An Act to make arrangements in relation to fuel security, and for related purposes
Part 1—Preliminary
1 Short title
This Act is the Fuel Security Act 2021.
2 Commencement
(1) Each provision of this Act specified in column 1 of the table commences, or is taken to have commenced, in accordance with column 2 of the table. Any other statement in column 2 has effect according to its terms.
Commencement information |
Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
Provisions | Commencement | Date/Details |
1. The whole of this Act | The day after this Act receives the Royal Assent. | 30 June 2021 |
Note: This table relates only to the provisions of this Act as originally enacted. It will not be amended to deal with any later amendments of this Act.
(2) Any information in column 3 of the table is not part of this Act. Information may be inserted in this column, or information in it may be edited, in any published version of this Act.
3 Objects
(1) The objects of this Act are the following:
(a) to improve security and confidence in Australia’s fuel supplies;
(b) to support sovereign capability to maintain fuel supplies;
(c) to contribute to meeting Australia’s obligations under the International Energy Agreement;
(d) to assist in preventing disruptions in fuel supplies.
(2) The objects are to be achieved by:
(a) requiring the holding of minimum quantities of stocks of certain fuels in Australia; and
(b) making payments for production of refined fuels to support the contribution made by refineries in Australia to the security of Australia’s fuel supplies.
4 Simplified outline of this Act
This Act contains 2 measures designed to improve fuel security:
(a) the minimum stockholding obligation; and
(b) a bounty called fuel security services payment.
Entities that undertake certain activities (broadly, refining or importing certain fuels) may become subject to the minimum stockholding obligation. This is an obligation for an entity to hold a minimum quantity of stocks of those fuels.
Refiners of certain fuels may, on application to the Minister, become entitled to fuel security services payment. This is a quarterly payment based on the quantity of those fuels refined in the quarter. Recipients commit to repaying the payment if the refinery ceases refining FSSP fuels before the end of a specified period.
advice window: see subsection 16(4).
affected entity, in relation to an audit under Division 7 of Part 2, means each of the following:
(a) the entity that is to be, or is being, audited;
(b) if that entity has an Australian controlling corporation—the Australian controlling corporation;
(c) any entity in possession of stocks of an MSO product that are held (within the meaning of Division 5 of Part 2):
(i) by the entity that is to be, or is being, audited; or
(ii) if the entity that is to be, or is being, audited is the Australian controlling corporation of a subsidiary that is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation—by the subsidiary.
approved form, in relation to a provision, means the form approved by the Secretary for that provision under section 81.
audit team leader means a registered greenhouse and energy auditor appointed under section 33 or 34.
audit team member, in relation to an audit, means a person assisting the audit team leader to carry out the audit.
Australia, when used in a geographical sense, does not include the external Territories.
Australian controlling corporation: see paragraph 8(2)(a).
Australian port means a port in Australia.
civil penalty provision has the same meaning as in the Regulatory Powers Act.
commitment period of a person, in relation to a committed refinery, means the period specified in:
(a) the notice given to the person in relation to the refinery under subsection 40(3); or
(b) if the person has been given a notice in relation to the refinery under subsection 41(3)—the most recent such notice.
committed refinery: see paragraph 40(3)(a).
constitutional corporation means a corporation to which paragraph 51(xx) of the Constitution applies.
designated: a quantity of stocks of an MSO product is designated for an entity on an obligation day in accordance with section 13.
feedstock: see subsection 25(3).
FSSP is short for fuel security services payment.
FSSP fuel means any of the following fuels that also meets any requirements prescribed by the rules for the fuel:
(a) gasoline;
(b) diesel;
(c) kerosene;
(d) a covered product within the meaning of the Petroleum and Other Fuels Reporting Act 2017 that is prescribed by the rules for the purposes of this paragraph.
hold: see section 19.
import: an entity imports an MSO product that was produced overseas if the entity:
(a) does an act that constitutes the importation of the product into Australia for home consumption; or
(b) does another act related to the importation of the product into Australia prescribed by the rules.
International Energy Agreement means the Agreement on an International Energy Program done at Paris on 18 November 1974, as in force for Australia from time to time.
Note: The Agreement is in Australian Treaty Series 1979 No. 7 ([1979] ATS 7) and could in 2021 be viewed in the Australian Treaties Library on the AustLII website (http://www.austlii.edu.au).
margin: see subsection 43(6).
MSO is short for minimum stockholding obligation.
Note: Section 7 sets out the substance of the minimum stockholding obligation.
MSO activity, in relation to an MSO product, means:
(a) refining the product; or
(b) importing the product; or
(c) a covered activity within the meaning of the Petroleum and Other Fuels Reporting Act 2017 that is prescribed by the rules for the purposes of this paragraph in relation to the product.
MSO product means any of the following products that also meets any requirements prescribed by the rules for the product:
(d) a covered product within the meaning of the Petroleum and Other Fuels Reporting Act 2017 that is prescribed by the rules for the purposes of this paragraph.
notice window: see subsection 15(5).
obligation day means a day prescribed by the rules.
offence against this Act includes an offence against Chapter 7 of the Criminal Code that relates to this Act.
quarter means a period of 3 months ending on 31 March, 30 June, 30 September or 31 December.
registered greenhouse and energy auditor means an individual who is registered in the register of greenhouse and energy auditors kept under section 75A of the National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting Act 2007.
regulated entity means:
(a) a constitutional corporation; or
(b) a trust, all of the trustees of which are constitutional corporations; or
(c) a body corporate that is incorporated in a Territory; or
(d) a body corporate that is taken to be registered in a Territory under section 119A of the Corporations Act 2001; or
(e) a trust, if the proper law of the trust and the law of the trust’s administration are the law of a Territory; or
(f) an entity, the core or routine activities of which are carried out in or in connection with a Territory.
Regulatory Powers Act means the Regulatory Powers (Standard Provisions) Act 2014.
responsible person: see subsections 72(1) and (2).
reviewable decision: see subsections 72(1) and (2).
rules means rules made under section 84.
Secretary means the Secretary of the Department.
stored in Australia: see section 21.
subject to the minimum stockholding obligation: see section 9.
subsidiary has the meaning given by section 46 of the Corporations Act 2001.
temporary reduction period: see subsection 18(3).
Division 1—Introduction to this Part
If a regulated entity undertakes an MSO activity in relation to an MSO product (broadly, if the entity refines or imports certain fuels), the entity may become subject to the minimum stockholding obligation. This is an obligation for the entity to hold a minimum quantity of stocks of the MSO product.
If the entity has an Australian controlling corporation, that corporation must also ensure that the entity meets the minimum stockholding obligation.
The Secretary will trigger the obligation if the entity’s activity in relation to the product exceeds a threshold prescribed by the rules.
Once triggered, the entity generally continues to be subject to the obligation until the Secretary is satisfied that it has ceased to undertake all MSO activities in relation to the product.
An entity that undertakes an MSO activity in relation to more than one MSO product may be subject to the minimum stockholding obligation for each product.
The rules may prescribe cases where an entity is exempt from the obligation. The requirement to meet the obligation may also be suspended in some circumstances.
The Secretary notifies entities from time to time of the quantity of stocks of the MSO product they are required to hold. The Secretary determines the quantity in accordance with the rules.
The rules in turn must provide for quantities to be determined by reference to a target number of days decided by the Minister. In deciding the target, the Minister must have regard to the emergency reserve commitment within the meaning of Article 2 of the International Energy Agreement (among other matters). Entities must advise the Secretary in relation to their quantity, and may apply to the Secretary for their quantity to be temporarily reduced.
An entity will be treated as holding stocks of an MSO product in defined circumstances. Generally, stocks must be in Australia, but entities do not necessarily need to own or have direct custody of them.
A range of enforcement mechanisms are available to the Secretary if entities do not meet the obligation, including civil penalties and injunctions.
Division 2—Minimum stockholding obligation
An entity that is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product on an obligation day must hold at least the quantity of stocks of the product designated for the entity on that day.
Civil penalty: The number of penalty units worked out in accordance with subsection 64(1).
8 Additional responsibility of Australian controlling corporation
(1) If an entity that is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product on an obligation day has an Australian controlling corporation, the Australian controlling corporation must ensure that the entity complies with section 7 in relation to the product on the obligation day.
Civil penalty: The number of penalty units worked out in accordance with subsection 64(2).
(2) An entity has an Australian controlling corporation if:
(a) the entity is a subsidiary of a corporation (the Australian controlling corporation of the entity) that is:
(i) a constitutional corporation incorporated in Australia; and
(ii) not a subsidiary of another body corporate incorporated in Australia; and
(b) the entity is not a subsidiary of another body corporate that:
(i) meets the requirement in subparagraph 46(a)(i) or (ii) of the Corporations Act 2001 in relation to the entity; and
(ii) is not a subsidiary of the Australian controlling corporation.
Note: Subsidiary has the meaning given by section 46 of the Corporations Act 2001 (see section 5 of this Act).
Division 3—Entities subject to the minimum stockholding obligation
Main case
(1) An entity is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product if:
(a) the minimum stockholding obligation has been triggered for the entity in relation to the product under section 10; and
(b) the entity has not ceased to be subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to the product under section 11.
