations;
has not been discharged; and
(d) the person was bound by that obligation when the person was the works licence holder or an associate;
the person remains bound by the obligation until the obligation is discharged.
(2) The Joint Authority may determine that the person is not subject to:
(a) a particular obligation under this section; or
(b) all the person’s remaining obligations under this section.
(3) A determination under subsection (2) is to be in writing.
PART 2.6—SPECIAL PURPOSE CONSENTS
Special purpose consents
315.(1) This Part provides for the grant of special purpose consents.
(2) A special purpose consent may be granted over:
(a) a standard block; or
(b) a reserved block; or
(c) a tender block.
(3) A special purpose consent may be granted over a block even if the block is in the licence area of a licence or the consent area of another special purpose consent.
(4) A special purpose consent can only be granted for:
(a) a scientific investigation; or
(b) a reconnaissance survey; or
(c) the collection of only small amounts of minerals.
(5) The exploration of an area is a reconnaissance survey if the exploration is carried out to work out whether the area explored is sufficiently promising to justify more detailed exploration under an exploration licence.
Activities authorised by a special purpose consent
316.(1) A special purpose consent holder may:
(a) explore for minerals; and
(b) take samples of or recover minerals;
in the consent area for the purposes specified in the consent.
Note 1: Under subsection 23(1) the concept of “exploration” extends to activities that are directly related to exploration.
Note 2: Under subsection 24(1) the concept of “recovery” extends to activities that are directly related to the recovery of minerals.
(2) The grant of a consent does not give the consent holder:
(a) any exclusive or proprietary rights over the blocks covered by the consent; or
(b) any option or preference when it comes to the grant of a licence over blocks covered by the consent.
Application for a consent
317. A person may apply to the Joint Authority for a special purpose consent.
How to apply
318.(1) The application must:
(a) be made in writing; and
(b) include details of the activities for which consent is being sought; and
(c) specify the blocks for which the consent is being sought; and
(d) be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(2) If the activity involves the collection of only small amounts of minerals (see paragraph 315(4)(c)), the application must also specify:
(a) the mineral to be recovered; and
(b) the proposed quantity of the mineral to be recovered.
Payment of fee
319.(1) The applicant must pay the application fee prescribed by the regulations.
(2) The fee must be paid when the application is made.
(3) The Joint Authority may refund any fee paid under subsection (1) but only if it is satisfied that special circumstances exist that justify the refund of the fee.
Applicant must obtain agreement of exploration, retention and mining licence holders affected by the application
320.(1) Subject to subsection (3), the applicant must obtain the agreement of interested licence holders to the application.
(2) The agreement must be in writing.
(3) The agreement of an interested licence holder is not necessary if:
(a) the application is for a scientific investigation; and
(b) Australia has obligations under international conventions to allow the investigation.
(4) For the purposes of this section, a licence holder is interested if:
(a) the holder holds an exploration, retention or mining licence; and
(b) the block concerned is inside the licence area.
Applicant to notify works licence holders affected by the application
321.(1) The applicant must notify interested works licence holders of the application.
(2) The notification:
(a) must be given to the interested works licence holders in writing; and
(b) must give details of the special purpose consent applied for; and
(c) must invite the interested works licence holder to give comments to the Designated Authority within 30 days after the day on which the notice was given.
(3) For the purposes of this section, a works licence holder is interested if the block concerned is inside the works licence area.
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Designated Authority must refer application to Joint Authority if certain requirements met
322.(1) This section applies if the application covers blocks in a Commonwealth-State offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does what is required by sections 318 to 321, the Designated Authority must refer the application to the Joint Authority.
(3) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 318 to 321, the Designated Authority:
(a) must not refer the application to the Joint Authority; and
(b) must give the applicant written notice that the application has been refused.
(4) The application lapses if a notice is given under subsection (3).
Commonwealth-State offshore area—Joint Authority may grant special purpose consent
323. If the Designated Authority for a Commonwealth-State offshore area refers the application to the Joint Authority under section 322, the Joint Authority may:
(a) grant a special purpose consent to the applicant; or
(b) refuse the application.
External territory offshore area—how application for special purpose consent dealt with
324.(1) This section applies if the application covers blocks in an external territory offshore area.
(2) If the applicant does not do what is required by sections 318 to 321, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for that offshore area) must refuse the application.
(3) If the applicant does what is required by sections 318 to 321, the responsible Commonwealth Minister (as the Joint Authority for that offshore area) may:
(a) grant a special purpose consent to the applicant; or
(b) refuse the application.
Matters to be specified in the consent
325.(1) The consent must specify:
(a) the blocks covered by the consent; and
(b) the activities authorised by the consent; and
(c) the period for which the consent is to have effect; and
(d) the consent conditions.
(2) If the activity involves the collection of only small amounts of minerals (see paragraph 315(4)(c)), the consent must also specify:
(a) the minerals to be collected; and
(b) the quantities to be collected.
(3) The period specified under paragraph (1)(c) is not to be more than 12 months.
Duration of consent
326. A consent has effect for the period specified under paragraph 325(1)(c).
Conditions of consent
327.(1) The Joint Authority may grant a special purpose consent subject to whatever conditions the Joint Authority thinks are appropriate.
(2) Without limiting subsection (1), the Joint Authority may impose conditions that relate to:
(a) reports to be provided by the consent holder about activities carried out under the consent; and
(b) environmental matters.
CHAPTER 3—REGISTRATION AND DEALINGS
PART 3.1—REGISTRATION
Division 1—Preliminary
Registers to be kept
328.(1) Each Designated Authority must keep an offshore mining register.
Note 1: The main matters entered in the register are:
• the grant or renewal of a licence (see sections 333 and 334);
• details of instruments that affect a licence (see section 337);
• details of instruments that affect an interest in a licence (see sections 338 and 339);
• details of interests in a licence that are acquired by devolution (see section 340);
• details of caveats (see section 345).
Note 2: Section 72 of the Crimes Act 1914 deals with offences in relation to the proper keeping of the register (for example, making false entries).
(2) The register for a particular Commonwealth-State offshore area is to be known as the Commonwealth-State Offshore Mining Register for that State.
(3) The register for a particular external territory offshore area is to be known as the External Territory Offshore Mining Register for that external territory.
Associated document files to be kept
329.(1) Each Designated Authority must keep an associated document file.
(2) In the associated document file are to be kept the documents that the Designated Authority is required to keep under this Part.
Note: The documents kept in the document file are:
• copies of licences (see subsection 333(6));
• copies of instruments that affect licences (see subsection 337(4));
• copies of transfers of licences (see subsection 338(6));
• copies of other dealings in licences (see subsection 339(4));
• caveats (see subsection 345(3));
• withdrawals of caveats (see subsection 346(2));
• consents to dealings given under section 350 (see subsection 350(6));
• copies of court orders under section 351.
Form of register and document file
330.(1) The register is to be kept in the form and manner determined by the Designated Authority.
(2) Without limiting subsection (1), the register may be kept in the form of a computer record.
(3) The document file is to be kept in the form and manner determined by the Designated Authority.
Correction of errors in the register
331.(1) Subject to subsection (4), the Designated Authority may correct the register if the Designated Authority is satisfied that:
(a) there is an omission of an entry from the register; or
(b) an entry in the register should not have been made; or
(c) there is an error or defect in an entry in the register.
(2) A person may apply to the Designated Authority for correction of the register under subsection (1).
(3) The application:
(a) must be in writing; and
(b) must specify the correction that is being requested.
(4) If:
(a) the Designated Authority intends to correct the register under subsection (1); and
(b) the correction relates to a licence; and
(c) the correction is not to be made in response to an application under subsection (2) by the licence holder;
the Designated Authority must notify the holder that the Designated Authority intends to correct the register.
(5) The notice:
(a) must be in writing; and
(b) must specify the correction the Designated Authority intends to make; and
(c) must invite the holder to make submissions to the Designated Authority about the proposed correction within the period specified in the notice.
(6) The period specified under paragraph (5)(c) is to be at least 14 days after the day on which the notice is given.
(7) If a notice is given under subsection (4):
(a) the Designated Authority is not to correct the register until the period specified in the notice has ended; and
(b) the Designated Authority is to have regard to any submissions made by the licence holder before the end of that period in exercising the power under subsection (1) to correct the register.
Inspection of register and documents
332.(1) A person may inspect the register and the document file if the person pays the fee prescribed by the regulations.
(2) The Designated Authority must make the register and the document file available for inspection at all convenient times.
Division 2—Matters to be entered in register
Subdivision A—Licences
Licences
333.(1) If the provisional grant of a licence is properly accepted, the Designated Authority must register:
(a) the holder’s name; and
(b) if there is more than one licence holder—the share of the licence held by each holder; and
(c) a description of the licence area, including a map or map reference; and
(d) the term of the licence; and
(e) the date of the provisional grant of the licence; and
(f) the date of registration of the licence; and
(g) an address for the service of notices under this Act.
(2) The address registered under paragraph (1)(g) is to be the address specified by the licence holder by notice in writing to the Designated Authority.
(3) If the holder has not given a notice under subsection (2), the address to be registered under paragraph (1)(g) is to be the address specified in the application that the holder made for the licence.
(4) If the Designated Authority registers a licence under subsection (1):
(a) the licence holder must give the licence to the Designated Authority; and
(b) the Designated Authority must endorse the date of registration on the licence.
(5) The Designated Authority may include in the register any other information about the holder or the terms and conditions of the licence that the Designated Authority thinks is appropriate.
(6) The Designated Authority must retain a copy of each licence granted by the Joint Authority.
(7) A licence is taken to be registered as soon as an entry complying with subsection (1) is made in the register.
Renewal of licences
334.(1) If the Designated Authority is given an application for the renewal of a licence, the Designated Authority must register the fact.
(2) If the provisional renewal of a licence is properly accepted, the Designated Authority must register:
(a) the renewal; and
(b) the term of the renewal; and
(c) the date of the provisional renewal; and
(d) the date of registration of the renewal.
(3) If the Designated Authority registers the renewal of a licence under subsection (2):
(a) the licence holder must give the licence to the Designated Authority; and
(b) the Designated Authority must endorse on the licence:
(i) the term of the renewal; and
(ii) the date of registration of the renewal.
(4) If the Joint Authority refuses to renew a licence, the Designated Authority must register the refusal.
Extension of exploration licences
335.(1) If the Designated Authority receives an application for the extension of the term of an exploration licence, the Designated Authority must register the fact.
