Reporting Form ARF 321.0
Statement of Financial Position (Offshore Operations)
Instruction Guide
This instruction guide is designed to assist in the completion of the Statement of Financial Position for the Offshore Operations reporting entity.
General directions and notes
Reporting entity
This form is to be completed by all locally incorporated banks and Special Service Providers (SSPs).
Foreign authorised deposit-taking institution (ADIs) operating through branches in Australia are not required to complete this form.
Securitisation deconsolidation principle
Except where stated otherwise on this form, reporting entities must treat any securitisation program special purpose vehicles (SPVs) in which the ADI (or a member of its consolidated group) participates in accordance with APRA’s clean sale and separation requirements as non-consolidated independent third parties. As a result, for reporting purposes all assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses of these SPVs must be excluded from the ADI’s reported amounts. Where relevant, report on this form any exposure to or other transaction between the ADI and any such SPV as if such transaction was conducted with an independent third party, regardless of whether the SPV or its assets is consolidated for accounting purposes.
APRA's clean sale and separation requirements are set out in APS 120 Funds Management and Securitisation and related Guidance Notes AGN 120.3 Purchase and Supply of Assets (including Securities Issued by SPVs) and AGN 120.1 Disclosure and Separation. Whenever the clean sale and separation requirements are not met, all the assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses of the SPV are to be consolidated with the ADI’s reported amounts.
Reporting period
The form is to be completed as at the last day of the stated reporting quarter. Locally incorporated banks and SSPs should submit the completed form to APRA within 20 business days after the end of the relevant reporting quarter.
Unit of measurement
Banks are asked to complete the form in millions of Australian dollars rounded to one decimal place. SSPs are asked to complete the form in whole Australian dollars (no decimal place).
Amounts denominated in foreign currency are to be converted to AUD in accordance with AASB 121 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates (AASB 121).
The general requirements of AASB 121 for translation are:
Transactions arising under foreign currency derivative contracts at the reporting date must be prepared in accordance with AASB 139 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement (AASB 139). However, those foreign currency derivatives that are not within the scope of AASB 139 (e.g. some foreign currency derivatives that are embedded in other contracts) remain within the scope of AASB 121.
For APRA purposes equity items must be translated using the foreign currency exchange rate at the date of investment or acquisition. Post acquisition changes in equity are required to be translated on the date of the movement.
As foreign currency derivatives are measured at fair value, the currency derivative contracts are translated at the spot rate at the reporting date.
Exchange differences should be recognised in profit and loss in the period which they arise. For foreign currency derivatives, the exchange differences would be recognised immediately in profit and loss if the hedging instrument is a fair value hedge. For derivatives used in a cash flow hedge, the exchange differences should be recognised directly in equity.
The ineffective portion of the exchange differences in all hedges would be recognised in profit and loss; and
A foreign operation is defined in AASB 121 as meaning an entity that is a subsidiary, associate, joint venture or branch of a reporting entity, the activities of which are based or conducted in a country or currency other than those of the reporting entity.
Netting
Unless otherwise specifically stated, institutions are allowed to take advantage of netting agreements in relation to disclosure of data items in this form. Institutions are to comply with the prerequisite for netting outlined in Australian accounting standards AASB 139, AASB 132 Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Presentation (AASB 132) and AASB 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures (AASB 7) and any relevant prudential standards.
Term to maturity
References to term to maturity in this form are references to residual term to maturity.
Basis of preparation
Unless otherwise specifically stated, institutions are to comply with Australian accounting standards regarding the measurement of asset, liability and equity items.
Classification schema
While this information is provided as a reference guide for the disclosure of the loans and advances portfolios and deposit portfolios as required in the form), it can be also be used as a general guide for other classifications in the form.
In defining sectors (refer below), the following three broad classifications are used:
1. Private/public classification
2. Level of Government classification
The Level of Government classification is:
3. Resident/non-resident classification
Sector definitions
Households
This comprises individuals, or groups of individuals whose dealings with other sectors are for personal or household purposes.
Exclude:
Community service organisations
Include:
Exclude:
Non-financial corporations
Private non-financial corporations
Private trading corporations
Private trading corporations are those owned and controlled by the private sector whose main activity is producing goods or non-financial services for sale.