Obligation assumed or divided
(2) An entity is also subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product if:
(a) a determination is made under section 37 that:
(i) the entity has assumed another entity’s minimum stockholding obligation in relation to the product; or
(ii) another entity’s minimum stockholding obligation in relation to the product has been divided with the entity; and
(b) the entity has not ceased to be subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to the product under section 11.
10 Triggering the minimum stockholding obligation
(1) The Secretary may, by written notice given to an entity, trigger the minimum stockholding obligation for the entity in relation to an MSO product if:
(a) the entity is a regulated entity; and
(b) in a period prescribed by the rules:
(i) the entity undertakes an MSO activity in relation to the product; and
(ii) in doing so the entity exceeds the volume prescribed by the rules (in megalitres) for undertaking the activity in relation to the product.
Note: A decision to trigger the obligation is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
(2) The notice must specify the quantity (in megalitres) of stocks of the product the entity must hold on the obligation days for which the notice is in force.
Note: A decision to specify a particular quantity of the product is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
(3) The Secretary must determine the quantity in accordance with the rules.
Note: See also subsection 14(4).
(4) The notice is in force for obligation days that occur in the period:
(a) starting on the day specified in the notice as the day the notice comes into force (which must not be earlier than the day the notice is given); and
(b) ending on the day before another notice given to the entity in relation to the product under section 15 comes into force.
Note: A notice under this section ceases to be in force during any temporary reduction period for the entity in relation to the product, and comes back into force when that period ends (see subsections 18(3) and (4)).
Main case
(1) An entity ceases to be subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product if the Secretary is satisfied under subsection 32(1) that the entity has permanently or indefinitely ceased undertaking all MSO activities in relation to the product.
Obligation assumed
(2) An entity ceases to be subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product if a determination is made under section 37 that another entity has assumed the entity’s minimum stockholding obligation in relation to the product.
Despite section 9, an entity is not subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product if, under the rules, the entity is exempt in relation to the product.
Division 4—Designated quantity of MSO product
13 Designated quantity of MSO product
Main case
(1) For the purposes of section 7, the quantity of stocks of an MSO product designated for an entity on an obligation day is the quantity specified in the notice in force for the obligation day that was given to the entity in relation to the product under section 10, 15 or 18.
Obligation assumed or divided
(2) The quantity of stocks of a product for an entity under subsection (1) is increased or decreased in accordance with the effect specified in any determination made under section 37.
(3) The reference in subsection (1) to a notice given to an entity in relation to a product under section 10, 15 or 18 includes a reference to a notice taken to have been given to the entity in accordance with a determination made under section 37.
(1) The Minister must, by notifiable instrument, declare a target number of days for the purposes of the minimum stockholding obligation.
(2) The target number of days may be different for different MSO activities and MSO products.
(3) In declaring the target number of days, the Minister must have regard to:
(a) the emergency reserve commitment within the meaning of Article 2 of the International Energy Agreement; and
(b) the objects of this Act; and
(c) any other matter the Minister considers relevant.
(4) Any rules made for the purposes of subsections 10(3), 15(3) and 16(3) must provide for the target number of days declared under subsection (1) of this section to be taken into account in determining the quantity or expected quantity of stocks of an MSO product.
(1) If, at the start of a notice window, an entity is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product, the Secretary must, before the end of the notice window, give the entity a written notice in accordance with this section.
(2) The notice must specify the quantity (in megalitres) of stocks of the product the entity must hold on the obligation days for which the notice is in force.
Note: A decision to specify a particular quantity of the product is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
(3) The Secretary must determine the quantity in accordance with the rules.
Note: See also subsection 14(4).
(4) The notice is in force for obligation days that occur in the period:
(a) starting on the day specified in the notice as the day the notice comes into force (which must be at least 3 months after the day the notice is given); and
(b) ending on the day before another notice given to the entity in relation to the product under this section comes into force.
Note: A notice under this section ceases to be in force during any temporary reduction period for the entity in relation to the product, and comes back into force when that period ends (see subsections 18(3) and (4)).
(5) A notice window is a period prescribed by the rules.
(1) If, at the start of an advice window, an entity is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product, the entity must, before the end of the advice window, give the Secretary written advice (in the approved form, if any) of:
(a) the quantity (in megalitres) of stocks of the product the entity expects to be notified of under section 15 before the end of the next notice window; and
(b) any matters that might affect the entity’s capacity to hold that quantity of stocks of the product.
(2) The entity must do so regardless of whether the entity intends to cease undertaking MSO activities in relation to the product.
(3) The entity must determine the expected quantity in accordance with the rules (if any).
Note: See also subsection 14(4).
(4) An advice window is a period prescribed by the rules ending at the start of a notice window.
(1) An entity that is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product may apply in writing to the Secretary to temporarily reduce the quantity of stocks of the product the entity must hold on obligation days.
(2) The application must:
(a) specify the reduced quantity being applied for; and
(b) set out the entity’s reasons for applying for the reduced quantity; and
(c) meet any other requirements prescribed by the rules.
(1) If an entity makes an application in accordance with section 17, and gives any further information as required under section 78, the Secretary must decide whether to:
(a) grant the application by reducing the quantity as applied for or by less than applied for; or
(b) refuse the application.
(2) If the Secretary decides to grant the application, the Secretary must, by written notice given to the entity, specify the reduced quantity of stocks of the product the entity must hold on the obligation days for which the notice is in force.
(3) The notice is in force for obligation days that occur during the period specified in the notice (the temporary reduction period). The temporary reduction period may start before the notice is given.
(4) During the temporary reduction period, a notice that would otherwise be in force for the entity in relation to the product under section 10 or 15 ceases to be in force. Any such notice comes back into force at the end of the temporary reduction period.
(5) If the Secretary decides to reduce the quantity by less than applied for, or to refuse the application, the Secretary must give the entity written notice of the decision.
Note: A decision to refuse the application, or to grant it by reducing the quantity by less than applied for, is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
(6) The Secretary’s decision under this section must be in accordance with any rules made for the purposes of this subsection.
Division 5—Holding stocks of an MSO product
An entity holds stocks of an MSO product if:
(a) the entity is the holder of the stocks under section 22, 23, 24 or 25; and
(b) the stocks are not excluded under section 20.
20 Excluded stocks
(1) Stocks of an MSO product are excluded for the purposes of paragraph 19(b) if the stocks are:
(a) being kept:
(i) for the exclusive use of the Australian Defence Force or the armed forces of a foreign country; or
(ii) wholly or principally for private or domestic use, except in the circumstances (if any) prescribed by the rules; or
(b) being stored:
(i) in a service station, retail store, personal vehicle, road tanker or rail tank car; or
(ii) in a seagoing ship for the purpose of powering the ship; or
(iii) in a pipeline, except in the circumstances (if any) prescribed by the rules.
(2) Stocks of an MSO product are also excluded for the purposes of paragraph 19(b) if the stocks do not meet standards (if any) prescribed by the rules.
21 Stocks that are stored in Australia
Stocks of an MSO product are stored in Australia if the stocks are stored:
(a) on land in Australia; or
(b) on a vessel:
(i) that is in an Australian port; or
(ii) that is moored waiting to enter an Australian port; or
(iii) that is travelling directly from an Australian port to another Australian port; or
(iv) in circumstances prescribed by the rules.
22 Holder of stocks: entity owns stocks and no other entity is the holder
(1) For the purposes of paragraph 19(a) and subject to subsection (2), an entity is the holder of stocks of an MSO product under this section if:
(a) the entity owns the stocks; and
(b) the stocks are being stored in Australia by the entity or another entity; and
(c) no other entity is the holder of the stocks under section 23 or 24.
(2) If more than one entity would be the holder of the same stocks of an MSO product under subsection (1):
(a) which of those entities is the holder of the stocks; or
(b) the share of those stocks each entity is the holder of;
must be determined in accordance with a method prescribed by the rules.
(3) Without limiting methods that may be prescribed for the purposes of subsection (2), a method may provide for the entities to agree on which of them is the holder of the stocks, or the share of the stocks each entity is the holder of.
23 Holder of stocks: entity entitled to take ownership of stocks and no other entity is the holder
For the purposes of paragraph 19(a), an entity (entity 1) is the holder of stocks of an MSO product under this section if:
(a) another entity (entity 2) owns the stocks; and
(b) the stocks are being stored in Australia by entity 2 or another entity; and
(c) a legally enforceable arrangement, that meets any requirements prescribed by the rules, is in force between entity 1 and entity 2 under which entity 1 is to take ownership of the stocks; and
(d) no other entity is the holder of the stocks under section 24.
24 Holder of stocks: stocks held, reserved or quarantined for entity and no other entity is the holder
For the purposes of paragraph 19(a), an entity (entity 1) is the holder of stocks of an MSO product if:
(a) another entity (entity 2) owns the stocks; and
(b) the stocks are being stored in Australia by entity 1, entity 2 or another entity; and
(c) a legally enforceable arrangement, that meets any requirements prescribed by the rules, is in force between entity 1 and entity 2 under which the stocks are held, reserved or quarantined (however described) by entity 2 for entity 1, for a specified period; and
(d) during the period, entity 1 gives reports in relation to the stocks under the Petroleum and Other Fuels Reporting Act 2017, in relation to the covered activity of holding stocks of a covered product (whether or not entity 2 also gives such reports); and
(e) the period has not ended.