(2) If the Joint Authority refuses to extend the term of an exploration licence, the Designated Authority must register the refusal.
Note: The grant of the extension of the term of an exploration licence is registered under subsection 337(1).
Expiry of licences
336.(1) If a licence expires because:
(a) its term ends; or
(b) a retention licence or mining licence is granted to the licence holder;
the Designated Authority must register the expiry of the licence.
Note: Cancellation is dealt with under section 337.
(2) If the Designated Authority registers the expiry of a licence under subsection (1):
(a) the licence holder must give the licence to the Designated Authority; and
(b) the Designated Authority must endorse the expiry and the date of the expiry on the licence.
Variations etc. to licences
337.(1) The Designated Authority must register:
(a) the details of any document under this Act that varies, surrenders, cancels or otherwise affects a licence; and
(b) the details of any document that varies or revokes a document referred to in paragraph (a).
Note: The documents referred to in paragraph (a) are:
• suspension of licence rights (see sections 48 (exploration licence), 135 (retention licence) and 195 (mining licence));
• amendment of licence conditions between provisional grant and registration (see sections 67 (exploration licence), 148 (retention licence), 211 (mining licence) and 280 (works licence))—these need to be registered at the same time as the grant is registered because if the conditions are amended between provisional grant and registration a replacement licence reflecting the change in conditions is not issued to the provisional holder;
• extension of term (see sections 90, 95 and 97 (exploration licence));
• surrender of the whole or a part of a licence (see sections 99, 100 and 127 (exploration licence), 158 and 187 (retention licence), 235 and 264 (mining licence) and 312 (works licence));
• voluntary surrender—special approval (see section 100 (exploration licence));
• mandatory reduction of licence area—special permission (see section 104 (exploration licence));
• amendment of licence conditions between provisional renewal and registration (see sections 111 (exploration licence), 170 (retention licence), 247 (mining licence) and 297 (works licence))—these need to be registered at the same time as the renewal because if the licence conditions are amended between provisional renewal and registration a replacement licence reflecting the changed conditions is not issued to the holder;
• variation of conditions (see sections 120 (exploration licence), 179 (retention licence), 256 (mining licence) and 306 (works licence));
• exemption from or suspension of condition (see sections 121 (exploration licence), 180 (retention licence) and 257 (mining licence) and 307 (works licence));
• cancellation (see sections 130 (exploration licence), 189 and 190 (retention licence), 265 (mining licence) and 313 (works licence));
• directions (see sections 387 and 392);
• security requirements (see section 399);
• approvals of transfers (see section 365).
(2) Paragraph (1)(a) applies to a document that suspends the rights of a holder of a licence.
(3) Details of a document may be registered by registering a summary of the contents of the document.
(4) The Designated Authority must retain the instrument referred to in subsection (1), or a copy of the instrument.
(5) A document referred to in subsection (1):
(a) has no effect until it is registered; and
(b) is taken to be registered as soon as an entry complying with subsection (1) is made in the register.
Transfer of licences
338.(1) The Designated Authority must register the transfer of a licence or a share in a licence if:
(a) a party to the transfer lodges the instrument of transfer for registration; and
(b) a party to the transfer lodges a copy of the instrument of transfer; and
(c) the transfer has been approved by the Joint Authority; and
(d) the licence is lodged with the Designated Authority for annotation under subsection (5); and
(e) the fee provided for in the Registration Fees Act is paid; and
(f) the fee prescribed by the regulations is paid; and
(g) section 341 (caveats) does not prevent the registration of the transfer.
Note: Paragraph (c): the Joint Authority’s approval is endorsed on the transfer (see subsection 365(3)).
(2) The Designated Authority must also register the date and time of registration of the transfer.
(3) If a document purports to be a transfer of a licence or a share in a licence, the Designated Authority is to register the document under this section without inquiring into or concerning itself with the legal effectiveness of the document.
(4) If an instrument that transfers a licence or a share in a licence is registered, the Designated Authority must register the name of the transferee as a licence holder.
(5) If the Designated Authority registers the transfer of a licence or a share in a licence, the Designated Authority must annotate the licence to show the transferee as a licence holder.
(6) The Designated Authority must keep the copy of the transfer.
(7) The Designated Authority must return the transfer to the person who lodged it.
(8) The Designated Authority must return the annotated licence to the person who lodged it.
(9) The registration of a document under this section does not give the document any greater effect than it would have had apart from this Act.
Other dealings in licences
339.(1) The Designated Authority must register a document (other than a transfer of a licence or a share in a licence) that creates, transfers, affects or otherwise deals with an interest in a licence if:
(a) a party to the dealing lodges the document for registration; and
(b) a party to the dealing lodges a copy of the document; and
(c) the fee provided for in the Registration Fees Act is paid; and
(d) the fee prescribed by the regulations is paid; and
(e) section 341 (caveats) does not prevent the registration of the dealing.
(2) The Designated Authority must also register the date and time of registration of the dealing.
(3) If a document purports to create, transfer, affect or otherwise deal with an interest in a licence, the Designated Authority is to register the document under this section without inquiring into or concerning itself with the legal effectiveness of the document.
(4) The Designated Authority must keep the copy of the document.
(5) The Designated Authority must return the document to the person who lodged it.
(6) The registration of a document under this section does not give the document any greater effect than it would have had apart from this Act.
Devolution of licences
340.(1) If:
(a) the rights of a licence holder have devolved to a person by operation of law; and
(b) the person applies to the Designated Authority in writing to be registered as a licence holder; and
(c) the licence is given to the Designated Authority for annotation under subsection (3); and
(d) the person pays the fee prescribed by the regulations; and
(e) the Designated Authority is satisfied that the applicant is entitled to those rights; and
(f) section 341 (caveats) does not prevent the registration of the person as a licence holder;
the Designated Authority must register the person as a licence holder.
(2) If the Designated Authority registers a person as a licence holder under subsection (1), the Designated Authority must also register the date and time of registration.
(3) If the Designated Authority registers a person as a licence holder under subsection (1), the Designated Authority must annotate the licence accordingly.
(4) The Designated Authority must return the annotated licence to the person who gave it to the Designated Authority.
(5) This section applies to 2 or more persons to whom rights have devolved in the same way as it applies to a single person to whom rights have devolved.
Subdivision B—Caveats
Effect of a caveat
341.(1) If a caveat is in force on a licence, the Designated Authority must not register a dealing in the licence unless:
(a) the Designated Authority is not required to give the caveat holder notice of the particular dealing; or
(b) the caveat holder consents to the registration of the dealing under section 350; or
(c) a court of competent jurisdiction orders the Designated Authority to register the dealing under section 338 or 339 despite the caveat.
Note 1: For “dealing” see section 4.
Note 2: Once the caveat holder has been given notice of the dealing, the caveat will lapse at the end of 30 days unless the caveat holder consents to the registration of the dealing or gets a court order extending the life of the caveat.
Note 3: The Designated Authority may not be required to give the caveat holder notice of the dealing because the caveat holder is a party to the dealing or because the dealing falls outside the class of dealings that the caveat holder has specified under subsection 343(2) (see subsection 349(6)).
(2) If a caveat is in force on a licence, the Designated Authority must not register a person under section 340 as a licence holder unless:
(a) the caveat holder consents to the registration under section 350; or
(b) a court of competent jurisdiction orders the Designated Authority to register the person under section 340 despite the caveat.
Note: Once the caveat holder has been given notice, the caveat will lapse at the end of 30 days unless the caveat holder consents to the registration or gets a court order extending the life of the caveat.
Lodgment of caveats
342.(1) A person who claims an interest in or affecting a licence may lodge with the Designated Authority a caveat on the licence.
(2) Without limiting subsection (1), a person may claim an interest in or affecting a licence even if the interest claimed arises under a document that has not been registered under section 338 or 339.
Form of caveat
343.(1) A caveat must:
(a) be in accordance with the approved form; and
(b) set out:
(i) the full name and address of the person claiming the interest; and
(ii) details of the interest claimed; and
(c) be signed by the person claiming the interest; and
(d) specify an address for service of notices within the State or Territory for which the Designated Authority is responsible.
(2) A caveat may specify the particular dealings that the caveat holder wants to be given notice of under section 349.
Payment of fee
344. The person lodging a caveat must pay the caveat fee that is specified by the regulations.
Caveat to be registered
345.(1) If:
(a) a caveat is lodged for registration; and
(b) the caveat complies with section 343; and
(c) the person lodging the caveat pays the fee required by section 344;
the Designated Authority must, subject to subsection (4), register the caveat.
(2) The Designated Authority must register the date on which the caveat was lodged.
(3) The Designated Authority must retain the original of the caveat and endorse on it the date on which it was lodged.
(4) Subsection (1) does not apply if:
(a) a court has made an order under subsection 351(2); and
(b) the order requires the court’s consent to the registration of the caveat; and
(c) the court has not consented to the registration of the caveat.
Withdrawal of caveat
346.(1) A caveat holder may withdraw the caveat at any time by lodging a written withdrawal with the Designated Authority.
(2) The Designated Authority must:
(a) register details of the withdrawal; and
(b) endorse details of the withdrawal on the original of the caveat; and
(c) retain the original of the withdrawal.
Form of withdrawal
347. A withdrawal of a caveat:
(a) must be in accordance with the approved form; and
(b) must give details of the caveat; and
(c) must be signed by the caveat holder.
Duration of caveat
348.(1) A caveat on a licence has effect from the time at which it is lodged with the Designated Authority.
(2) A caveat on a licence ceases to have effect if:
(a) a court of competent jurisdiction makes an order for the removal of the caveat under section 351; or
(b) the caveat is withdrawn under section 346; or
(c) the caveat holder is given notice under subsection 349(1), (2) or (3) and 30 days have passed since the caveat holder was given the notice.
(3) Paragraph (2)(c) does not apply if, before the end of the 30 days, the caveat holder consents to the registration of the dealing or to the registration under section 340.
(4) Paragraph (2)(c) does not apply if, before the end of the 30 days:
(a) the caveat holder applies to a court of competent jurisdiction for an order under section 351 that the caveat be extended beyond the period; and
(b) the court makes an order extending the period.
(5) If a court makes an order under paragraph 351(1)(c), the caveat ceases to have effect at the end of the extended period.
(6) Subsection (5) does not apply if, before the end of the extended period, the caveat holder consents to the registration of the dealing under section 350 or to the registration under section 340.