Include:
Exclude:
Private unincorporated businesses
This comprises family trusts and individuals acting as sole proprietors or in partnerships, for commercial or professional purposes. The major businesses to be included in this sub-sector are unincorporated farms, unincorporated retailers, unincorporated professional practices (medical, legal, dental, accounting, etc.), unincorporated businesses of tradesmen such as plumbers, carpenters, etc.
Public non-financial corporations
Commonwealth Government
Trading enterprises owned by the Commonwealth are those businesses which are owned and controlled by the Commonwealth Government and which produce goods or non-financial services for sale at market prices.
Include:
All resident trading enterprises owned 50% or more by the Commonwealth Government or controlled by the Commonwealth Government through legislation, decree or regulation (e.g. Australia Post, and Australian Government Solicitor).
Exclude:
State, Territory and local government
State, Territory and local government trading enterprises are those businesses, which are owned and controlled by State, Territory or local governments, which produce goods or non-financial services for sale at market prices.
Include:
All resident trading enterprises, owned 50% or more by a State, Territory or local government or controlled by a State or Territory government through legislation, decree or regulation (e.g. state rail and water authorities, gas and fuel authorities, housing commissions, port authorities, non-privatised power authorities)
Exclude:
Financial corporations
Central bank
Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA)
The RBA is a public financial corporation and has responsibility for monetary policy, issuing banknotes, holding Australia’s international reserves and providing banking services to the Commonwealth.
Other central bank institutions
This sub-sector includes APRA.
Depository corporations
Banks
Banks refers to corporations, in relation to which an authority under subsection 9(3) is in force and which holds a consent under section 66 of the Banking Act 1959 to use the word bank.
Include:
Exclude:
Other ADIs
Other ADIs refers to corporations, in relation to which an authority under subsection 9(3) is in force, but which do not hold a consent under section 66 under the Banking Act 1959 to use the word bank.
Registered Financial Corporations (RFCs)
Registered financial corporations (RFCs) refers to corporations registered under the Financial Sector (Collection of Data) Act 2001 that are classified to Categories D through G, and cash management trusts.
Include:
A list of corporations registered under the Financial Sector (Collection of Data) Act 2001 and their classification are available on request.
Exclude:
Insurance corporations and pension funds
Life insurance
Life insurance companies must be registered with APRA. They offer insurance for death or disability and also offer investment and superannuation products.
Include:
Exclude:
Pension funds
The pension funds sub-sector includes all superannuation funds that are regarded as complying funds for the purposes of the Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Act 1993 and other autonomous funds established for the benefit of public sector employees. Superannuation funds with all of their assets invested with insurance offices are included.
Superannuation funds and Approved Deposit Funds (ADFs) are established to provide benefits for their members on retirement, resignation, death or disablement. Superannuation funds and ADFs usually take the legal form of trust funds.
Include:
Exclude:
Other insurance corporations
The other insurance corporations’ sub-sector includes all corporations that provide insurance other than life insurance. Included are general, fire, accident, employer liability, household and consumer credit insurers and health insurance funds. These companies must be registered with APRA. They mainly offer house, car and marine insurance.
Include:
Central borrowing authorities
These are corporations established by State and Territory governments to provide finance for government authorities and to manage their surplus funds.
Include
Other financial institutions
Financial auxiliaries
These are corporations and quasi-corporations engaged primarily in activities closely related to financial intermediation, but which do not themselves perform an intermediation role.
Include:
Financial intermediaries
Securitisers
These are financial vehicles that issue short and/or long-term securities (called asset-backed securities) using specifically selected assets (e.g. mortgages, receivables). They provide backing (collateral) for the securities and generate the payment streams necessary to fulfill interest and principal requirements for investors.
Unit trusts
Include:
Exclude:
Other financial intermediaries
Comprise all financial intermediaries other than central bank institutions, depository corporations, insurance corporations, pension funds, CBAs, securitisers and unit trusts.
Include:
General government
Commonwealth general government
Commonwealth government departments and agencies principal function is to provide non-market goods and services, principally financed by taxes, to regulate economic activity, maintain law and order and to redistribute income and wealth by means of transfers.
Include:
Exclude:
State, Territory and local general government
State, Territory and local general government provides non-market goods and services principally financed by taxes to regulate economic activity, maintain law and order and to redistribute income and wealth by means of transfers and hence provided free of charge or at nominal prices well below the cost of production.