25 Taking feedstocks at refinery into account
(1) For the purposes of section 7 (minimum stockholding obligation), stocks of feedstock are treated as if they were stocks of an MSO product, of a quantity determined in accordance with the rules, if:
(a) the feedstock is used, by an entity that is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to the product, to refine the product at a refinery in Australia; and
(b) the stocks are being stored at the refinery; and
(c) any other requirements prescribed by the rules are met.
(2) For the purposes of paragraph 19(a), the holder of those stocks is:
(a) the entity mentioned in paragraph (1)(a); or
(b) if another entity would be the holder of the stocks under section 24, if that section applied in relation to stocks of feedstock—that other entity.
(3) Any of the following is feedstock:
(a) crude oil that meets any requirements prescribed by the rules;
(b) any other refinery feedstock prescribed by the rules;
(c) any unfinished refinery product prescribed by the rules.
26 Rules in relation to legally enforceable arrangements
Without limiting requirements that may be prescribed for the purposes of paragraph 23(c) or 24(c), requirements may relate to any or all of the following:
(a) the nature of arrangements;
(b) the parties able to enter arrangements, including accreditation or other requirements for the purposes of satisfying the Secretary that parties are fit and proper persons to be party to such arrangements;
(c) conditions on arrangements, including the condition that arrangements be registered with the Secretary.
Division 6—Suspension of minimum stockholding obligation
(1) The Minister may, by legislative instrument, suspend section 7 (minimum stockholding obligation) in relation to a specified MSO product, for a specified period, if the Minister is satisfied that:
(a) the suspension is necessary to prevent or alleviate disruption or likely disruption to supply of the product; and
(b) any other requirements prescribed by the rules are satisfied.
(2) During the specified period, entities are not required to comply with section 7 in relation to the specified MSO product.
Note: Even though it is not required to comply with section 7, an entity remains subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to the product within the meaning of section 9, and sections 15 and 16 continue to apply in relation to the entity, during a suspension.
(3) The specified period must not exceed 6 months. However, the Minister may make another instrument or instruments under subsection (1) suspending section 7 in relation to the product for consecutive periods, each not exceeding 6 months.
(4) Without limiting subsection (1), the Minister must consider exercising the power in that subsection if requested to consider exercising the power by an Energy Minister (within the meaning of the Liquid Fuel Emergency Act 1984).
(1) An entity that is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product may apply in writing to the Secretary to suspend section 7 for the entity in relation to the product.
(2) The application must meet any requirements, and include any information, prescribed by the rules.
29 Secretary’s decision on suspension application
(1) If an entity makes an application in accordance with section 28, and gives any further information as required under section 78, the Secretary must decide whether to:
(a) grant the application:
(i) under subsection (2) in relation to the entity; or
(ii) under subsection (3) in relation to a class of entities; or
(b) refuse the application.
(2) The Secretary may, by written notice given to the entity, suspend section 7 for the entity in relation to the product, for a specified period, in accordance with the rules.
Note: A decision to suspend section 7 for a particular period is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
(3) The Secretary may, on the Secretary’s own initiative, by notifiable instrument, suspend section 7 for a specified class of entities that includes the applicant, in relation to the product, for a specified period, in accordance with the rules.
(4) Without limiting what may be prescribed by rules for the purposes of subsections (2) and (3), the rules may prescribe any or all of the following:
(a) matters to which the Secretary may have regard or must take into account in deciding whether to grant an application or suspend section 7 for a class of entities that includes the applicant;
(b) circumstances in which the Secretary may or must grant an application;
(c) circumstances in which the Secretary may suspend section 7 for a class of entities.
(5) During the specified period, the entity to which the notice applies, or each entity in the class of entities to which the instrument applies, is not required to comply with section 7 in relation to the product.
Note: Even though they are not required to comply with section 7, entities remain subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to the product within the meaning of section 9, and sections 15 and 16 continue to apply in relation to the entities, during a suspension.
(6) The specified period must not exceed 3 months. However, the Secretary may:
(a) for a notice given to an entity under subsection (2)—grant a subsequent application or applications to suspend section 7 for the entity in relation to the product for consecutive periods, each not exceeding 3 months; or
(b) for an instrument made under subsection (3)—make another instrument or instruments suspending section 7 for the class of entities in relation to the product for consecutive periods, each not exceeding 3 months.
(7) If the Secretary decides to suspend section 7 for a class of entities for a specified period, the Secretary must give the applicant and the other entities in the class written notice of the decision.
Note: A decision to suspend section 7 for a class of entities for a particular period is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
(8) If the Secretary decides to refuse the application, the Secretary must give the entity written notice of the decision.
Note: A decision to refuse the application is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
Division 7—Other duties
(1) A regulated entity must give the Secretary a written notice in accordance with subsection (2) in the following situations:
(a) the entity is not subject to the minimum stockholding obligation and intends to undertake an MSO activity that may result in paragraph 10(1)(b) applying to the entity in relation to an MSO product (section 10 deals with triggering the minimum stockholding obligation);
(b) the entity is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product and intends:
(i) to undertake another MSO activity in relation to the product; or
(ii) to cease undertaking an MSO activity in relation to the product in circumstances in which section 31 (notice of intention to cease all MSO activities in relation to MSO product) does not apply;
(c) a situation prescribed by the rules.
Civil penalty: 50 penalty units.
(2) The notice must:
(a) set out details of the situation to which the notice relates; and
(b) set out any matters that might affect the entity’s capacity to meet the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product; and
(c) be in accordance with any other requirements prescribed by the rules; and
(d) be given to the Secretary within the period (if any) prescribed by the rules for the situation.
Note: The Secretary may require further information in relation to the notice (see section 78).
31 Notice of intention to cease all MSO activities in relation to MSO product
(1) An entity that is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product must give the Secretary written notice in accordance with subsection (2) if the entity intends to permanently or indefinitely cease undertaking all MSO activities in relation to the MSO product.
Civil penalty: 50 penalty units.
(2) The notice must meet any requirements, and include any information, prescribed by the rules.
Note: The Secretary may require further information in relation to the notice (see section 78).
32 Secretary’s decision about cessation of all MSO activities in relation to MSO product
(1) If an entity gives a notice in accordance with section 31, and any further information as required under section 78, the Secretary must decide whether or not the Secretary is satisfied that the entity has permanently or indefinitely ceased undertaking all MSO activities in relation to the product.
(2) The Secretary must take all reasonable steps to make the decision within 30 days of being given the notice and must make the decision within 45 days of being given the notice.
(3) The Secretary must give the entity written notice of:
(a) the Secretary’s decision under subsection (1); and
(b) if the Secretary is satisfied as mentioned in that subsection—the date that the Secretary is satisfied that the entity permanently or indefinitely ceased undertaking all MSO activities in relation to the product, which can be earlier than the day the notice is given.
Note: A decision that the Secretary is not satisfied as mentioned in subsection (1) is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
(4) The Secretary is taken to have decided that the Secretary is not satisfied as mentioned in subsection (1) if the Secretary has not notified the entity of a decision before the end of the 45 days mentioned in subsection (2).
33 Compliance audits
(1) This section applies if the Secretary has reasonable grounds to suspect that an entity has contravened, is contravening, or is proposing to contravene, section 7 (minimum stockholding obligation).
(2) The Secretary may, by written notice given to the entity, require the entity to:
(a) appoint as an audit team leader:
(i) a registered greenhouse and energy auditor of its choice; or
(ii) if the Secretary specifies a registered greenhouse and energy auditor in the notice—that auditor; or
(iii) if the Secretary specifies more than one registered greenhouse and energy auditor in the notice—any one of those auditors; and
(b) arrange for the audit team leader to carry out an audit on one or more aspects of the entity’s compliance with section 7; and
(c) arrange for the audit team leader to give the entity a written report setting out the results of the audit; and
(d) give the Secretary a copy of the audit report on or before the day specified in the notice.
(3) The notice must specify the:
(a) type of audit to be carried out; and
(b) matters to be covered by the audit; and
(c) form of the audit report and the kinds of details it is to contain.
(4) An affected entity in relation to an audit must provide the audit team leader and any audit team members with all reasonable facilities and assistance necessary for the effective exercise of the audit team leader’s duties under this Division or rules made for the purposes of this Division.
Civil penalty: 250 penalty units.
(5) If the Secretary gives an entity written notice under subsection (2), the entity must comply with the requirements of the notice.
Note: Under section 93 of the Regulatory Powers Act, an entity may be liable for an additional civil penalty for each day, after the day mentioned in paragraph (2)(d) of this section, for which the entity fails to provide an audit report in accordance with this section.
Civil penalty: 1,000 penalty units.
34 Other audits
(1) The Secretary may appoint a registered greenhouse and energy auditor as an audit team leader to carry out an audit of compliance with one or more aspects of this Act or the rules by:
(a) an entity that is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation; or
(b) if an entity that is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation has an Australian controlling corporation—the Australian controlling corporation.
(2) The Secretary must give the entity that is to be audited written notice of a decision to appoint an audit team leader under subsection (1). The notice must:
(a) specify the audit team leader; and
(b) specify the period within which the audit is to be undertaken; and
(c) specify the type of audit to be carried out; and
(d) specify the matters to be covered by the audit; and
(e) be given to the entity at a reasonable time before the audit is to be undertaken.
(3) An affected entity in relation to an audit must provide the audit team leader and any audit team members with all reasonable facilities and assistance necessary for the effective exercise of the audit team leader’s duties under this Division or rules made for the purposes of this Division.