Notice to caveat holder
349.(1) If:
(a) a transfer of a licence or a share in a licence is lodged with the Designated Authority under section 338; and
(b) a caveat is in force on the licence;
the Designated Authority must, subject to subsection (6), notify the caveat holder that the transfer has been lodged for registration.
(2) If:
(a) a dealing in a licence (other than a transfer of the licence or a share in the licence) is lodged with the Designated Authority under section 339; and
(b) a caveat is in force on the licence;
the Designated Authority must, subject to subsection (6), notify the caveat holder that the dealing has been lodged for registration.
(3) If:
(a) a person applies to the Designated Authority under section 340 to be registered as a licence holder; and
(b) a caveat is in force on the licence;
the Designated Authority must notify the caveat holder that the application has been made.
(4) If:
(a) a licence holder surrenders the licence or surrenders a block or some of the blocks covered by the licence; and
(b) a caveat is in force on the licence;
the Designated Authority must notify the caveat holder of the surrender.
(5) Notification under subsection (1), (2), (3) or (4) must be by registered post or certified mail.
(6) Notice is not to be given under subsection (1) or (2) if:
(a) the caveat holder is a party to the transfer or dealing concerned; or
(b) the caveat holder has specified the class of dealings the caveat holder wants to receive notice of (see subsection 343(2)) and the transfer or dealing falls outside that class.
Caveat holder may consent to approval or registration
350.(1) If a caveat holder is given notice under subsection 349(1), the caveat holder may consent to the registration of the transfer.
(2) If a caveat holder is given notice under subsection 349(2), the caveat holder may consent to the registration of the dealing.
(3) If a caveat holder is given notice under subsection 349(3), the caveat holder may consent to the registration of the person as a licence holder.
(4) A consent under this section must be in writing and must be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(5) A consent under this section is only effective if it is given within 30 days after the day on which the caveat holder receives the notice concerned.
(6) The Designated Authority must:
(a) register details of the consent; and
(b) endorse details of the consent on the original of the caveat; and
(c) retain the original of the consent.
Orders that can be made by a court in relation to caveats
351.(1) A court of competent jurisdiction may:
(a) order the removal of a caveat from a licence; or
(b) order the Designated Authority to register a dealing despite a caveat; or
(c) extend the period provided for by paragraph 348(2)(c).
(2) If:
(a) a court makes an order under paragraph (1)(a) or (b) in relation to the licence; and
(b) the court is satisfied that caveats are being used vexatiously to delay the registration of a document;
the court may also make an order that the Designated Authority is not to register any caveats in respect of the licence unless the court has consented to the registration.
(3) An order under subsection (2) may be for an indefinite period or for a specified period.
(4) If an application is made to the court for an order under subsection (2), the Designated Authority becomes a party to the proceedings.
(5) If a court makes an order under this section, the Designated Authority must:
(a) register details of the order; and
(b) retain a copy of the order.
Division 3—Miscellaneous
Fees for registration
352.(1) The Joint Authority is to determine the amount of the fee payable under the Registration Fees Act for registration of any document or fact.
(2) If:
(a) a document creates, transfers, affects or otherwise deals with a licence or an interest in a licence; and
(b) the Designated Authority determines under subsection (1) the amount of the fee payable under the Registration Fees Act on the basis of the information contained in the document; and
(c) the Designated Authority subsequently becomes satisfied that the document does not fully and truly set out:
(i) the consideration for the transaction it relates to; or
(ii) all the other facts and circumstances (if any) that affect the amount of the fee payable under the Registration Fees Act in respect of the document;
the Designated Authority may make a fresh determination under subsection (1) of the amount of the fee.
Protection from legal actions
353.(1) This section applies to:
(a) a Joint Authority; and
(b) a member of a Joint Authority; and
(c) a person acting under the direction or authority of a Joint Authority; and
(d) a Designated Authority; and
(e) a delegate of a Designated Authority; and
(f) a person acting under the direction or authority of a Designated Authority or a delegate of a Designated Authority.
(2) A person to whom this section applies is not liable to an action, suit or proceeding in relation to an act or matter if:
(a) the act or matter is done or omitted to be done in the exercise or purported exercise of a power or authority given by this Part; and
(b) the act or matter is done or omitted to be done in good faith.
Appeals
354.(1) The Supreme Court, on the application of a person aggrieved by:
(a) the omission of an entry from a register; or
(b) an entry wrongly existing in a register; or
(c) an error or defect in an entry in a register;
may make any order it thinks appropriate directing correction of the register.
(2) In proceedings under subsection (1), the Supreme Court may decide any necessary or expedient question concerning the rectification of the register.
(3) A copy of a Supreme Court order may be served on the Designated Authority concerned.
(4) If the Designated Authority receives a copy of an order under subsection (3), the Designated Authority must amend the register so that the register accords with the order.
Appeals against determinations under section 352
355.(1) If a person is dissatisfied with a determination by the Designated Authority under section 352, the person may appeal to the Supreme Court against the determination.
(2) Written notice of an appeal under subsection (1) must be given to the Designated Authority concerned.
(3) The Designated Authority may appear before the Supreme Court in a hearing of an appeal under subsection (1).
(4) If the Supreme Court directs the Designated Authority to appear, the Designated Authority must do so.
(5) On hearing an appeal under subsection (1), the Supreme Court may affirm, revoke or amend the determination of the Designated Authority.
Supreme Court
356. In this Division, “Supreme Court” means the Supreme Court of, or having jurisdiction in, the State or territory concerned.
Evidentiary value of register
357.(1) An offshore mining register is admissible in proceedings as evidence of the matters registered in it.
(2) If the register is kept by the use of a computer, the Designated Authority may issue a document containing the details of a matter taken from the register.
(3) The document issued under subsection (2) is admissible in proceedings as evidence of the matter.
(4) The Designated Authority may give a person a certified copy of, or extract from, the register if the person pays the fee prescribed by the regulations.
(5) The certified copy is admissible in proceedings without any further proof of, or the production of, the original.
Certified copy of document on associated document file
358.(1) The Designated Authority may give a person a certified copy of a document that is kept on the associated document file if the person pays the fee prescribed by the regulations.
(2) The certified copy is admissible in proceedings without any further proof of, or the production of, the original.
Certification of registration action
359.(1) The Designated Authority may give a person a signed certificate that:
(a) a thing required or allowed by this Part has been done; or
(b) a thing required or allowed by this Part has not been done;
if the person pays the fee prescribed by the regulations.
(2) The certificate is admissible in proceedings as evidence of the facts asserted by the certificate.
PART 3.2—DEALINGS IN REGISTERED LICENCES
Division 1—Dealings in licences to be in writing and registered
Dealings in licences to be in writing
360.(1) An interest in a licence may be created, transferred, affected or otherwise dealt with only by a written document.
Note: A transfer must be in writing because it is a dealing.
(2) Subsection (1) does not apply to the rights of a licence holder that devolve to a person by operation of law.
Note 1: Rights might devolve to a person, for example, by operation of the laws relating to intestacy or bankruptcy.
Note 2: For the registration of rights that devolve to a person by operation of law see section 340.
Dealings in interests in licences not effective until registered
361. A document that creates, transfers, affects or otherwise deals with an interest in a licence has no effect until it is registered under Part 3.1.
Note 1: A transfer is a dealing and does not take effect until registered.
Note 2: Transfers are registered under section 338 and other dealings under section 339.
Division 2—Approval of transfer of licences
Transfers require approval by Joint Authority
362.(1) The transfer of a licence has no effect before the transfer is approved by the Joint Authority.
Note 1: For “transfer” of a licence see subsection 7(1).
Note 2: A transfer is a dealing and under section 361 does not take effect until registered.
(2) The transfer of a share of a licence has no effect before the transfer is approved by the Joint Authority.
Note 1: For “transfer” of a share of a licence see subsections 7(2) and (3).
Note 2: A transfer is a dealing and under section 361 does not take effect until registered.
Application for approval of transfer
363.(1) A person may apply to the Joint Authority for approval of the transfer.
(2) The application:
(a) must be in writing; and
(b) must be lodged with the Designated Authority.
(3) The application must be accompanied by:
(a) the transfer document (duly signed or executed); and
(b) a copy of the transfer document; and
(c) if a caveat holder has consented to the registration of the transfer under subsection 350(1)—a copy of the consent.
(4) The application may include a statement of any matter that the applicant wants the Joint Authority to take into account in deciding whether to approve the transfer.
(5) Without limiting subsection (4), the application may include a statement about:
(a) the technical qualifications of a party to the transfer; or
(b) the technical qualifications of the employees of a party to the transfer; or
(c) the technical advice available to a party to the transfer; or
(d) the financial resources of a party to the transfer.
(6) The application must be accompanied by the fee prescribed by the regulations.
Designated Authority may ask for further information
364.(1) If:
(a) an application is made under section 363 for approval of a transfer; and
(b) the Designated Authority has reason to believe that a person possesses or controls a document that relates to:
(i) the transfer document; or
(ii) the transfer transaction; or
(iii) the application for approval of the transfer;
the Designated Authority may ask the person:
(c) to give the document to the Designated Authority; or
(d) to make the document available for inspection by or on behalf of:
(i) the Designated Authority; or
(ii) the Joint Authority.
(2) The request under subsection (1) must be made by giving to the person a written notice containing the request.
(3) A person must not fail to comply with a request under subsection (1) without reasonable excuse.
Maximum penalty: 50 penalty units.
Joint Authority’s response to application for approval
365.(1) If an application is made under section 363, the Joint Authority may:
(a) approve the transfer; or
(b) refuse to approve the transfer.
(2) The Joint Authority may, under paragraph (1)(a), approve the transfer on the conditions that it considers necessary or desirable in the public interest.
(3) If the Joint Authority approves the transfer, the Designated Authority must endorse on:
(a) the transfer document; and
(b) a copy of the transfer document;
a record of the approval.
Note: A record of the approval will also be entered in the offshore mining register (see subsection 337(1)).
Protection from legal actions
366.(1) This section applies to:
(a) a Joint Authority; and
(b) a member of a Joint Authority; and
(c) a person acting under the direction or authority of a Joint Authority; and
(d) a Designated Authority; and
(e) a delegate of a Designated Authority; and
(f) a person acting under the direction or authority of a Designated Authority or a delegate of a Designated Authority.