Include:
Exclude:
Rest of the world/non-residents
The rest of the world sector consists of all non-resident units that enter into transactions, or have other economic links, with Australian resident units. The concept of residence is based on the concept of the economic territory of a country rather than legal or political concepts. A non-resident unit is any individual, enterprise or other organisation ordinarily domiciled in a country other than Australia.
Include:
Exclude:
Other definitions
Personal refers to individuals, or groups of individuals whose dealings with other sectors are for personal (i.e. non-business) purposes.
Commercial refers to transactions conducted with Private trading companies, Public trading enterprises, Private unincorporated businesses, and Community service organisations, for use in connection with businesses carried on by them.
‘Parent entity’, ‘controlled entity’(subsidiary), ‘associated entity’ These terms are defined in accordance with AASB 127 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements (AASB 127), AASB 3 Business Combinations (AASB 3) and AASB 128 Investments in Associates (AASB 128).
Specific instructions
Assets
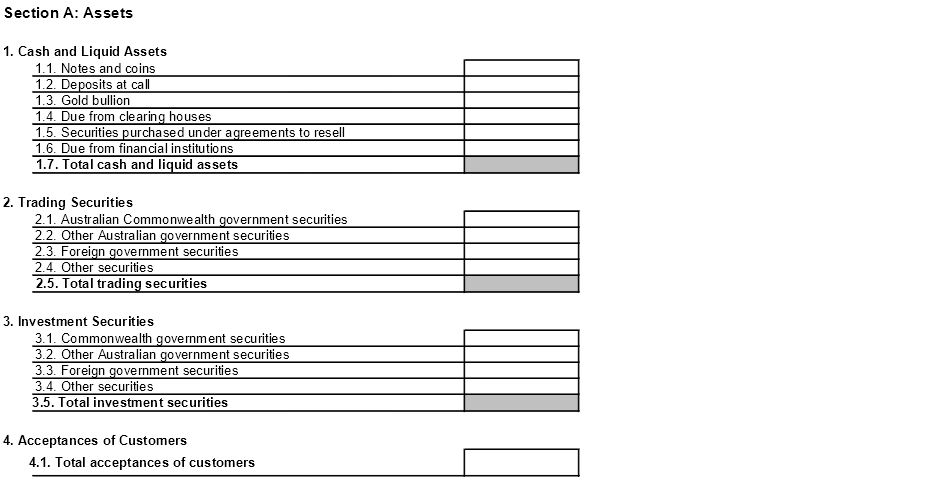
1. Cash and liquid assets
Generally include:
Exclude:
This reporting item should be brought to account at the face value or the gross value of the outstanding balance where appropriate. Interest is taken to profit and loss when earned.
1.1 Notes and coins
Include:
1.2 Deposits at call
Include:
1.3 Gold bullion
Include:
Exclude:
1.4 Due from clearing houses
Include:
1.5 Securities purchased under agreements to resell
Where the transferee of the stock effectively receives a lender’s rate of return (i.e. the underlying risks and rewards of ownership of the underlying stock is not effectively transferred), these transactions are to be accounted for as collateralised borrowing activities (treating stock borrowing as on balance sheet exposures). Securities purchased under agreements to resell, represents the receivable due from counterparties from whom the stock has been borrowed and with whom cash has been lodged. Under this method of accounting the bank’s physical stock positions recorded on the balance sheet in either Trading Securities or Investment Securities sections is not affected. This treatment is consistent with AASB 139.
1.6 Due from financial institutions
Generally include:
Exclude:
This reporting item should be brought to account at the gross value of the outstanding balance. Interest is taken to profit and loss when earned.
Due from RBA/due from central banks
Include:
Due from banks
Include:
Due from other financial institutions
Include:
1.7 Total cash and liquid assets
Sum all cash and liquid asset reporting items above.
2. Trading Securities
2.1 Australian Commonwealth Government securities
Include:
The following securities should be reported:
- treasury bonds;
- treasury notes; and
- treasury adjustable rate bonds.
2.2 Other Australian Government securities
Include:
The following securities should be reported:
- inscribed stock;
- indexed bonds;
- zero coupon bonds;
- promissory notes; and
- commercial paper.
2.3 Foreign government securities
Include:
2.5 Total trading securities
Sum all “Trading securities” reporting items above.