Civil penalty: 250 penalty units.
(4) If an entity is given a notice under subsection (2), the entity must arrange for the audit team leader to carry out the audit.
Civil penalty: 250 penalty units.
35 Conduct of audits
(1) The rules may prescribe requirements to be met by registered greenhouse and energy auditors in relation to any or all of the following:
(a) preparing for and carrying out audits under this Division;
(b) preparing audit reports in relation to audits under this Division;
(c) using and disclosing information obtained in the course of the activities mentioned in paragraphs (a) and (b).
(2) The rules may prescribe different requirements for:
(a) different types of audits; and
(b) different types of audit reports.
(3) A registered greenhouse and energy auditor must comply with requirements prescribed under subsection (1).
36 MSO compliance plan
(1) An entity that is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation must prepare, and keep up to date, a written plan that deals with:
(a) the matters prescribed by the rules; and
(b) any other matters as requested by the Secretary under subsection (2).
Civil penalty: 50 penalty units.
(2) The Secretary may, in writing, request the entity to ensure that its plan deals with any matters specified in the request.
Note: A decision to request an entity to ensure that its plan deals with specified matters is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
(3) The entity must make the plan available to the Secretary from time to time as requested by the Secretary or required by the rules.
Civil penalty: 50 penalty units.
Division 8—Assumption or division of minimum stockholding obligation
37 Determination of assumption or division of minimum stockholding obligation
(1) The Secretary may, in writing, make a determination that the Secretary is satisfied that an entity’s (the divesting entity’s) minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product is being assumed by, or divided with, another entity or entities (the receiving entity or receiving entities).
Note: A decision to make a determination is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
(2) The Secretary may make the determination:
(a) on application by a divesting entity or receiving entity; or
(b) on the Secretary’s own initiative.
(3) Before making a determination, the Secretary must invite submissions from the entities and take any such submissions into account.
(4) The Secretary must give the determination to the entities.
(5) The determination must specify the effect the determination is to have on any notices in force under section 10, 15 or 18.
Note: A decision about the effect of the determination on the notices is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
(6) If the Secretary decides to refuse an entity’s application to make a determination under this section, the Secretary must give the entity written notice of the decision.
Note: A decision to refuse an application is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
(7) A determination under this section, including the effect specified for the purposes of subsection (5), must be in accordance with any rules made for the purposes of this subsection.
(8) Without limiting what may be prescribed by rules made for the purposes of subsection (7), the rules may make provision for a determination to specify as an effect:
(a) that a notice is taken to have been given to more than one entity, or to a different entity; or
(b) that a notice is taken to specify a different quantity.
Part 3—Fuel security services payment
Division 1—Introduction to this Part
38 Simplified outline of this Part
Refiners of certain fuels may apply to the Minister for fuel security services payment, which is a form of bounty.
Generally, fuel security services payment is paid quarterly, based on the quantity of fuels (known as FSSP fuels) refined in the quarter. The rate is set in rules made by the Minister.
The payment is paid for quarters that end in a period known as the recipient’s commitment period.
Recipients of fuel security services payment commit to repaying any amounts received if the refinery ceases refining FSSP fuels before the end of the recipient’s commitment period.
Division 2—Fuel security services payment
39 Application for fuel security services payment
(1) A person may apply in writing to the Minister for fuel security services payment in relation to a refinery in Australia at which the person refines FSSP fuel.
(2) The application must include the person’s consent to the imposition of repayment obligations under section 50.
(3) The application must:
(a) be in the approved form (if any); and
(b) meet any other requirements, and include any information, prescribed by the rules.
(4) Rules made for the purposes of paragraph (3)(b) may make provision for or in relation to empowering the Minister to require the person to give security to the Commonwealth in relation to the fulfilment by the person of any requirement to repay fuel security services payment under section 50.
40 Decision on application
(1) If a person makes an application in accordance with section 39, and gives any further information as required under section 78, the Minister must decide whether to grant or refuse the application.
(2) The Minister must, by written notice given to the person, grant the application if:
(a) the person is a constitutional corporation; and
(b) the person refines FSSP fuel at a refinery in Australia; and
(c) the refining meets the requirements (if any) prescribed by the rules; and
(d) any other requirements prescribed by the rules are met in relation to the application.
(3) The notice must specify:
(a) the refinery (the committed refinery); and
(b) the person’s commitment period in relation to the committed refinery.
Note: A decision about the duration of a person’s commitment period is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
(4) If the Minister decides to refuse the application, the Minister must give the person written notice of the decision.
Note: A decision to refuse an application is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
(5) The Minister must take all reasonable steps to ensure that a decision is made on the application:
(a) if the Minister required further information under subsection 78(1) in connection with the application—within 60 days after the person gave the Minister the information; or
(b) otherwise—within 60 days after the application was made.
41 Commitment period
(1) In determining the commitment period to be specified in a notice given to a person under subsection 40(3), the Minister:
(a) must do so in accordance with any requirements prescribed by the rules; and
(b) must not determine a period that ends before 30 June 2027.
(2) The Minister may, in accordance with a written application made by the person, vary or terminate the person’s commitment period by written notice given to the person.
(3) A variation or termination must not be inconsistent with any requirements prescribed by the rules, but (subject to the rules) may have the effect that the period as varied or terminated ends before 30 June 2027.
(4) If the Minister decides to refuse the application, the Minister must give the person written notice of the decision.
Note: A decision to refuse an application is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
42 Payability of fuel security services payment
(1) Subject to this Part and the rules, fuel security services payment is payable to a person for each quarter that ends in the person’s commitment period.
(2) However, fuel security services payment is not payable to a person for a quarter:
(a) if there is no time in the quarter at which the person refines any FSSP fuel at the committed refinery; or
(b) if the amount of the payment would be nil; or
(c) in any circumstances relating to a matter mentioned in subsection 40(2) that are prescribed by the rules.
43 Amount of fuel security services payment
(1) The amount of fuel security services payment payable to a person for a quarter is the amount worked out in accordance with the following method statement.
Method statement
Step 1. For each FSSP fuel refined by the person at the committed refinery in the quarter:
(a) work out the number of litres refined; and
(b) multiply that number of litres by the number of cents per litre prescribed, or worked out using a method prescribed, by the rules for that FSSP fuel.
Step 2. Add up the amounts worked out under step 1 for each FSSP fuel.
(2) The number of cents per litre for an FSSP fuel prescribed, or worked out using a method prescribed, by the rules:
(a) must not be a number higher than 1.8; and
(b) may be 0.
(3) The rules may make provision in relation to determining the number of litres of FSSP fuel refined by a person at a committed refinery.
(4) The Minister may, by notifiable instrument, make guidelines in relation to the prescribing of, or the prescribing of a method for working out, a number of cents per litre for an FSSP fuel. The Minister must take any guidelines into account in making rules for the purposes of subsection (1).
(5) In making rules for the purposes of subsections (1) and (3) and guidelines under subsection (4), the Minister must have regard to:
(a) in relation to fuel security services payment payable for quarters ending on or before 30 June 2030—the determination made by the Minister under subsection 44(1); and
(b) the principle that (subject to paragraph (2)(a)) the amount of fuel security services payment paid to a person for quarters ending in the person’s commitment period should be guided by the margin that is sufficient to ensure that refineries operating in Australia over the person’s commitment period do not make a loss.
(6) For the purposes of paragraph (5)(b) and section 44, the margin sufficient to ensure that refineries operating in Australia do not make a loss is the excess of the sale price of FSSP fuels and fuel oils refined by the refineries over the costs of feedstock and transport in relation to FSSP fuels, expressed in cents per litre.
(7) For the purposes of subsection (6), the following matters are relevant to working out the margin sufficient to ensure that refineries operating in Australia do not make a loss over a period:
(a) government payments and benefits other than fuel security services payment in relation to the period;
(b) costs of operating the refinery incurred in relation to the period;
(c) capital expenditure in relation to the period;
(d) any other matters the Minister considers relevant.
The Minister may rely on estimates or other indicators of a matter if the Minister considers it appropriate to do so.
44 Determination of margin sufficient to ensure refineries do not make a loss
(1) The Minister must, in writing, determine the number of cents per litre that, at the time the determination is made, the Minister estimates is likely to be the margin sufficient to ensure that refineries operating in Australia over the period starting on the day this Act commences and ending on 30 June 2027 do not make a loss.
(2) The Minister must make the determination before the end of the period of one month starting on the day this Act commences.
(3) The Minister must give a copy of the determination to any applicant under section 39 (application for fuel security services payment).
(4) A determination:
(a) cannot be varied; and
(b) cannot be revoked before 1 July 2030.
(5) A determination made under subsection (1) is not a legislative instrument.
45 Payment of fuel security services payment
Fuel security services payment that is payable to a person is to be paid to the person by the Secretary in accordance with any rules prescribed for the purposes of this section.
46 Publication of information
The Secretary must publish on the Department’s website:
(a) the total amount of fuel security services payment paid for quarters ending in each financial year; and
(b) any other information required by the rules.
Division 3—Reporting and notification obligations
47 Reporting during commitment period
(1) During a person’s commitment period, the person must give the Secretary reports in accordance with this section.
Civil penalty: 250 penalty units.
(2) Each report must:
(a) include the information prescribed by the rules; and
(b) be in the approved form (if any); and
(c) be given within the period prescribed by the rules.