(2) A person to whom this section applies is not liable to an action, suit or proceeding in relation to an act or matter if:
(a) the act or matter is done or omitted to be done in the exercise or purported exercise of a power or authority given by this Part; and
(b) the act or matter is done or omitted to be done in good faith.
CHAPTER 4—ADMINISTRATION
PART 4.1—INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
Designated Authority may ask person for information
367.(1) The Designated Authority may ask a person to give the Authority information if:
(a) the information is relevant to the operation of this Act; and
(b) the Authority has reasonable grounds for believing that the person is able to give the information.
Note: The person must comply with the request (see section 372).
(2) The Designated Authority may ask the person to give the information to:
(a) the Designated Authority; or
(b) an inspector nominated by the Designated Authority.
(3) The request must:
(a) be made by written notice given to the person; and
(b) specify the person to whom the information is to be given; and
(c) specify the period within which the information is to be given.
(4) The information must be given:
(a) in writing; and
(b) before the end of the period specified in the request.
(5) The document containing the information must be signed by:
(a) if the information is given by a body corporate—an authorised officer of the body corporate; or
(b) if the information is provided by an individual—the individual.
Power to ask person to appear
368.(1) If the Designated Authority has reasonable grounds for believing that a person is able to give information that is relevant to the operation of this Act, the Designated Authority may ask the person to appear personally to:
(a) give the information; and
(b) answer questions about the activity to which the information relates.
Note: The person must comply with the request (see section 372).
(2) The Designated Authority may ask a person to appear before:
(a) the Designated Authority; or
(b) an inspector nominated by the Designated Authority.
(3) The request must:
(a) be made by written notice given to the person; and
(b) specify the activity about which the information is sought or questions will be asked; and
(c) specify the address at which the person is to attend; and
(d) specify the day on which and the time at which the person is to attend; and
(e) indicate whether the appearance is to be before the Designated Authority or before a nominated inspector.
Power to examine on oath or affirmation
369.(1) If a person appears before the Designated Authority or a nominated inspector, the Designated Authority or the inspector may administer an oath or affirmation to the person.
(2) The oath or affirmation to be administered is an oath or affirmation that the person will truthfully answer the questions put by the Designated Authority or the inspector.
Designated Authority may ask for documents
370.(1) The Designated Authority may ask a person to give the Designated Authority a document if:
(a) the document is relevant to the operation of this Act; and
(b) the Designated Authority has reasonable grounds for believing that the person is able to give the document.
Note: The person must comply with the request (see section 372).
(2) The Designated Authority may ask the person to give the document to:
(a) the Designated Authority; or
(b) an inspector nominated by the Designated Authority.
(3) The request:
(a) must be made by written notice given to the person; and
(b) must specify the person to whom the document is to be given; and
(c) must specify:
(i) the period within which the document is to be given; or
(ii) specify the day on which and the time and place at which the document is to be given; and
(d) may specify whether the original or a copy of the document is to be given.
(4) The regulations may provide for the manner in which the Designated Authority is to deal with the document.
(5) Without limiting subsection (4), the regulations may authorise the Designated Authority or inspector to take a copy of the document.
Designated Authority may ask for samples
371.(1) The Designated Authority may ask a person to give the Designated Authority a sample taken from the seabed or subsoil in the offshore area if:
(a) the sample is relevant to the operation of this Act; and
(b) the Designated Authority has reasonable grounds for believing that the person is able to give the sample.
Note: The person must comply with the request (see section 372).
(2) The Designated Authority may ask the person to give the sample to:
(a) the Designated Authority; or
(b) an inspector nominated by the Designated Authority.
(3) The request:
(a) must be made by written notice given to the person; and
(b) must specify the person to whom the sample is to be given; and
(c) must specify:
(i) the period within which the sample is to be given; or
(ii) the day on which and the time and place at which the sample is to be given.
(4) The regulations may provide for the manner in which the Designated Authority or inspector is to deal with the sample.
(5) Without limiting subsection (4), the regulations may authorise the Designated Authority or inspector to test or analyse the sample.
Obligation to comply with request under section 367, 368, 370 or 371
372.(1) A person must not, without reasonable excuse, fail to comply with a request under section 367, 368, 370 or 371.
Maximum penalty: 100 penalty units.
(2) A person is not excused from complying with the request on the ground that complying with the request might tend to incriminate the person or make the person liable to a penalty.
Note: Section 373 provides immunity for the response to the request.
(3) A person must not give false or misleading information:
(a) in response to a request under section 367 or 368; or
(b) in response to a question asked under subsection 368(1).
Maximum penalty: 100 penalty units.
Immunity from use of information etc. given in response to request under section 367, 368, 370 or 371
373.(1) If a person gives the Designated Authority information in response to a request under section 367 or 368, the following are not admissible in evidence against the person in any proceedings:
(a) the information given in response to the request;
(b) any information, document or thing obtained as a direct or indirect consequence of the giving of the information.
(2) For the purposes of subsection (1), an answer given in response to a question under paragraph 368(1)(b) is information given in response to a request under section 368.
(3) If a person gives the Designated Authority a document in response to a request under section 370, the following are not admissible in evidence against the person in any proceedings:
(a) the document;
(b) the fact of the production of the document by the person;
(c) any information, document or thing obtained as a direct or indirect consequence of the giving of the document.
(4) If a person gives the Designated Authority a sample in response to a request under section 371, the following are not admissible in evidence against the person in any proceedings:
(a) the sample;
(b) the fact of the production of the sample by the person;
(c) any information, document or thing obtained as a direct or indirect consequence of the giving of the sample.
(5) The immunity provided by subsections (1), (3) and (4) does not apply to proceedings for an offence against subsection 372(3).
Restrictions on release of confidential material
374.(1) Subject to sections 375 and 376, if the Designated Authority holds confidential information:
(a) the Designated Authority; and
(b) a State or Commonwealth Minister who is given the information under section 375; and
(c) a person who is given the information under subsection 376(3); must not:
(d) publish the information; or
(e) make the information available to a person.
Maximum penalty: Imprisonment for 2 years.
(2) Subject to section 375, if the Designated Authority holds a confidential sample:
(a) the Designated Authority; and
(b) a Commonwealth or State Minister who is given access to the sample under section 375; and
(c) a person who is given access to the sample under subsection 375(4);
must not:
(d) allow a person to inspect the sample; or
(e) publish information about the sample.
Maximum penalty: Imprisonment for 2 years.
Circumstances in which confidential material may be released
375.(1) If:
(a) a licence holder gives confidential information to the Designated Authority; and
(b) the holder:
(i) makes the information publicly available; or
(ii) consents in writing to the information being made publicly available;
the Designated Authority or a Commonwealth or State Minister who is given access to the information may make the information available to any person.
(2) If:
(a) a licence holder gives a confidential sample to the Designated Authority; and
(b) the holder:
(i) publishes details of the sample; or
(ii) consents in writing to the details being made publicly available; or
(iii) consents in writing to the sample being made available for public inspection;
the Designated Authority or a Commonwealth or State Minister who is given access to the sample may:
(c) make details of the sample available to any person; or
(d) allow any person to inspect the sample.
Note 1: For “confidential information” and “confidential sample” see sections 27 and 28.
Note 2: A Commonwealth or State Minister may be given access to confidential information or a confidential sample under section 416.
(3) Confidential information may be made available to a person if the information is made available for the purposes of the administration of this Act or an associated revenue Act.
(4) A person may be given access to a confidential sample if the access is given for the purposes of the administration of this Act or an associated revenue Act.
Certain reports to be made available
376. If:
(a) in order to comply with:
(i) the regulations; or
(ii) a compliance direction ; or
(iii) a licence condition;
a licence holder gives the Designated Authority a report; and
(b) the report relates to blocks that are no longer covered by the licence or by a successor licence to the licence; and
(c) another person requests the Designated Authority to make the report available to the person;
the Designated Authority must make the report available to the person.
PART 4.2—MONITORING AND ENFORCEMENT
Division 1—Inspections
Compliance inspections
377. For the purposes of this Act, a compliance inspection is an inspection carried out to determine whether a licence holder, a special purpose consent holder or an associate has complied with or is complying with:
(a) this Act or the regulations; or
(b) an associated revenue Act or regulations made under an associated revenue Act; or
(c) the licence or consent conditions; or
(d) a compliance direction.
Note 1: For “associated revenue Act” see section 4.
Note 2: An inspector may carry out a compliance inspection under:
• section 379 (inspection of licence-related premises etc. without a warrant);
• section 380 (inspection of other premises etc. with consent of the occupier);
• section 381 (inspection of premises etc. with a warrant).
Powers exercisable in course of inspection
378.(1) If an inspector may carry out a compliance inspection, the inspector may do anything that is reasonable and necessary to carry out the inspection.
(2) Without limiting subsection (1), the inspector may:
(a) examine things that are being used in activities carried out under a licence or special purpose consent and things that appear to the inspector to be intended to be used in those activities; and
(b) test equipment (for example, by operating it); and
(c) examine, and copy, documents; and
(d) remove documents; and
(e) take photographs; and
(f) examine, and take samples of, cores or cuttings from the seabed or subsoil; and
(g) enter or go onto any land, building or structure; and
(h) enter or board any vehicle, vessel or aircraft.
(3) If the compliance inspection is being carried out under a warrant under section 382, subsection (2) has effect subject to the restrictions that are specified in the warrant.
(4) Subject to subsections (5) and (6), if an inspector removes a document under paragraph (2)(d), the inspector may retain the document for as long as is necessary and reasonable to determine whether the licence holder, the consent holder or the associate has complied with or is complying with:
(a) this Act and the regulations; or
(b) an associated revenue Act or regulations made under an associated revenue Act; or
(c) the licence or consent conditions; or
(d) a compliance direction.
(5) Subject to subsection (6), the inspector must not retain the document for more than 60 days.
(6) If:
(a) proceedings for an offence against a provision of this Act or the regulations are instituted within that period of 60 days; and
(b) the document may afford evidence of the commission of the offence;
the inspector may retain the document until the proceedings are completed.
(7) For the purposes of subsection (6):
(a) an offence against section 5, 6, 7 or 7A or paragraph 86(1)(a) of the Crimes Act 1914 that relates to a provision of this Act is taken to be an offence against a provision of this Act; and
(b) an offence against section 5, 6, 7 or 7A or paragraph 86(1)(a) of the Crimes Act 1914 that relates to a provision of the regulations is taken to be an offence against a provision of the regulations; and
(c) the proceedings for an offence are taken to include any appeal to a court in relation to those proceedings.