3. Investment Securities
Investment securities are those securities, which are not Trading Securities, as defined in accordance with AASB 130 Disclosures in the Financial Statements of Banks and Similar Financial Institutions (AASB 130), AASB 132 and AASB 7.
These are generally securities purchased with the intent that they be generally held to maturity or held for a period of time, though not necessarily maturity (i.e. equity securities).
Investment securities are to be recorded in accordance with AASB 139.
Interest earned on trading securities is reported as interest income in ARF 330.1.
Dividends received on equity securities are viewed as dividend income and accordingly, are to be classified as other operating income in ARF 330.2.
All realised gains and losses are reported in ARF 330.2.
Include:
- all securities (stock) lent or sold under repurchase agreements. The payable due to counterparties with whom the stock has been lent or sold and from whom cash has been lodged is recorded in securities sold under agreements to repurchase.
Exclude:
- all securities borrowed or purchased under resale agreements. The receivable due from counterparties from whom the stock has been borrowed or purchased and with whom cash has been lodged is recorded in securities purchased under agreements to resell.
Loans and advances” should not be affected by the reporting of “Securities lent or sold under repurchase agreements.
Include holdings of debt securities issued by controlled entities and associates.
3.1 Commonwealth Government securities
Include:
- both long and short-term debt securities issued by the Australian Commonwealth Government. Do not include securities issued by government business enterprises.
The following securities should be reported:
- treasury bonds;
- treasury notes; and
- treasury adjustable rate bonds.
3.2 Other Australian Government securities
Include:
- both long and short-term debt securities issued by Australian State, Territory and local government and Australian state and territory CBAs. Do not include securities issued by Australian State, Territory and local government business enterprises.
The following securities should be reported:
- inscribed stock;
- indexed bonds;
- zero coupon bonds;
- promissory notes; and
- commercial paper.
3.3 Foreign government securities
Include:
- both long and short-term debt securities issued by foreign governments. Do not include securities issued by government business enterprises.
3.5 Total investment securities
Sum all “investment securities” reporting items above.
4. Acceptances of customers
4.1 Total acceptances of customers - Net
Acceptances comprise undertakings by an ADI to pay bills of exchange drawn on customers. The ADI expects most acceptances to be presented before being reimbursed by the customers. These bills of exchange are not held as part of the ADI’s asset portfolio. Acceptances are accounted for and disclosed as a liability with a corresponding contra asset. The contra asset is recognised to reflect the ADI’s claim against each drawer of the bills of exchange.
Bills of exchange that have been accepted and held in an ADI’s asset portfolio should be excluded from this item. Include these holdings of own acceptances under either Trading Securities or Investment Securities.
Netting is allowed in accordance with the requirements specified in the Australian accounting standards (i.e. only if there is a legal right to set off and there is an intention to settle on a net basis, or realise the assets and settle the liability simultaneously).
Acceptances generate fee income that is taken to profit and loss when earned.
5. Loans and advances
Note: Loans and advances are investments of the ADI, which are deemed for this form not be evidenced by the financing/issue of debt securities (e.g. bill financing). This type of financing/investing is to be either recorded in the Trading Securities or Investment Securities.
Generally include:
- overdrafts;
- secured and unsecured lending;
- financial lease agreements;
- account balances which do not qualify as deposits;
- credit card outstanding balances;
- term loans;
- mortgage lending;
- commercial loans;
- equity participation in leveraged leases;
- redeemable preference share finance;
- subordinated loans; and
- loans to controlled entities and associates.
Exclude:
- bills of exchange, commercial paper and promissory notes (report as Investment or Trading securities);
- bills of exchange both discounted and held (report as Investment or Trading securities);
- bonds, debentures, medium term notes (MTNs), transferable certificates of deposit (TCDs), floating-rate notes (FRNs) (show as Investment or Trading securities);
- account balances with financial intermediaries such as banks (show as deposits or due from other financial institutions); and
- receivables due from counterparties arising from the first leg of a repurchase agreement. This receivable should be reported to securities purchased under agreements to resell.
Loans and advances are recognised at amortised cost, after assessing required provisions.
Loans and advances should be recorded net of unearned revenue; this is mainly with respect to unearned lease receivables.
Netting is permitted in accordance with the requirements of the Australian accounting standards (i.e. were there is a legal right to set off the recognised amounts and there is an intention to settle on a net basis, or realise the assets and settle the liability simultaneously).