(3) Without limiting information that may be prescribed for the purposes of paragraph (2)(a), the rules may prescribe information for the purposes of enabling the Secretary to be satisfied that the person meets the criteria under subsection 40(2) at the time a report is given to the Secretary under this section.
48 Notification of events during commitment period
(1) During a person’s commitment period in relation to a committed refinery, the person must notify the Secretary, in accordance with subsections (2) and (3), if any of the following events occur or are expected by the person to occur:
(a) any change to the person’s legal identity;
(b) any change of ownership of the committed refinery;
(c) the committed refinery permanently ceases refining one or more FSSP fuels;
(d) the committed refinery voluntarily ceases refining one or more FSSP fuels for a period of more than 24 hours;
(e) the committed refinery involuntarily ceases refining one or more FSSP fuels for a period of more than 24 hours;
(f) an event prescribed by the rules.
Civil penalty: 250 penalty units.
(2) The notice must:
(a) set out details of the event to which the notice relates; and
(b) be in the approved form (if any); and
(c) be in accordance with any other requirements prescribed by the rules.
(3) The notice must be given to the Secretary as soon as practicable after the event occurs, or the person forms the expectation that the event will occur, but no later than:
(a) for an event covered by paragraph (1)(a), (b) or (c)—7 days after the event occurs or the person forms the expectation that the event will occur; and
(b) for an event covered by paragraph (1)(d) or (e)—24 hours after the event occurs or the person forms the expectation that the event will occur; and
(c) for an event covered by paragraph (1)(f)—the time prescribed by the rules for the event.
49 False or misleading information
A person must not, in an application made under section 39, a report given under section 47 or a notice given under section 48, provide information that:
(a) either:
(i) is false or misleading in a material particular relevant to the payment of fuel security services payment; or
(ii) omits a matter or thing without which the information is misleading in a material particular relevant to the payment of fuel security services payment; and
(b) results in the person being paid an amount of fuel security services payment that the person was not entitled to be paid.
Civil penalty: 300 penalty units.
Division 4—Repayment obligations
50 Repayment if committed refinery ceases refining FSSP fuel
Repayment
(1) A person is required to repay the Commonwealth the amount worked out under subsection (2) if:
(a) a committed refinery ceases to refine all FSSP fuels; and
(b) the cessation continues for 120 days; and
(c) the start of the 120 days occurs during the person’s commitment period in relation to the committed refinery.
Note 1: The person’s application for fuel security services payment under section 39 included the person’s consent to the imposition of repayment obligations under this section.
Note 2: Repayment obligations under this section may be affected by rules made under section 51.
(2) For the purposes of subsection (1), the amount is:
(a) the total amount of fuel security services payment paid to the person for quarters ending in the person’s commitment period; or
(b) in the circumstances (if any) prescribed by rules made for the purposes of section 51—an amount worked out in accordance with those rules that is less than the total amount.
(3) Subsection (1) applies regardless of whether the person owns or operates the committed refinery at the time it ceases to refine FSSP fuel.
When amount is due and payable
(4) An amount repayable by a person under this section is due and payable on the day that is 60 days after the end of the later of:
(a) the 120 days referred to in paragraph (1)(b); or
(b) if the Secretary has extended the 120‑day period under section 52—that period as extended.
Amount is a debt due to the Commonwealth
(5) An amount repayable by a person under this section is a debt due to the Commonwealth that may be recovered by the Secretary, on behalf of the Commonwealth, in:
(a) the Federal Court of Australia; or
(b) the Federal Circuit and Family Court of Australia (Division 2); or
(c) a court of a State or Territory that has jurisdiction in relation to the matter.
(6) The Secretary may, on behalf of the Commonwealth:
(a) write off a debt or class of debts arising under this section, if the Secretary is satisfied that it is appropriate to do so; or
(b) waive the right of the Commonwealth to recover a debt or class of debts arising under this section, in accordance with any requirements prescribed by the rules; or
(c) make arrangements to allow an amount of a debt that is payable by a person to the Commonwealth under this section to be paid in instalments, in accordance with any requirements prescribed by the rules.
51 Rules in relation to repayment obligation
(1) Subsection 50(1) does not apply in the circumstances (if any) prescribed by the rules.
(2) The rules may prescribe circumstances, and a method for working out the amount in those circumstances, for the purposes of paragraph 50(2)(b).
(3) Rules made for the purposes of subsection (1) or (2) may prescribe circumstances by reference to decisions of the Minister.
(4) Rules prescribing circumstances as mentioned in subsection (1) or (2) cannot be repealed, or amended in a way that removes or limits a prescribed circumstance, without the agreement of each person whose commitment period started while the rules were in force.
(5) Rules prescribing a method for working out an amount as mentioned in subsection (2) cannot be repealed, or amended in a way that results in an increased amount being worked out, without the agreement of each person whose commitment period started while the rules were in force.
(6) Subsections (4) and (5) do not apply to a repeal by operation of section 42 (disallowance) of the Legislation Act 2003.
52 Secretary may extend period of cessation
(1) The Secretary may, on written application by a person, by written notice given to the person, extend the period mentioned in paragraph 50(1)(b) in circumstances prescribed by the rules.
(2) If the Secretary decides to refuse the person’s application, the Secretary must give the person written notice of the decision.
Note: A decision to refuse to extend the period is a reviewable decision and reasons and notice of review rights must be given (see sections 72 and 73).
53 Secretary must notify person of amount repayable under section 50
(1) If a person is required to repay an amount under section 50, the Secretary must, by written notice given to the person, notify the person of:
(a) the fact that the person must repay the amount; and
(b) the amount worked out in accordance with subsection 50(2); and
(c) the day the amount is due and payable under subsection 50(4).
(2) The Secretary must give the notice within 30 days after the end of the later of:
(a) the 120 days referred to in paragraph 50(1)(b); or
(b) if the Secretary has extended the 120‑day period under section 52—that period as extended.
54 Repayment in other circumstances
(1) A person is required to repay the Commonwealth the amount worked out under subsection (2) if:
(a) an amount is paid to the person by way of fuel security services payment; and
(b) either:
(i) fuel security services payment was not payable to the person; or
(ii) the amount paid is more than the correct amount of fuel security services payment payable to the person.
(2) For the purposes of subsection (1), the amount is:
(a) if fuel security services payment was not payable to the person—the whole of the amount mentioned in paragraph (1)(a); or
(b) otherwise—the amount by which the amount mentioned in paragraph (1)(a) exceeds the correct amount of fuel security services payment payable to the person.
(3) An amount repayable by a person under this section is due and payable on the day the amount mentioned in paragraph (1)(a) is paid.
(4) An amount repayable by a person under this section is a debt due to the Commonwealth that may be recovered by the Secretary, on behalf of the Commonwealth, in:
(a) the Federal Court of Australia; or
(b) the Federal Circuit and Family Court of Australia (Division 2); or
(c) a court of a State or Territory that has jurisdiction in relation to the matter.
55 Secretary must notify person of amount repayable under section 54
(1) If the Secretary becomes aware that a person is required to repay an amount under section 54, the Secretary must, by written notice given to the person, notify the person of:
(a) the fact that the person must repay the amount; and
(b) the amount as worked out in accordance with subsection 54(2); and
(c) the day the amount became due and payable under subsection 54(3).
(2) The Secretary must give the notice within 30 days after becoming aware that the person is required to repay the amount.
Division 5—Other matters
56 Defeasibility of statutory rights
A person’s application for fuel security services payment is granted on the basis that:
(a) fuel security services payment may not be payable to the person for a quarter (see subsection 42(2)) or the amount of fuel security services payment payable to the person may be nil (see paragraph 43(2)(b)); and
(b) the person’s entitlement to fuel security services payment may be cancelled, revoked, terminated or varied by or under later legislation; and
(c) no compensation is payable in any of the events in the above paragraphs.
57 Uniformity
A power conferred on any person by this Part must not be exercised in such a manner that bounty would not be uniform throughout the Commonwealth within the meaning of paragraph 51(iii) of the Constitution.
58 Appropriation
The Consolidated Revenue Fund is appropriated, to the extent of $2,047 million, for the purposes of paying fuel security services payment under this Part in relation to quarters ending on or before 30 June 2030.
Part 4—Compliance and enforcement
59 Simplified outline of this Part
To ensure obligations under this Act are met, various powers under the Regulatory Powers Act are available:
(a) monitoring and investigation powers; and
(b) a civil penalty and infringement notice regime; and
(c) the ability to accept enforceable undertakings and seek injunctions.
60 Monitoring powers
Provisions subject to monitoring
(1) The following provisions are subject to monitoring under Part 2 of the Regulatory Powers Act:
(a) a civil penalty provision of this Act;
(b) an offence provision of the Crimes Act 1914 or the Criminal Code that relates to this Act.
Note: Part 2 of the Regulatory Powers Act creates a framework for monitoring whether this Act has been complied with. It includes powers of entry and inspection.
Information subject to monitoring
(2) Information given in compliance or purported compliance with the following provisions is subject to monitoring under Part 2 of the Regulatory Powers Act:
(a) section 16 (entity’s advice about expected designated quantity);
(b) section 17 (application to temporarily reduce quantity of stocks of MSO product);
(c) section 28 (application for suspension by Secretary);
(d) section 30 (notice of MSO activity in relation to MSO product);
(e) section 31 (notice of intention to cease all MSO activities in relation to MSO product);
(h) section 36 (MSO compliance plan);
(i) section 39 (application for fuel security services payment);
(j) section 47 (reporting during commitment period);
(k) section 48 (notification of events during commitment period);
(l) section 78 (further information about applications, notices and advice).