(8) While an inspector is retaining the document under subsection (4), the inspector must allow a person to inspect the document if the person would have a right to inspect the document if it were not in the inspector’s possession.
Inspection of licence-related premises etc. without warrant
379.(1) Subject to subsections (2), (3) and (4), an inspector may, without a warrant, carry out a compliance inspection of:
(a) licence-related land; or
(b) a licence-related building, structure, vehicle, vessel or aircraft;
if the inspection is reasonably necessary.
(2) An inspection under subsection (1) must be made at a reasonable time.
(3) An inspector may not enter premises under subsection (1) if:
(a) the premises are a residence; and
(b) the occupier has not consented to the entry.
(4) An inspector may not carry out a compliance inspection under subsection (1) if:
(a) the person occupying or in charge of the land, building, structure, vehicle, vessel or aircraft concerned asks the inspector to produce the inspector’s identity card for inspection by the person; and
(b) the inspector does not comply with the person’s request.
(5) For the purposes of this section, land or a building, structure, vehicle, vessel or aircraft is licence-related if:
(a) it is used in connection with activities carried out under a licence or special purpose consent; or
(b) records about activities of that kind are kept there.
Inspection of other premises etc. with occupier’s consent
380. An inspector may carry out a compliance inspection of land or a building, structure, vehicle, vessel or aircraft with the consent of the person who occupies or is in charge of the land, building, structure, vehicle, vessel or aircraft.
Inspection of other premises etc. with warrant
381. An inspector may carry out a compliance inspection in accordance with a warrant issued under section 382.
Procedure for obtaining warrant
382.(1) An inspector may apply to a magistrate for a warrant to carry out a compliance inspection of land or of a building, structure, vehicle, vessel or aircraft.
(2) The application must be supported by an information on oath or affirmation that sets out the grounds on which the inspector is applying for the warrant.
(3) If the magistrate is satisfied that the compliance inspection is reasonably necessary, the magistrate may issue a warrant to the inspector to carry out the inspection.
(4) The warrant must state:
(a) the name of the inspector; and
(b) whether the inspection may be carried out at any time or only during specified hours of the day; and
(c) the day on which the warrant ceases to have effect; and
(d) the purposes for which the warrant is issued.
(5) The day specified under paragraph (4)(c) is not to be more than 7 days after the day on which the warrant is issued.
(6) The purposes specified under paragraph (4)(d) must include the identification of:
(a) the land, building, structure, vehicle, vessel or aircraft to be inspected; and
(b) any equipment that the inspector may test; and
(c) any documents that the inspector may examine and copy; and
(d) any cores or cuttings from the seabed or subsoil that the inspector may examine and take samples of.
Warrant authorises reasonable assistance and force
383. If a warrant for a compliance inspection is issued to an inspector under section 382, the warrant authorises the inspector to carry out the inspection:
(a) with such assistance as is reasonable and necessary; and
(b) by such force as is reasonable and necessary.
Occupier to cooperate with inspector
384. If an inspector carries out a compliance inspection of land or of a building, structure, vehicle, vessel or aircraft under section 379 or 381, the person who occupies or is in charge of it must provide the inspector with the facilities and assistance that the inspector reasonably requires for carrying out the inspection.
Maximum penalty: 50 penalty units.
Division 2—Directions
Directions by Designated Authority must be obeyed
385.(1) A person must not fail to comply with a compliance direction.
Maximum penalty: 100 penalty units.
(2) A person must not fail to comply with a supplementary direction given by the Designated Authority under subsection 391(2).
Maximum penalty: 50 penalty units.
Scope of compliance directions
386.(1) A Designated Authority may give a compliance direction if it is necessary or convenient to do so to carry out or give effect to this Act or the regulations.
(2) Without limiting subsection (1), compliance directions may be given in relation to:
(a) the control of offshore exploration or mining activities; and
(b) the conservation and protection of the mineral resources of offshore areas; and
(c) the remedying of:
(i) damage caused to the seabed or subsoil in an offshore area by offshore exploration or mining activities; or
(ii) damage caused by the escape of substances as a result of offshore exploration or mining activities; and
(d) the protection of the environment; and
(e) the keeping of records, cores and samples; and
(f) the giving of records, cores and samples to the Designated Authority for inspection; and
(g) the making of returns.
Note: For “offshore exploration or mining activities” see section 4.
(3) For the purposes of subsection (2), the control of offshore exploration or mining activities extends to the control of:
(a) the construction, maintenance and operation of installations used in or for use in offshore exploration or mining activities; and
(b) the flow or discharge of fluids arising from offshore exploration or mining activities; and
(c) the safety, health and welfare of people working in offshore exploration or mining activities; and
(d) the maintenance of structures, equipment and property used in or for use in offshore exploration or mining activities.
Note: For “offshore exploration or mining activities” see section 4.
Designated Authority may give directions
387.(1) Subject to subsections (2), (3) and (4), the Designated Authority may direct a licence holder or special purpose consent holder to do or not to do the thing specified in the direction.
(2) The direction must be in writing and is given by serving it on the holder.
(3) The Designated Authority must not give a direction of a permanent or standing nature unless the Joint Authority has approved the direction.
(4) Subsection (3) does not apply to the Designated Authority of an external territory offshore area.
Note: The responsible Commonwealth Minister is both the Designated Authority and the Joint Authority for an external territory offshore area.
(5) A failure to comply with subsection (3) does not affect the validity of the direction concerned.
Direction may incorporate material in another document
388.(1) A direction under section 387 may apply, adopt or incorporate a code of practice or a standard that is contained in another document.
(2) The application, adoption or incorporation of the other document may be made with or without modification.
(3) The other document may be one issued outside Australia.
(4) The direction may apply, adopt or modify the other document:
(a) as in force at the time when the direction is given; or
(b) as in force from time to time.
(5) If a direction applies, adopts or incorporates material in another document, a copy of the document must be attached to the direction when it is given to the licence holder or special purpose consent holder.
Direction may impose absolute prohibition
389. Without limiting section 387:
(a) a direction may prohibit absolutely the doing of a thing; and
(b) a direction may prohibit the doing of a thing unless a person’s consent or approval is obtained.
Compliance direction may extend to associates
390.(1) A compliance direction to a licence holder or special purpose consent holder may extend to an associate specified in the direction.
(2) The direction may provide that only particular obligations specified in the direction extend to a particular associate.
Note: An associate may be specified by name or as a member of a class of associates (see subsection 46(2) of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901).
Holder to give notice of direction to associates
391.(1) If a direction under section 387 extends to an associate, the licence holder or special purpose consent holder must either:
(a) give a copy of the direction to the associate; or
(b) display a copy of the direction at a place that the associate goes to in the course of carrying out activities under the licence or consent.
Maximum penalty: 50 penalty units.
(2) The Designated Authority may give the licence holder or special purpose consent holder a supplementary direction that specifies:
(a) the manner in which copies of a direction are to be displayed under paragraph (1)(b); or
(b) the places at which copies of a direction are to be displayed under paragraph (1)(b).
Power to give directions after licence etc. ends
392.(1) If a person is bound by an obligation because of section 131, 191, 266 or 314, the Designated Authority may direct the person to do a thing or not to do a thing specified in the direction.
(2) A direction may be given only for the following purposes:
(a) to ensure that the obligation is complied with;
(b) a purpose that is incidental to the purpose in paragraph (a).
Note: Sections 131, 191, 266 and 314 provide for undischarged obligations to continue to bind a former licence holder or associate after the licence ends.
(3) A direction must be in writing and is given by serving it on the person bound by the obligation.
Effect of a compliance direction on other instruments
393.(1) A later compliance direction overrides an earlier compliance direction if they are inconsistent.
(2) A compliance direction has effect despite anything in:
(a) the regulations; or
(b) a State offshore law that is applied to an offshore area by section 428; or
(c) a licence condition that relates to safety or environmental matters.
Designated Authority may specify time for compliance
394. If the Designated Authority gives compliance direction to a licence holder or special purpose consent holder, the Designated Authority may:
(a) specify in the direction a time for compliance with the direction; or
(b) give the holder a supplementary direction under this section specifying a time for compliance with the direction.
Designated Authority may take action if holder fails to comply
395.(1) The Designated Authority may do all or any of the things required by a compliance direction if:
(a) the time for compliance specified under section 394 has ended; and
(b) the person to whom the direction was given or to whom it extended has not complied with the direction.
(2) The Designated Authority must not take action under subsection (1) without the Joint Authority’s approval if the direction required that approval.
Costs incurred by Designated Authority in taking action under section 395
396.(1) If:
(a) the Designated Authority takes action under section 395 in relation to a compliance direction given to a licence holder or special purpose consent holder; and
(b) the direction does not extend to an associate of the holder;
the costs and expenses incurred by the Designated Authority in taking that action are a debt due to the Commonwealth by the holder.
(2) If:
(a) a compliance direction specifies that a particular associate of a licence holder or special purpose consent holder is subject to a particular obligation; and
(b) the Designated Authority takes action under section 395 in relation to that obligation;
the costs and expenses incurred by the Designated Authority in taking that action are a debt due to the Commonwealth by the holder and the associate.
(3) The associate and the holder are jointly and severally liable to pay the debt arising under subsection (2).
(4) A debt under this section is recoverable in a court of competent jurisdiction.
Defences to actions to recover debts
397.(1) It is a defence to an action to recover the debt from the licence holder or special purpose consent holder if:
(a) the holder produces evidence that the holder took all reasonable steps to comply with the compliance direction; and
(b) the evidence is not rebutted.
(2) It is a defence to an action to recover the debt from the associate if:
(a) the associate produces evidence that the associate did not know of, and could not reasonably be expected to know of, the existence of the compliance direction; and
(b) the evidence is not rebutted.
Division 3—Securities
Securities
398.(1) A person may be required to lodge a security with the Designated Authority under:
(a) section 399 (security as prerequisite for proper acceptance of provisional grant or provisional renewal); or
(b) section 118 (exploration licence conditions), 177 (retention licence conditions), 254 (mining licence conditions) or 304 (works licence conditions).
(2) Securities are required as a way of ensuring compliance with this Act and with licence conditions. Securities may only be used for the purposes laid down in section 400.
Determination of requirement to lodge security
399.(1) The Joint Authority may determine that a person who has been provisionally granted a licence must lodge a security with the Designated Authority.