Loan loss provisioning
Provisions assessed on an individual facility basis in accordance with the Australian equivalents to International Financial Reporting Standards (AIFRS) are to be treated as specific provisions in the reporting forms for regulatory reporting purposes (APS 220 Credit Quality (APS 220)). Specific provisions also include that portion of provisions assessed on a collective basis that are not eligible for regulatory purposes to be included in General Reserve for Credit Losses as defined by APS.
Note:
Specific provisions and General Reserve for Credit Losses for products and counterparties where indicated in the form are to be reported only if the data is already recorded and allocated on that basis by the institution. Otherwise the specific provision and General Reserve for Credit Losses can be disclosed in aggregate.
Do not include associated deferred tax assets (DTA) in the amounts reported for General Reserve for Credit Losses or specific provisions. Include associated DTA in 'Other Assets - DTA - General Reserve for Credit Losses’.
5.1 Loans to households
5.1.1.1.(1) Housing
Including revolving credit or redraw facilities that are exclusively or predominantly for purpose of housing.
Owner occupied – Balance outstanding:
Include:
- the value of housing loans to householders, for the construction or purchase of dwellings for owner occupation.
This reporting item should be reported gross of any specific provisions and General Reserve for Credit Losses.
5.1.1.1.(2) Housing
Including revolving credit or redraw facilities that are exclusively or predominantly for purpose of housing.
Owner occupied – Specific provisions:
Report the specific provisions for impairment applied to this loan item.
5.1.1.1.(3) Housing
Including revolving credit or redraw facilities that are exclusively or predominantly for purpose of housing.
Owner occupied – General Reserve for Credit Losses:
Report the General Reserve for Credit Losses applied to this loan item if already recorded/allocated by the institution, otherwise leave blank.
5.1.1.2.(1) Housing
Including revolving credit or redraw facilities that are exclusively or predominantly for purpose of housing.
Investment – Balance outstanding:
Include:
- the value of investment housing loans to householders, for the construction or purchase of dwellings for non-owner occupation.
This reporting item should be reported gross of any specific provisions and General Reserve for Credit Losses.
5.1.1.2.(2) Housing
Including revolving credit or redraw facilities that are exclusively or predominantly for purpose of housing.
Investment – Specific provision:
Report the specific provisions for impairment applied to this loan item.
5.1.1.2.(3) Housing
Including revolving credit or redraw facilities that are exclusively or predominantly for purpose of housing.
Investment – General Reserve for Credit Losses:
Report the General Reserve for Credit Losses applied to this loan item if already recorded/allocated by the institution, otherwise leave blank.
5.1.3.(1) Revolving credit – Balance
Include:
- the gross value of loans of a revolving credit nature to householders, for a purpose other than housing, which have been included in Housing above.
A revolving credit is a loan arrangement in which the borrowing party may repay funds on loan and immediately borrow it again up to an agreed limit.
This reporting item should be reported gross of any specific provisions and General Reserve for Credit Losses.
5.1.3.(2) Revolving credit – Specific provision
Report the specific provisions for impairment applied to this loan item, if this is recorded or allocated by the institution on this basis.
5.1.3.(3) Revolving credit – General Reserve for Credit Losses
Report the General Reserve for Credit Losses for this reporting line, if this is recorded or allocated by the institution on this basis.
5.1.4.(1) Credit card – Balance
Include:
- the gross value of credit card liabilities by householders.
This reporting item should be reported gross of any specific provisions and General Reserve for Credit Losses.
5.1.4.(2) Credit card – Specific provision
Report the specific provisions for impairment applied to this loan item, if this is recorded or allocated by the institution on this basis.
5.1.4.(3) Credit card – General Reserve for Credit Losses
Report the General Reserve for Credit Losses for this reporting line, if this is recorded or allocated by the institution on this basis.
5.1.5.(1) Leasing - Balance
Include:
- the gross value of lease financing to householders.
This reporting item should be reported net of unearned revenue and gross of specific provisions for impairment and General Reserve for Credit Losses.
5.1.5.(2) Leasing - Specific provision
Report the specific provisions for impairment applied to this loan item, if this recorded or allocated by the institution on this basis.
5.1.5.(3) Leasing – General Reserve for Credit Losses
Report the General Reserve for Credit Losses for this reporting line, if this recorded or allocated by the institution on this basis.