Note: Part 2 of the Regulatory Powers Act creates a framework for monitoring whether the information is correct. It includes powers of entry and inspection.
Related provisions
(3) For the purposes of Part 2 of the Regulatory Powers Act, each of the following provisions is related to the provisions mentioned in subsection (1) and the information mentioned in subsection (2):
(a) section 11 of the Petroleum and Other Fuels Reporting Act 2017;
(b) a civil penalty provision of the Fuel Quality Standards Act 2000;
(c) an offence provision of the Fuel Quality Standards Act 2000.
Authorised applicant, authorised person, issuing officer, relevant chief executive and relevant court
(4) For the purposes of Part 2 of the Regulatory Powers Act, as that Part applies in relation to the provisions mentioned in subsection (1) and the information mentioned in subsection (2):
(a) the Secretary is an authorised applicant; and
(b) a person appointed under section 80 is an authorised person; and
(c) a magistrate is an issuing officer; and
(d) the Secretary is the relevant chief executive; and
(e) each of the following is a relevant court:
(i) the Federal Court of Australia;
(ii) the Federal Circuit and Family Court of Australia (Division 2);
(iii) a court of a State or Territory that has jurisdiction in relation to the matter.
(5) The relevant chief executive may, in writing, delegate the powers and functions mentioned in subsection (6) to an SES employee, or acting SES employee, in the Department.
Note: The expressions SES employee and acting SES employee are defined in section 2B of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
(6) The powers and functions that may be delegated are the relevant chief executive’s powers and functions:
(a) under Part 2 of the Regulatory Powers Act in relation to the provisions mentioned in subsection (1) or the information mentioned in subsection (2); and
(b) under the Regulatory Powers Act that are incidental to a power or function mentioned in paragraph (a).
(7) A person exercising powers or performing functions under a delegation under subsection (5) must comply with any directions of the relevant chief executive.
Additional monitoring power
(8) For the purposes of determining:
(a) whether a provision mentioned in subsection (1) has been, or is being, complied with; or
(b) the correctness of information mentioned in subsection (2);
the additional power mentioned in subsection (9) is taken to be included in the monitoring powers under Part 2 of the Regulatory Powers Act.
(9) The additional monitoring power is the power to take, test and analyse samples of any fuel or fuel additives on premises entered under Part 2 of the Regulatory Powers Act in relation to the provisions mentioned in subsection (1) or the information mentioned in subsection (2).
Person assisting
(10) An authorised person may be assisted by other persons in exercising powers or performing functions or duties under Part 2 of the Regulatory Powers Act in relation to the provisions mentioned in subsection (1) and the information mentioned in subsection (2).
61 Investigation powers
Provisions subject to investigation
(1) The following provisions are subject to investigation under Part 3 of the Regulatory Powers Act:
(a) a civil penalty provision of this Act;
(b) an offence provision of the Crimes Act 1914 or the Criminal Code that relates to this Act.
Note: Part 3 of the Regulatory Powers Act creates a framework for investigating whether a provision has been contravened. It includes powers of entry, search and seizure.
Related provisions
(2) For the purposes of Part 3 of the Regulatory Powers Act, each of the following provisions is related to evidential material that relates to a provision mentioned in subsection (1):
(a) section 11 of the Petroleum and Other Fuels Reporting Act 2017;
(b) a civil penalty provision of the Fuel Quality Standards Act 2000;
(c) an offence against the Fuel Quality Standards Act 2000.
Authorised applicant, authorised person, issuing officer, relevant chief executive and relevant court
(3) For the purposes of Part 3 of the Regulatory Powers Act, as that Part applies in relation to evidential material that relates to a provision mentioned in subsection (1):
(a) the Secretary is an authorised applicant; and
(b) a person appointed under section 80 is an authorised person; and
(c) a magistrate is an issuing officer; and
(d) the Secretary is the relevant chief executive; and
(e) each of the following is a relevant court:
(i) the Federal Court of Australia;
(ii) the Federal Circuit and Family Court of Australia (Division 2);
(iii) a court of a State or Territory that has jurisdiction in relation to the matter.
(4) The relevant chief executive may, in writing, delegate the powers and functions mentioned in subsection (5) to an SES employee, or acting SES employee, in the Department.
Note: The expressions SES employee and acting SES employee are defined in section 2B of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
(5) The powers and functions that may be delegated are the relevant chief executive’s powers and functions:
(a) under Part 3 of the Regulatory Powers Act in relation to evidential material that relates to a provision mentioned in subsection (1); and
(b) under the Regulatory Powers Act that are incidental to a power or function mentioned in paragraph (a).
(6) A person exercising powers or performing functions under a delegation under subsection (4) must comply with any directions of the relevant chief executive.
Additional investigation power
(7) The additional power mentioned in subsection (8) is taken to be included in the investigation powers under Part 3 of the Regulatory Powers Act, as that Part applies in relation to evidential material that relates to a provision mentioned in subsection (1) or (2).
(8) The additional investigation power is the power to take, test and analyse samples of any fuel or fuel additives on premises entered under Part 3 of the Regulatory Powers Act in relation to evidential material that relates to a provision mentioned in subsection (1) or (2).
Person assisting
(9) An authorised person may be assisted by other persons in exercising powers or performing functions or duties under Part 3 of the Regulatory Powers Act in relation to evidential material that relates to a provision mentioned in subsection (1).
62 Civil penalty provisions
Enforceable civil penalty provisions
(1) Each civil penalty provision of this Act is enforceable under Part 4 of the Regulatory Powers Act.
Note: Part 4 of the Regulatory Powers Act allows a civil penalty provision to be enforced by obtaining an order for a person to pay a pecuniary penalty for the contravention of the provision.
Authorised applicant
(2) For the purposes of Part 4 of the Regulatory Powers Act, each of the following persons is an authorised applicant in relation to the civil penalty provisions of this Act:
(a) the Secretary;
(b) an SES employee, or acting SES employee, in the Department with responsibilities in relation to this Act.
Note: The expressions SES employee and acting SES employee are defined in section 2B of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Relevant court
(3) For the purposes of Part 4 of the Regulatory Powers Act, each of the following courts is a relevant court in relation to the civil penalty provisions of this Act:
(a) the Federal Court of Australia;
(b) the Federal Circuit and Family Court of Australia (Division 2);
(c) a court of a State or Territory that has jurisdiction in relation to the matter.
Liability of Crown
(4) Part 4 of the Regulatory Powers Act, as that Part applies in relation to the civil penalty provisions of this Act, does not make the Crown liable to a pecuniary penalty.
63 Requirement for person to assist with applications for civil penalty orders
(1) A person commits an offence if:
(a) the relevant chief executive requires, in writing, the person to give all reasonable assistance in connection with an application for a civil penalty order; and
(b) the person fails to comply with the requirement.
Penalty: 10 penalty units.
(2) A requirement under subsection (1) is not a legislative instrument.
(3) The relevant chief executive may require a person to assist under subsection (1) only if:
(a) it appears to the relevant chief executive that the person is unlikely to have:
(i) contravened the civil penalty provision to which the application relates; or
(ii) committed an offence constituted by the same, or substantially the same, conduct as the conduct to which the application relates; and
(b) the relevant chief executive suspects or believes that the person can give information relevant to the application.
(4) The relevant chief executive cannot require a person to assist under subsection (1) if the person is or has been a lawyer for the person suspected of contravening the civil penalty provision to which the application relates.
(5) A relevant court may order a person to comply with a requirement under subsection (1) in a specified way. Only the relevant chief executive may apply to the court for an order under this subsection.
(6) For the purposes of this section, it does not matter whether the application for the civil penalty order has actually been made.
Note: Subsection (1) does not abrogate or affect the law relating to legal professional privilege or the privilege against self‑incrimination.
64 Determining pecuniary penalty for contravention of minimum stockholding obligation
Maximum pecuniary penalty for contravention of section 7
(1) If:
(a) an entity is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product on an obligation day; and
(b) the entity contravenes section 7 by not holding at least the quantity of stocks of the product designated for the entity on the obligation day;
then, for the purposes of the pecuniary penalty set out at the foot of section 7, the number of penalty units is worked out using the following formula:

where:
applicable multiplier means:
(a) if the entity is a body corporate—2; and
(b) otherwise—0.2.
designated quantity of stocks means the quantity (in megalitres) of stocks of the product designated for the entity on the obligation day (see section 13).
number of non compliant days for the obligation day means:
(a) 1; or
(b) if the entity also contravenes section 7 on the next obligation day by not holding at least the quantity of stocks of the product designated for the entity on that next obligation day—the number of days in the period:
(i) starting on the obligation day; and
(ii) ending on the day before the next obligation day.