Note 1: The provisional holder will be given notice of the determination under section 66 or 83 (exploration licence), 147 (retention licence), 210 or 227 (mining licence) or 279 (works licence).
Note 2: If the provisional holder does not lodge the security within a particular time provided for in this Act, the provisional grant will lapse (see section 72 or 86 (exploration licence), 153 (retention licence), 216 or 230 (mining licence) or 285 (works licence)).
(2) If the Joint Authority provisionally renews a licence, the Joint Authority may determine that the licence holder must lodge a security with the Designated Authority.
Note 1: The licence holder will be given notice of the determination under section 110 (exploration licence), 169 (retention licence), 246 (mining licence) or 296 (works licence).
Note 2: If the holder does not lodge the security within a particular time provided for in this Act, the provisional renewal will lapse (see section 116 (exploration licence), 175 (retention licence), 252 (mining licence) or 302 (works licence)).
(3) A determination under subsection (1) or (2) must specify:
(a) the amount of the security required; and
(b) the kind of security required; and
(c) the manner and form in which the security is to be lodged.
(4) Without limiting subsections (1) and (2), a determination may require the lodgment of a security in the form of a guarantee and if a guarantee is required the determination may specify:
(a) the kind of person who is to give the guarantee; and
(b) the terms of the guarantee.
(5) The determination is to be in writing.
(6) If the person is provisionally granted a licence over a tender block, the amount determined as a security under subsection (1) is to be the amount of security referred to in the tender block licence notice.
Application of security
400.(1) If:
(a) a person is a licence holder; and
(b) the person has lodged a security with the Designated Authority;
the Joint Authority may use the security to discharge the person’s obligations arising from a failure to comply with:
(c) this Act; or
(d) the licence conditions; or
(e) a compliance direction.
(2) Without limiting subsection (1), the holder’s financial obligations include the obligation to pay a penalty imposed under the licence conditions.
(3) Subject to subsection (1), the Joint Authority is to deal with a security in accordance with the regulations.
Division 4—Restoration of environment
Removal of property from offshore area
401.(1) The regulations may provide for:
(a) the removal from an offshore area of property that:
(i) has been brought into the offshore area for use in offshore exploration or mining activities; and
(ii) is not being used and is not intended to be used in exploration or mining activities in accordance with a licence; and
(b) the disposal by the Designated Authority of property removed under regulations made for the purposes of paragraph (a); and
(c) the recovery of costs and expenses incurred by the Designated Authority in removing or disposing of property in accordance with regulations made for the purposes of paragraphs (a) and (b).
(2) Regulations made for the purposes of paragraph (1)(a) may provide for removal by the Designated Authority or by someone else.
(3) Regulations made for the purposes of paragraph (1)(c) may provide for the recovery of costs by way of deduction from the proceeds of the disposal.
(4) Subject to the regulations, no action lies in respect of the removal or disposal of property in accordance with the regulations.
(5) In this section:
“property” includes a structure or equipment.
Rehabilitation of damaged areas
402.(1) The regulations may provide for:
(a) the rehabilitation of an area in an offshore area that has been damaged or affected by exploration or mining activities of a licence holder; and
(b) the recovery of costs and expenses incurred by the Designated Authority in rehabilitating an area under regulations made for the purposes of paragraph (a).
(2) Regulations made for the purposes of paragraph (1)(a) may provide for the rehabilitation to be carried out by the Designated Authority or someone else.
(3) Regulations made for the purposes of paragraph (1)(a) may provide for the recovery of costs and expenses by way of deduction from the licence holder’s security.
Division 5—Safety zones
Declaration of safety zone around a structure or equipment
403.(1) The Designated Authority may declare a safety zone around a structure or equipment in an offshore area.
(2) A declaration may only be made for the purpose of protecting the structure or equipment.
(3) The safety zone may extend not more than 500 metres from the outer edge of the structure or equipment.
(4) The declaration is to be made by notice published in the Gazette.
(5) The declaration may apply to:
(a) all vessels; or
(b) all vessels except those specified in the declaration.
Effect of declaration of safety zone
404.(1) If a safety zone is declared around a structure or equipment, a vessel to which the declaration applies is not to enter or remain in the safety zone without the written consent of the Designated Authority.
(2) If:
(a) a safety zone is declared around a structure or equipment; and
(b) the Designated Authority consents to a vessel entering or remaining in the safety zone; and
(c) the consent is given on conditions;
the vessel is to enter or remain in the safety zone only in accordance with the conditions.
(3) The owner of a vessel and the person in command or in charge of a vessel are each guilty of an offence against this section if the vessel enters or remains in a safety zone in contravention of subsection (1) or (2).
Maximum penalty: Imprisonment for 5 years.
(4) It is a defence to a prosecution of a person for an offence against subsection (3) if the person satisfies the court that:
(a) an unforeseen emergency made it necessary for the vessel to enter or remain in the safety zone to attempt to secure the safety of:
(i) a human life; or
(ii) the vessel; or
(iii) another vessel; or
(iv) a well, pipeline, structure or equipment; or
(b) the vessel entered or remained in the safety zone in circumstances beyond the control of the person who was in command or in charge of the vessel (for example, adverse weather).
(5) It is a defence to a prosecution of the owner of a vessel for an offence against subsection (3) if the owner satisfies the court that the owner:
(a) did not aid, abet, counsel or procure the vessel’s entering or remaining in the safety zone; and
(b) was not in any way, directly or indirectly, knowingly concerned in, or party to, the vessel’s entering or remaining in the safety zone.
Division 6—Offences
General regime for criminal offences
405.(1) The following provisions of this Act create offences:
(a) section 38 (exploration or recovery without appropriate authorisation);
(b) section 44 (interference with rights);
(c) sections 123, 183, 259 and 308 (failure to comply with work practice requirements);
(d) sections 124, 184, 261 and 309 (failure to keep records);
(e) sections 125, 185, 262, 310 and 384 (failure to assist inspector);
(f) section 364 (failure to give document relevant to application for approval of a transfer);
(g) section 372 (failure to appear or to provide information, document or samples);
(h) section 374 (failure to keep information etc. confidential);
(i) section 385 (failure to comply with a direction given by Designated Authority);
(j) subsection 391(1) (failure to give associate notice of a direction);
(k) section 404 (failure to comply with safety zone conditions);
(l) section 423 (failure to return an inspector identity card).
Note: See section 11.
(2) The Crimes Act 1914 contains provisions that are relevant to the operation of this Act.
Note 1: See sections 4AA, 4AB and 4B of the Crimes Act 1914 for further details on penalties. Section 4AA provides for the amount of a “penalty unit”.
Note 2: See section 29B of the Crimes Act 1914 for a general offence of making untrue representations with a view to obtaining a benefit or advantage. This is relevant to statements made in applications under this Act and statements made in documents that are relevant to the calculation of fees (for example, fees payable under the Registration Fees Act for transfers and other dealings).
Note 3: See section 70 of the Crimes Act 1914 for a general offence of unauthorised disclosure of information by a “Commonwealth officer”. Inspectors under this Act are “Commonwealth officers” for the purposes of this offence (see subsection 3(1) of the Crimes Act 1914).
Note 4: See section 72 of the Crimes Act 1914 for a general offence of falsification of books and records by “Commonwealth officers”. This offence is relevant to the offshore mining registers.
Note 5: See also the following provisions of the Crimes Act 1914:
• section 4J (when indictable offences can be dealt with summarily);
• section 4K (continuing offences);
• section 15B (time for bringing prosecutions);
• section 35 (giving false testimony);
• section 76 (obstructing a public officer—relevant to inspectors).
Note 6: The Proceeds of Crimes Act 1987 provides for pecuniary penalties and forfeiture orders.
PART 4.3—REVIEW OF DECISIONS MADE ABOUT THE
OFFSHORE AREAS OF EXTERNAL TERRITORIES
Definitions
406. In this Part:
“application period” means:
(a) the period of 30 days from the day on which the applicant is given notice of the decision; or
(b) if the Designated Authority extends the application period under subsection 407(3)—the extended period;
“decision” has the same meaning as it has in the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975;
Note: Under subsection 3(2) of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975:
“decision” includes:
• making, suspending, revoking or refusing to make an order or determination;
• making, suspending, revoking or refusing to give a certificate, direction, approval, consent or permission;
• imposing a condition;
• making a demand or requirement;
• refusing to return an article;
• doing or refusing to do any other act;
• not doing an act within the specified time.
“Designated Authority” means the responsible Commonwealth Minister acting as Designated Authority for an external territory offshore area;
“reviewable decision” means a decision made by the Designated Authority (including a decision made under subsection 407(3));
“reviewable delegated decision” means a decision made by a delegate of the Designated Authority under section 419.
Review of delegated decisions
407.(1) A person whose interests are affected by a reviewable delegated decision may apply to the Designated Authority for reconsideration of the decision.
(2) An application under subsection (1) must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) be given to the Designated Authority before the end of the application period; and
(c) set out the applicant’s reasons for seeking a review of the decision.
(3) The Designated Authority may extend the application period if the applicant asks for an extension before the end of the period.
(4) The Designated Authority must reconsider a reviewable delegated decision as soon as possible after receiving an application under subsection (1).
(5) The Designated Authority may:
(a) confirm the reviewable delegated decision; or
(b) revoke the decision; or
(c) revoke the decision and make a new decision instead of the revoked decision.
(6) The Designated Authority must give the applicant a written notice that informs the applicant:
(a) of the outcome of the reconsideration; and
(b) that the applicant may apply to the Administrative Appeals Tribunal for review of the reconsideration; and
(c) that the applicant may request a statement of reasons in relation to the reconsideration under section 28 of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975.
(7) If an applicant is not given notice of the result of the reconsideration within 60 days after the day on which the applicant lodged the application, the Designated Authority is taken to have confirmed the reviewable delegated decision.
(8) Failure to comply with the requirements of subsection (6) in relation to a reviewable delegated decision does not affect the validity of the decision.
(9) A person whose interests are affected by a reviewable decision may apply to the Administrative Appeals Tribunal for review of the decision.
PART 4.4—PROCEDURES OF JOINT AUTHORITIES AND
DESIGNATED AUTHORITIES
Procedure of Joint Authority
408. A Joint Authority may conduct its business:
(a) at meetings of the Authority; or
(b) by written or other communication between the members of the Authority.
Decision-making
409.(1) This section applies to decisions to be made by a Joint Authority on matters that are within the Authority’s functions.