Maximum pecuniary penalty for contravention of subsection 8(1)
(2) If:
(a) an entity that has an Australian controlling corporation is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation in relation to an MSO product on an obligation day; and
(b) the Australian controlling corporation contravenes subsection 8(1) by not ensuring that the entity complies with section 7 in relation to the product on the obligation day;
then, for the purposes of the pecuniary penalty set out at the foot of subsection 8(1), the number of penalty units is worked out using the following formula:
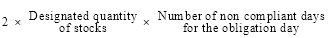
where:
designated quantity of stocks means the quantity (in megalitres) of stocks of the product designated for the entity on the obligation day (see section 13).
number of non compliant days for the obligation day means:
(a) 1; or
(b) if the Australian controlling corporation also contravenes subsection 8(1) on the next obligation day by not ensuring that the entity holds at least the quantity of stocks of the product designated for the entity on that next obligation day—the number of days in the period:
(i) starting on the obligation day; and
(ii) ending on the day before the next obligation day.
Corporate multiplier not applicable
(3) Despite paragraph 82(5)(a) of the Regulatory Powers Act, the pecuniary penalty an entity is ordered to pay under section 82 of that Act for a contravention of section 7 of this Act must not be more than the amount worked out using the formula in subsection (1) of this section (whether or not the entity is a body corporate).
(4) Despite paragraph 82(5)(a) of the Regulatory Powers Act, the pecuniary penalty an Australian controlling corporation is ordered to pay under section 82 of that Act for a contravention of subsection 8(1) of this Act must not be more than the amount worked out using the formula in subsection (2) of this section.
Relevant matter in determining pecuniary penalty
(5) For the purposes of subsection 82(6) of the Regulatory Powers Act, the matter mentioned in subsection (6) of this section is a relevant matter that a court must take into account in determining the pecuniary penalty that an entity must pay for contravening the civil penalty provision in section 7, or subsection 8(1), of this Act.
(6) The matter is the difference between:
(a) the quantity of stocks of the MSO product held by the entity on the obligation day; and
(b) the quantity of stocks of the product designated for the entity on the obligation day.
65 Civil penalties for contravention of minimum stockholding obligation
(1) Proceedings for a civil penalty order against the Australian controlling corporation of an entity for a contravention of subsection 8(1) (additional responsibility of Australian controlling corporation) (the subordinate proceedings) are stayed if proceedings are commenced or have already been commenced against the entity for a civil penalty order for the corresponding contravention of section 7 (the priority proceedings).
(2) The subordinate proceedings may be resumed if an order is not made against the entity in the priority proceedings. Otherwise:
(a) the subordinate proceedings are dismissed; and
(b) costs must not be awarded in relation to the subordinate proceedings.
(3) A relevant court must not make a civil penalty order against an entity for a contravention of section 7 if a civil penalty order has been made against the Australian controlling corporation of the entity for the corresponding contravention of subsection 8(1).
(4) A relevant court must not make a civil penalty order against the Australian controlling corporation of an entity for a contravention of subsection 8(1) if a civil penalty order has been made against the entity for the corresponding contravention of section 7.
66 Infringement notices
Provisions subject to an infringement notice
(1) A civil penalty provision of this Act is subject to an infringement notice under Part 5 of the Regulatory Powers Act.
Note: Part 5 of the Regulatory Powers Act creates a framework for using infringement notices in relation to provisions.
Infringement officer
(2) For the purposes of Part 5 of the Regulatory Powers Act, each of the following persons is an infringement officer in relation to the provisions mentioned in subsection (1):
(a) the Secretary;
(b) an SES employee, or acting SES employee, in the Department with responsibilities in relation to this Act.
Note: The expressions SES employee and acting SES employee are defined in section 2B of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Relevant chief executive
(3) For the purposes of Part 5 of the Regulatory Powers Act, the Secretary is the relevant chief executive in relation to the provisions mentioned in subsection (1).
(4) The relevant chief executive may, in writing, delegate the relevant chief executive’s powers and functions under Part 5 of the Regulatory Powers Act in relation to the provisions mentioned in subsection (1) to an infringement officer.
(5) A person exercising powers or performing functions under a delegation under subsection (4) must comply with any directions of the relevant chief executive.
Single infringement notice may deal with more than one contravention
(6) Despite subsection 103(3) of the Regulatory Powers Act, a single infringement notice may be given to a person in respect of:
(a) 2 or more alleged contraventions of a provision mentioned in subsection (1); or
(b) alleged contraventions of 2 or more provisions mentioned in subsection (1).
However, the notice must not require the person to pay more than one amount in respect of the same conduct.
Additional matters to be included in infringement notices
(7) In addition to the matters included in subsection 104(1) of the Regulatory Powers Act, an infringement notice given in relation to an alleged contravention of a provision mentioned in subsection (1) of this section must also state that the giving of the notice and the payment of the amount payable under the notice may be publicised under section 68 of this Act.
67 Penalties in infringement notices
(1) Despite subsections 104(2) and (3) of the Regulatory Powers Act, the amount to be stated in an infringement notice for the purposes of paragraph 104(1)(f) of that Act, in relation to a civil penalty provision, is the following:
(a) if the notice relates to only one alleged contravention of the provision by the person—one‑fifth of the maximum penalty that a court could impose on the person for the contravention;
(b) if the notice relates to more than one alleged contravention of the provision by the person—one‑fifth of the amount worked out by adding together the maximum penalty that a court could impose on the person for each alleged contravention.
(2) Despite subsection (1), if a civil penalty provision of this Act is prescribed by the rules for the purposes of this subsection, the amount to be stated in the notice is the amount prescribed by the rules for the provision (which must be lower than the amount mentioned in subsection (1)).
68 Secretary may publicise certain contraventions
(1) The Secretary may publicise, in any way the Secretary thinks appropriate, either or both of the following:
(a) that a person has been given an infringement notice under Part 5 of the Regulatory Powers Act, the provision that the person is alleged to have contravened, the nature of the conduct constituting the alleged contravention, and the person’s name;
(b) that a person has paid the amount stated in an infringement notice given under Part 5 of the Regulatory Powers Act.
Note: This subsection constitutes an authorisation for the purposes of other laws, such as the Privacy Act 1988.
(2) Subsection (1) does not:
(a) limit the power of the Secretary or anyone else to publicise a matter or a person’s name; or
(b) prevent anyone else from publicising a matter or a person’s name; or
(c) affect any obligation (however imposed) on anyone to publicise a matter or a person’s name.
69 Enforceable undertakings
Enforceable provisions
(1) The following provisions are enforceable under Part 6 of the Regulatory Powers Act:
(a) section 7 (minimum stockholding obligation);
(b) subsection 8(1) (additional responsibility of Australian controlling corporation).
Note: Part 6 of the Regulatory Powers Act creates a framework for accepting and enforcing undertakings relating to compliance with provisions.
Authorised person
(2) For the purposes of Part 6 of the Regulatory Powers Act, each of the following persons is an authorised person in relation to the provisions mentioned in subsection (1):
(a) the Secretary;
(b) an SES employee, or acting SES employee, in the Department with responsibilities in relation to this Act.
Note: The expressions SES employee and acting SES employee are defined in section 2B of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Relevant court
(3) For the purposes of Part 6 of the Regulatory Powers Act, each of the following courts is a relevant court in relation to the provisions mentioned in subsection (1):
(a) the Federal Court of Australia;
(b) the Federal Circuit and Family Court of Australia (Division 2);
(c) a court of a State or Territory that has jurisdiction in relation to the matter.
Other undertakings
(4) An authorised person may accept an undertaking that an entity that is subject to the minimum stockholding obligation, in relation to an MSO product, will, on the specified obligation days, hold a specified quantity of the product that is more than the designated quantity. The undertaking must be expressed to be an undertaking under this subsection.
(5) The power in subsection (4) is in addition to the power of an authorised person under subsection 114(1) of the Regulatory Powers Act.
(6) Part 6 of the Regulatory Powers Act, other than subsection 114(1), applies to an undertaking accepted under subsection (4) of this section as if it were an undertaking accepted under subsection 114(1) of the Regulatory Powers Act.
Enforceable undertaking may be published on Department’s website
(7) An authorised person in relation to a provision mentioned in subsection (1) may publish an undertaking given in relation to the provision on the Department’s website.
70 Injunctions
Enforceable provisions
(1) The following provisions are enforceable under Part 7 of the Regulatory Powers Act:
(a) section 7 (minimum stockholding obligation);
(b) subsection 8(1) (additional responsibility of Australian controlling corporation);
(c) section 16 (entity’s advice about expected designated quantity);
(d) section 47 (reporting during commitment period).
Note: Part 7 of the Regulatory Powers Act creates a framework for using injunctions to enforce provisions.
Authorised person
(2) For the purposes of Part 7 of the Regulatory Powers Act, each of the following persons is an authorised person in relation to the provisions mentioned in subsection (1):
(a) the Secretary;
(b) an SES employee, or acting SES employee, in the Department with responsibilities in relation to this Act.
Note: The expressions SES employee and acting SES employee are defined in section 2B of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Relevant court
(3) For the purposes of Part 7 of the Regulatory Powers Act, each of the following courts is a relevant court in relation to the provisions mentioned in subsection (1):
(a) the Federal Court of Australia;
(b) the Federal Circuit and Family Court of Australia (Division 2);
(c) a court of a State or Territory that has jurisdiction in relation to the matter.
Consent injunctions
(4) A relevant court may grant an injunction under Part 7 of the Regulatory Powers Act in relation to a provision mentioned in subsection (1) by consent of all the parties to proceedings brought under that Part, whether or not the court is satisfied that section 121 of that Act applies.
Part 5—Other matters
Division 1—Introduction to this Part
71 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part deals with review of decisions and other administrative matters such as seeking further information about applications and notices, appointing authorised persons and approving forms, and delegations.
This Part also deals with the Minister’s power to make rules.
Division 2—Review of decisions
72 Reviewable decisions
Decisions for which the Secretary is responsible person
(1) Each of the following decisions of the Secretary is a reviewable decision and the Secretary is the responsible person for the decision:
(a) a decision under subsection 10(1) to trigger the minimum stockholding obligation for an entity in relation to an MSO product;
(b) a decision to specify a particular quantity of an MSO product in a notice under section 10 or 15;
(c) a decision under section 18 to refuse an application to temporarily reduce the quantity of stocks of an MSO product an entity must hold, or to grant the application by reducing the quantity by less than applied for;
(d) a decision under section 29 to refuse an application to suspend section 7 for an entity in relation to an MSO product;
(e) a decision under section 29 to suspend section 7 for a class of entities, or to suspend section 7 (whether for an entity or a class of entities) for a particular period;
(f) a decision under subsection 32(1) that the Secretary is not satisfied that an entity has permanently or indefinitely ceased undertaking all MSO activities in relation to an MSO product;
(g) a decision under subsection 36(2) to request an entity to ensure its plan deals with specified matters;
(h) a decision to make a determination under section 37 (determination of assumption or division of minimum stockholding obligation) or to refuse an application to make such a determination;
(i) a decision about the effect a determination under section 37 is to have on any notices in force under section 10, 15 or 18;
(j) a decision under section 52 to refuse an application to extend the period of cessation for the purposes of the repayment obligation in section 50.
Decisions for which the Minister is responsible person
(2) Each of the following decisions of the Minister is also a reviewable decision and the Minister is the responsible person for the decision:
(a) a decision under section 40 to refuse an application for fuel security services payment;
(b) a decision under section 40 about the duration of a person’s commitment period;
(c) a decision under section 41 to refuse an application to vary or terminate a person’s commitment period.
73 Notice of reasons and review rights
If the responsible person for a reviewable decision is required by this Act to notify a person of the decision, the responsible person must also notify the person of the reasons for the decision and the person’s right to have the decision reviewed.
74 Applications for reconsideration of decisions made by delegates
(1) A person affected by a reviewable decision made by a delegate of the responsible person may apply to the responsible person for the responsible person to reconsider the decision.
(2) The application must:
(a) be in the approved form (if any); and
(b) set out the reasons for the application; and
(c) be accompanied by the fee (if any) prescribed by the rules.
(3) The application must be made within:
(a) 28 days after the applicant is informed of the decision; or
(b) if, either before or after the end of that period of 28 days, the responsible person extends the period within which the application may be made—the extended period.
75 Reconsideration by responsible person
(1) If a person makes an application under section 74 to the responsible person for a reviewable decision, the responsible person must:
(a) reconsider the decision; and
(b) affirm, vary or revoke the decision.
(2) The responsible person’s decision on reconsideration of a decision has effect as if it had been made under the provision under which the original decision was made.
(3) The responsible person must give the applicant a written notice stating the responsible person’s decision on the reconsideration.
(4) Within 28 days after making the decision on reconsideration, the responsible person must give the applicant a written statement of the responsible person’s reasons for the decision.
(5) If the responsible person’s functions under this section are performed by a delegate of the responsible person, the delegate who reconsiders the reviewable decision:
(a) must not have been involved in making the reviewable decision; and
(b) must hold a position, or perform duties, of at least the same level as the delegate who made the reviewable decision.
Note: The Secretary may delegate functions and powers to certain APS employees in the Department (see section 83).
76 Deadline for reconsideration
(1) The responsible person for a reviewable decision must make a decision on reconsideration of the decision within 90 days after receiving an application for reconsideration.
(2) The responsible person is taken, for the purposes of this Part, to have made a decision affirming the original decision if the responsible person has not informed the applicant of the responsible person’s decision on the reconsideration before the end of the period of 90 days.
77 Review by the Administrative Appeals Tribunal
(1) Applications may be made to the Administrative Appeals Tribunal to review a reviewable decision if the responsible person for the decision has affirmed or varied the decision under section 75.
(2) Applications may be made to the Administrative Appeals Tribunal to review a reviewable decision if the decision was not made by a delegate of the responsible person for the decision.
Division 3—Other matters
78 Further information about applications, notices and advice
(1) If an entity makes an application or gives a notice or advice to the Secretary or Minister (the decision maker) under a provision of Part 2 or 3, the decision maker may, by written notice given to the entity, require the entity to give the decision maker, within the period specified in the decision maker’s notice, specified further information in relation to the entity’s application, notice or advice.
(2) If the entity does not comply with a requirement under subsection (1) in relation to an application made by the entity to the decision maker under Part 2 or 3, the decision maker may, by written notice given to the entity:
(a) refuse to consider the application; or
(b) refuse to take any action, or any further action, in relation to the application.
(3) The entity must comply with a requirement under subsection (1) in relation to a notice or advice given by the entity to the decision maker under a provision of Part 2 or 3.
Civil penalty: 50 penalty units.
79 Treatment of trusts
(1) This Act applies to a trust as if it were a person, but with the changes set out in this section.
Trusts with a single trustee
(2) If the trust has a single trustee:
(a) an obligation that would otherwise be imposed on the trust by this Act is imposed on the trustee instead; and
(b) an offence against this Act that would otherwise have been committed by the trust is taken to have been committed by the trustee.
Trusts with multiple trustees
(3) If the trust has 2 or more trustees:
(a) an obligation that would otherwise be imposed on the trust by this Act is imposed on each trustee instead, but may be discharged by any of the trustees; and
(b) an offence against this Act that would otherwise have been committed by the trust is taken to have been committed by each trustee of the trust, at the time the offence was committed, who:
(i) did the relevant act or made the relevant omission; or
(ii) aided, abetted, counselled or procured the relevant act or omission; or
(iii) was in any way knowingly concerned in, or party to, the relevant act or omission (whether directly or indirectly and whether by any act or omission of the trustee).
Contraventions of civil penalty provisions
(4) This section applies to a contravention of a civil penalty provision in a corresponding way to the way in which it applies to an offence.
80 Appointment of authorised persons
(1) The Secretary may, in writing, appoint a person who is any of the following for the purposes of paragraphs 60(4)(b) and 61(3)(b):
(a) an APS employee in the Department;
(b) a person who is engaged as a consultant or contractor to perform services in relation to this Act;
(c) a member or special member of the Australian Federal Police.
Note: A person appointed under this section is an authorised person for the purposes of Parts 2 and 3 of the Regulatory Powers Act (monitoring and investigation), as those Parts apply in relation to this Act.
(2) The Secretary must not appoint a person unless the Secretary is satisfied that the person has the knowledge or experience necessary to properly exercise the powers of an authorised person under Parts 2 and 3 of the Regulatory Powers Act.
(3) A person appointed under subsection (1) must, in exercising powers under Parts 2 and 3 of the Regulatory Powers Act, as those Parts apply in relation to this Act, comply with any directions of the Secretary.
(4) If a direction is given under subsection (3) in writing, the direction is not a legislative instrument.
81 Approved forms
The Secretary may, in writing, approve a form for the purposes of a provision of this Act or the rules.
82 Delegation by Minister
(1) Subject to subsection (2), the Minister may, in writing, delegate the Minister’s functions or powers under Part 3 (fuel security services payment) or this Part, or under rules made for the purposes of Part 3 or this Part, to:
(a) the Secretary; or
(b) an SES employee, or an acting SES employee, in the Department.
Note 1: The expressions SES employee and acting SES employee are defined in section 2B of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Note 2: Sections 34AA to 34A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901 contain provisions relating to delegations.
(2) The Minister must not delegate the Minister’s power:
(a) to make guidelines under subsection 43(4); or
(b) to make rules under section 84.
(3) In performing a delegated function or exercising a delegated power, the delegate must comply with any written directions of the Minister.
83 Delegation by Secretary
(1) The Secretary may, in writing, delegate all or any of the Secretary’s functions or powers under this Act or the rules to an SES employee, or an acting SES employee, in the Department.
Note 1: The expressions SES employee and acting SES employee are defined in section 2B of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Note 2: Sections 34AA to 34A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901 contain provisions relating to delegations.
(2) In performing a delegated function or exercising a delegated power, the delegate must comply with any written directions of the Secretary.
84 Rules
(1) The Minister may, by legislative instrument, make rules prescribing matters:
(a) required or permitted by this Act to be prescribed by the rules; or
(b) necessary or convenient to be prescribed for carrying out or giving effect to this Act.
(2) To avoid doubt, the rules may not do the following:
(a) create an offence or civil penalty;
(b) provide powers of:
(i) arrest or detention; or
(ii) entry, search or seizure;
(c) impose a tax;
(d) set an amount to be appropriated from the Consolidated Revenue Fund under an appropriation in this Act;
(e) directly amend the text of this Act.
(3) Rules made for the purposes of this Act may make provision in relation to a matter by applying, adopting or incorporating any matter contained in any other instrument or writing:
(a) as in force or existing at a particular time; or
(b) as in force or existing from time to time.
Note: This subsection expresses a contrary intention for the purposes of subsection 14(2) of the Legislation Act 2003.