(2) If the responsible Commonwealth Minister and the responsible State Minister disagree about a decision, the responsible Commonwealth Minister may decide the matter and the responsible Commonwealth Minister’s decision has effect as the Authority’s decision.
(3) If:
(a) the responsible Commonwealth Minister gives the responsible State Minister written notice of a decision that the responsible Commonwealth Minister thinks should be made on a matter; and
(b) the responsible State Minister has not told the responsible Commonwealth Minister what decision the responsible State Minister thinks should be made within 30 days after the notice is given;
the responsible Commonwealth Minister may decide the matter and his or her decision has effect as the Authority’s decision.
Opinion or state of mind of Joint Authority
410. For the purposes of this Act, the opinion or state of mind of the Joint Authority is:
(a) if the responsible Commonwealth Minister and the responsible State Minister agree on the matter concerned—the opinion or state of mind of the 2 Ministers; or
(b) if the 2 Ministers do not agree—the opinion or state of mind of the responsible Commonwealth Minister.
Records of proceedings of Joint Authority
411.(1) The Designated Authority is to keep written records of the decisions of the Joint Authority.
(2) A record kept under subsection (1) is evidence that the decision was duly made as recorded if the record is signed by a person who was a member of the Joint Authority at the time when the decision was made.
Signing of documents
412.(1) If a document is signed by the Designated Authority on behalf of the Joint Authority, the document is taken to have been duly executed by the Joint Authority.
(2) The document is taken to be in accordance with a decision of the Joint Authority unless the contrary is proved.
Communications with Joint Authority
413. All communications to or by the Joint Authority are to be made through the Designated Authority.
Ministerial colleague acting on behalf of responsible Commonwealth Minister
414. Another Commonwealth Minister may act for and on behalf of the responsible Commonwealth Minister for the purposes of this Act.
Acting responsible Commonwealth Minister
415.(1) The functions and powers of the responsible Commonwealth Minister under this Act may be performed and exercised by another Commonwealth Minister acting for and on behalf of the responsible Commonwealth Minister.
(2) The functions and powers referred to in subsection (1) include functions and powers that the responsible Commonwealth Minister has as a member of a Joint Authority.
Circumstances in which confidential material released
416.(1) If:
(a) the Designated Authority holds confidential information or a confidential sample; and
(b) the responsible Commonwealth Minister seeks access to the information or sample;
the Designated Authority must make the information or sample available to the Minister.
Note: This subsection cannot apply to the Designated Authority of an external territory offshore area because the responsible Commonwealth Minister is the Designated Authority.
(2) If:
(a) the Designated Authority holds any document:
(i) associated with confidential information or a confidential sample; and
(ii) received or issued by the Designated Authority for the purposes of this Act; and
(b) the responsible Commonwealth Minister seeks access to the document;
the Designated Authority must make the document available to the Minister.
Note: This subsection cannot apply to the Designated Authority of an external territory offshore area because the responsible Commonwealth Minister is the Designated Authority.
(3) If:
(a) the Designated Authority holds any document:
(i) associated with confidential information or a confidential sample; and
(ii) that is a copy of a notice or direction issued by the Designated Authority for the purposes of this Act; and
(b) the responsible Commonwealth Minister seeks access to the document;
the Designated Authority must make the document available to the Minister.
Note: This subsection cannot apply to the Designated Authority of an external territory offshore area because the responsible Commonwealth Minister is the Designated Authority.
(4) The Designated Authority may make confidential information or a confidential sample held by the Designated Authority available to:
(a) a State Minister; or
(b) a Commonwealth Minister.
Note: For “confidential information” and “confidential sample” see sections 27 and 28.
Execution and issue of documents on behalf of Joint Authority
417.(1) If this Act requires or allows a Joint Authority to execute or issue a document, the Designated Authority is to execute or issue the document.
(2) For the purposes of any proceedings, a document that purports to be executed or issued by the Designated Authority is taken to have been executed or issued in accordance with a decision of the Joint Authority unless the contrary is proved.
Service of notices on behalf of Joint Authority
418.(1) If this Act requires or allows a Joint Authority to:
(a) give a notice; or
(b) communicate a matter;
the Designated Authority is to give the notice or communicate the matter.
(2) For the purposes of any proceedings, a notice that purports to be given by the Designated Authority is taken to have been given in accordance with a decision of the Joint Authority unless the contrary is proved.
(3) For the purposes of any proceedings, a communication that purports to be made by the Designated Authority is taken to have been made in accordance with a decision of the Joint Authority unless the contrary is proved.
Delegation by Designated Authority
419.(1) A Designated Authority may by signed instrument delegate to a person all or any of the powers or functions of the Designated Authority under:
(a) this Act; or
(b) an associated revenue Act; or
(c) regulations made under this Act.
Note 1: See also section 34AB of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Note 2: For “associated revenue Act” see section 4.
(2) A delegation under this section may be made to the person who holds, or performs the duties of, a specified office under the Commonwealth or a State.
(3) If a Designated Authority delegates a power or function under this section, the delegation continues in force despite:
(a) a vacancy in the office of Designated Authority; or
(b) a change in the identity of the holder of the office of Designated Authority.
(4) Despite subsection (3), a delegation under this section may be revoked by a Designated Authority.
(5) A copy of each instrument making, varying or revoking a delegation under this section must be published in the Gazette.
Application of this Part to external territories
420.Sections 408, 409, 410, 411, 412, 413, 417 and 418 do not apply to the Joint Authority for an external territory.
PART 4.5—INSPECTORS
Appointment of inspectors
421.(1) The Joint Authority may appoint inspectors for the purposes of this Act and the regulations.
Note: Inspectors have powers under sections 367, 368, 369, 370, 371, 378, 379, 380 and 381.
(2) The appointment must be in writing.
Identity cards
422.(1) The Designated Authority must issue an inspector with an identity card.
(2) The card must:
(a) contain a recent photograph of the inspector; and
(b) be in the form approved by the Designated Authority.
Return of identity card
423.(1) A person who stops being an inspector must return his or her identity card to the Designated Authority as soon as practicable.
(2) A person must not contravene subsection (1) without reasonable excuse.
Maximum penalty: One penalty unit.
PART 4.6—FINANCE
Fees received on behalf of the Commonwealth
424.Money received by the Designated Authority as fees payable under this Act is taken to be received by the Designated Authority on behalf of the Commonwealth.
Payments by the Commonwealth to the States—Royalty Act payments
425.(1) The Commonwealth must pay to each State 60% of royalties payable under the Royalty Act in respect of minerals in the Commonwealth-State offshore area for that State.
(2) Payments under subsection (1) are to be made not later than the end of the month that follows the month in which the royalties concerned were received by the Commonwealth.
(3) In this section:
“royalty” includes any penalty for late payment of royalty.
Payments by the Commonwealth to the States—other payments
426.(1) The Commonwealth must pay each State amounts equal to all money that is payable to the Designated Authority for the Commonwealth-State offshore area for that State on behalf of the Commonwealth:
(a) under this Act; or
(b) under an associated revenue Act other than the Royalty Act.
Note: For “associated revenue Act” see section 4.
(2) Payments under subsection (1) are to be made in accordance with arrangements approved by the responsible Commonwealth Minister.
Appropriation
427. The Consolidated Revenue Fund is appropriated to the extent necessary for the purposes of sections 425 and 426.
CHAPTER 5—MISCELLANEOUS
PART 5.1—APPLICATION OF LAWS
State’s or external territory’s offshore laws apply to mineral exploration and recovery in offshore area
428.(1) The laws in force in a State apply to offshore exploration and mining activities in the Commonwealth-State offshore area for that State.
(2) An external territory’s laws apply to offshore exploration and mining activities in the external territory offshore area for that territory.
(3) Subsections (1) and (2) apply subject to:
(a) sections 429 to 434 (inclusive); and
(b) regulations made for the purposes of subsection (5).
(4) For the purposes of subsections (1) and (2):
(a) an external territory’s laws are the laws (other than laws of the Commonwealth) that are in force in the external territory; and
(b) laws include unwritten laws (the common law); and
(c) laws include instruments that have effect under laws as defined in paragraphs (a) and (b).
(5) The regulations may provide that a law:
(a) does not apply under subsection (1) in an offshore area; or
(b) applies under subsection (1) in an offshore area with the modifications that are specified in the regulations.
(6) For the purposes of subsection (5), “modifications” includes additions, omissions and substitutions.
(7) For the purposes of this section, “offshore exploration and mining activities” includes all acts, omissions, matters, circumstances and things that arise out of or are otherwise connected with those activities.
Criminal laws not applied
429.(1) Section 428 does not apply to laws that are criminal laws within the meaning of the Crimes at Sea Act 1979.
(2) Subsection (1) does not detract from the operation of the Crimes at Sea Act 1979.
Laws inconsistent with Commonwealth laws not applied
430. Section 428 does not apply to a law to the extent that the law would be inconsistent with a law of the Commonwealth.
Tax laws not applied
431. Section 428 does not apply to a law that imposes a tax.
Applied laws not to confer Commonwealth judicial power
432. Section 428 does not apply to a State law to the extent to which it would confer judicial power of the Commonwealth on a court, tribunal, authority or officer of a State or external territory.
Applied laws not to contravene constitutional restrictions on conferring powers on courts
433. Section 428 does not apply to a State law to the extent that it would confer on a State court a power that cannot, under the Constitution, be conferred by the Parliament on such a court.
Applied laws not to appropriate Territory Consolidated Revenue Fund
434. Section 428 does not apply to a law of an external territory so as to appropriate the public moneys of the territory.
Jurisdiction of State courts
435.(1) Subject to subsections (2) and (4), a State’s courts are invested with federal jurisdiction in all matters arising under the laws of the State applied under section 428.
(2) Jurisdiction is invested under subsection (1) within the limits (other than limits of locality) of the jurisdiction of the court.
(3) Subsection (2) applies to limits as to subject matter or other limits.
(4) The regulations may provide that subsection (1) does not apply to the jurisdiction of a particular court.
(5) For the purposes of this section, the Northern Territory is not to be treated as though it were a State.
Jurisdiction of Territory courts
436.(1) Jurisdiction is conferred on the courts that have jurisdiction in a Territory in all matters arising under the laws of the Territory applied under section 428.
(2) Jurisdiction is conferred under subsection (1) within the limits (other than limits of locality) of the jurisdiction of the court.
(3) Subsection (2) applies to limits as to subject matter or other limits.
(4) For the purposes of this section, the Territories are:
(a) the Northern Territory; and
(b) the external territories to which this Act extends under section 36.
Validation of certain actions
437.If:
(a) a person or a court does an act in the purported exercise of a power or performance of a function under State or external territory law; and
(b) the act could have been done by the person or court in the exercise of a power or performance of a function under the State or territory laws applied under section 428;
the act is taken to have been done in the exercise of the power or function under the applied law.
PART 5.2—MISCELLANEOUS
Service of documents on licence holders etc.
438.(1) A document that is to be given to a licence holder may be given to the holder by posting it to the address that is the holder’s registered address for service.
Note: See section 333 for registration of an address for service.
(2) A document that is to be given to an applicant for a licence may be given to the applicant by posting it to the address that the applicant specified in the applicant’s application for the licence.
Vesting jurisdiction in State courts
439.(1) Subject to subsection (4), the several courts of a State are invested with federal jurisdiction with respect to matters arising under:
(a) this Act; and
(b) the associated revenue Acts; and
(c) the regulations.
(2) Subject to subsection (4), jurisdiction is conferred on the several courts of a Territory with respect to matters arising under:
(a) this Act; and
(b) the associated revenue Acts; and
(c) the regulations.
Note: For “associated revenue Act” see section 4.
(3) Subsections (1) and (2) do not apply to matters that arise under the provisions that are applied under Part 5.1.
(4) Jurisdiction is invested or conferred under subsection (1) or (2) within the limits (other than limits of locality) of the jurisdiction of the court.
(5) Subsection (4) applies to limits as to subject matter or other limits.
(6) For the purposes of this section:
(a) the Northern Territory is not to be treated as though it were a State; and
(b) the Territories are:
(i) the Northern Territory; and
(ii) the external territories to which this Act extends under section 36.
Regulations
440.(1) The Governor-General may make regulations prescribing all matters:
(a) required or permitted by this Act to be prescribed; or
(b) necessary or convenient to be prescribed for carrying out or giving effect to this Act.
(2) Without limiting subsection (1), the regulations may provide for:
(a) the control of offshore exploration and mining activities; and
(b) procedures for giving notice to people whose interests might be affected by the grant of a licence; and
(c) the conservation and protection of the mineral resources of offshore areas; and
(d) the remedying of:
(i) damage caused to the seabed or subsoil in an offshore area by offshore exploration and mining activities; or
(ii) damage caused by the escape of substances as a result of offshore exploration and mining activities; and
(e) the protection of the environment; and
(f) the keeping of records, cores or samples; and
(g) the giving of records, cores or samples to a Designated Authority for inspection; and
(h) the making of returns; and
(i) the imposition and recovery of fees in respect of access to reports under section 376.
Note: For “offshore exploration or mining activities” see section 4.
(3) For the purposes of subsection (2), the control of offshore exploration and mining activities extends to the control of:
(a) the construction, maintenance and operation of installations used in or for use in offshore exploration and mining activities; and
(b) the flow or discharge of fluids arising from offshore exploration and mining activities; and
(c) the safety, health and welfare of people working in offshore exploration and mining activities; and
(d) the maintenance of structures, equipment and property used in or for use in offshore exploration and mining activities.
Note: For “offshore exploration or mining activities” see section 4.
(4) For the purposes of paragraph (2)(b), interests that might be affected by the grant of a licence include native title rights and interests that might be affected by the grant of the licence.
(5) The regulations may provide for offences against the regulations.
(6) The penalties imposed in respect of offences against the regulations are not to exceed:
(a) a fine of 10 penalty units; or
(b) a fine of 10 penalty units for each day on which the offence is taken to continue.
(7) In this section:
“control” includes restrict.
SCHEDULE 1
SAVINGS AND TRANSITIONAL PROVISIONS
PART 1—GENERAL
Correspondence of permits etc. under 1981 Act and licences under this Act
1. For the purposes of this Schedule:
(a) an exploration permit under the 1981 Act and an exploration licence under this Act correspond to each other; and
(b) a production licence under the 1981 Act and a mining licence under this Act correspond to each other; and
(c) a works authority under the 1981 Act and a works licence under this Act correspond to each other; and
(d) an instrument of consent under section 74 of the 1981 Act and a special purpose consent under this Act correspond to each other.
Correspondence of provisions
2.(1) If one provision of the 1981 Act and one provision of this Act have the same legal effect, the 2 provisions correspond to each other.
(2) If:
(a) one provision of the 1981 Act has a particular legal effect in relation to a number of permit types; and
(b) a provision of this Act has that legal effect in relation to one only of those permit types;
the 2 provisions correspond to each other for the purposes of applying this Schedule to that permit type.
(3) In this clause:
“legal effect” includes conferring the power to issue a document;
“permit type” means:
(a) in relation to the 1981 Act:
(i) an exploration permit; or
(ii) a production licence; or
(iii) a works authority; or
(iv) an instrument of consent under section 74 of that Act; and
(b) in relation to this Act:
(i) a retention licence; or
(ii) an exploration licence; or
SCHEDULE 1—continued
(iii) a mining licence; or
(iv) a works licence; or
(v) a special purpose consent.
References in documents to provisions of the 1981 Act
3. A reference in a document to a provision of the 1981 Act is to be construed as a reference to the corresponding provision of this Act.
PART 2—SAVINGS AND TRANSITIONAL PROVISIONSAPPLICABLE ON THE TRANSITION FROM THE MINERALS (SUBMERGED LANDS) ACT 1981 TO THIS ACT
Instruments in force under the 1981 Act on the commencement of this Act
4.(1) An instrument that was in force under a provision of the 1981 Act immediately before the commencement of this Act has effect, from that commencement, as if it were an instrument made under the corresponding provision of this Act.
(2) Without limiting subsection (1), the instrument may be:
(a) a determination; or
(b) a direction; or
(c) an approval; or
(d) a notice; or
(e) a declaration.
(3) Subsection (1) does not apply to a delegation under section 20 of the 1981 Act.
(4) If an instrument to which subsection (1) applies was, when made, to have effect only for a limited period, the instrument has effect under subsection (1) only for so much of the period as had not already expired before the commencement of this Act.
Regulations under the 1981 Act
5.(1) Subject to subsection (3), any regulations made under the 1981 Act and in force immediately before the commencement of this Act continue in force as if they were made under this Act.
(2) A reference in a regulation so continued in force to a provision of the 1981 Act is taken to be a reference to the corresponding provision of this Act.
(3) This section does not apply to a regulation the making of which would not be authorised by this Act.
SCHEDULE 1—continued
Saving of application for permit etc. under the 1981 Act
6.(1) If:
(a) a person applied for an exploration permit under the 1981 Act before the commencement of this Act; and
(b) the application is not determined before that commencement;
the application has effect from that commencement as if it were an application for an exploration licence under this Act.
(2) If:
(a) a person applied for a production licence under the 1981 Act before the commencement of this Act; and
(b) the application is not determined before that commencement;
the application has effect from that commencement as if it were an application for a mining licence under this Act.
(3) If:
(a) a person applied for a works authority under the 1981 Act before the commencement of this Act; and
(b) the application is not determined before that commencement;
the application has effect from that commencement as if it were an application for a works licence under this Act.
(4) If:
(a) a person applied for a consent under section 74 of the 1981 Act before the commencement of this Act; and
(b) the application is not determined before that commencement;
the application has effect from that commencement as if it were an application for a special purpose consent under this Act.
Saving of exploration permits
7.(1) An exploration permit that was in force under the 1981 Act immediately before the commencement of this Act has effect from that commencement as if it were an exploration licence in force under this Act.
(2) If subsection (1) applies to an exploration licence:
(a) the licence remains in force for a period of 2 years commencing on the day on which the licence is granted; and
(b) section 104 of this Act does not apply to the licence.
(3) If:
(a) subsection (1) applies to an exploration licence; and
(b) the licence holder applies to renew the licence;
SCHEDULE 1—continued
the holder must surrender on each surrender day of the licence:
(c) 75% of the number of blocks in the licence area; or
(d) if 75% of that number is a whole number and a fraction—the next higher whole number.
Saving of instruments under the 1981 Act
8. If an instrument:
(a) is an instrument of a kind referred to in column 2 of the following Table; and
(b) was in force immediately before the commencement of this Act;
then the instrument continues in force immediately after that commencement as if, at the time it had been made, it had been made in the same terms as an instrument of the kind referred to in the corresponding item in column 3 of the Table:
TABLE |
Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
Item | Instrument made under the Minerals (Submerged Lands) Act 1981 | Instrument made under this Act |
1. | Declaration under section 22 of a reserved block. | Declaration under section 18 of a reserved block. |
2. | Direction under section 65. | Direction under section 387. |
3. | Prohibition under section 76. | Declaration under section 403. |
4. | Direction under section 78. | Directions under sections 368, 370, 371 and 387. |
5. | Appointment of person under subsection 80(1) to be an inspector. | Appointment of person under section 421 to be an inspector. |
6. | Certificate under subsection 80(2). | Identity card under section 422. |
7. | Request under section 82. | Request under section 367. |
SCHEDULE 2
MAP OF THE COMMONWEA

Section 13
ATE OFFSHORE AREAS
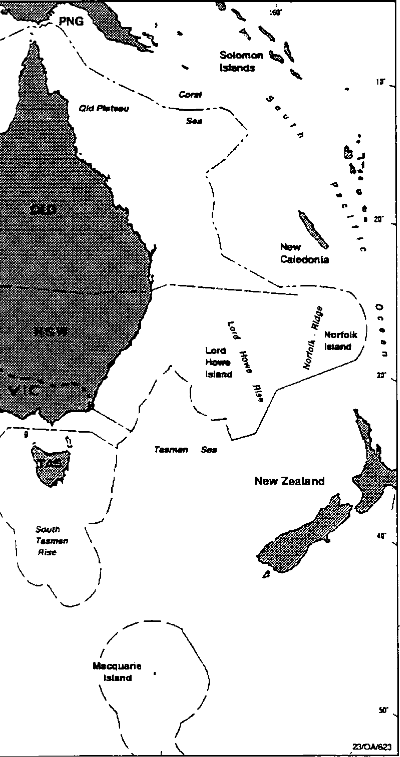
[Minister’s second reading speech made in—
House of Representatives on 16 December 1993
Senate on 8 February 1994]

![]()