5.1.6.(1) Other personal term loans – Balance
Include:
- the gross value of personal term loans to householders for purposes other than housing and other than revolving credit, credit card and lease financing.
This reporting item should be reported gross of any specific provisions and General Reserve for Credit Losses.
5.1.6.(2) Other personal term loans – Specific provision
Report the specific provisions for impairment applied to this loan item, if this is recorded or allocated by the institution on this basis.
5.1.6.(3) Other personal term loans – General Reserve for Credit Losses
Report the General Reserve for Credit Losses for this reporting line, if this is recorded or allocated by the institution on this basis.
5.1.7.(1) Total loans to households – Balance
Sum the gross value of loans to householders.
This reporting item should be reported gross of any specific provisions and General Reserve for Credit Losses.
5.1.6.(2) Total loans to households – Specific provision
Report the specific provisions applying to loans to householders.
5.1.6.(3) Total loans to households – General Reserve for Credit Losses
Report the General Reserve for Credit Losses for this reporting line.
5.2.(1) Loans to community service organisations/non-profit institutions serving households
5.2.(1) Loans to community service organisations/non-profit institutions serving households – Balance
Include:
- the total gross value of loans to Australian and offshore community service organisations.
This reporting item should be reported gross of any specific provisions and General Reserve for Credit Losses.
5.2.(2) Loans to community service organisations/non-profit institutions serving households – Specific provision
Report the specific provisions for impairment applied to this loan item.
5.2.(3) Loans to community service organisations/non-profit institutions serving households – General Reserve for Credit Losses
Report the General Reserve for Credit Losses for this reporting line, if this recorded or allocated by the institution on this basis.
5.3 Loans to non-financial corporations
5.3.1.(1) Loans to private trading corporations – Balance
Include:
- the gross value of loans to Australian and offshore private trading corporations.
5.3.2.(1) Loans to private unincorporated businesses – Balance
Include:
- the gross value of loans to Australian and offshore private unincorporated businesses.
5.3.3.(1) Loans to Commonwealth and foreign government non-financial corporations – Balance
Include:
- the gross value of loans to Australian Commonwealth government and foreign government non-financial corporations.
5.3.4.(1) Loans to State, Territory and local government and foreign regional non-financial corporations – Balance
Include:
- the gross value of loans to Australian State, Territory and local government and foreign regional government non-financial corporations.
5.4 Loans to government
Include:
- overdrafts;
- secured and unsecured borrowings;
- financial lease agreements;
- account balances which do not qualify as deposits;
- credit card outstanding balances; and
- term loans.
Exclude:
- bills of exchange, commercial paper and promissory notes (there are separate categories for short-term debt securities);
- bills of exchange both discounted and held; and
- bonds, debentures, MTNs, TCDs, FRNs (show as long-term debt securities).
Loans and advances are recognized at amortised cost, after assessing required provisions for impairment.
5.4.1 Loans to Commonwealth Government
Include:
- the gross value of loans to the Australian Commonwealth.
This reporting item should be reported gross of any specific provisions.
5.4.2 Loans to foreign governments
Include:
- the gross value of loans to foreign governments.
This reporting item should be reported gross of any specific provisions.
5.4.3 Loans to Australian State, Territory and local government
Include:
- the gross value of loans to Australian State, Territory and local governments.
This reporting item should be reported gross of any specific provisions.
5.5 Loans to financial corporations
Include:
- treasury related short term lending to other banks;
- corporate banking customer relationship lending to other financial institutions;
- placements with other banks;
- loans and advances to other banks;
- loans with banks and non-bank financial institutions;
- nostro balances with banks and non-bank financial institutions; and
- loans and advances to controlled entities and associates.
Exclude:
- certificates of deposit (should be reported as Investment or Trading securities).
This reporting item should be brought to account at the gross value of the outstanding balance. Interest is taken to profit and loss when earned.
5.5.1 Loans to RBA
Include:
- the gross value of loans to the RBA.
This reporting item should be reported gross of any specific provisions.
5.5.2 Loans to foreign central banks
Include:
- the gross value of loans to central banks other than the RBA.
This reporting item should be reported gross of any specific provisions.
5.5.3 Loans to banks
Include:
- the gross value of loans to Australian and offshore banks.
This reporting item should be reported gross of any specific provisions.
5.5.4 Loans to other financial institutions
Include:
- the gross value of loans to Australian and offshore financial institutions other than the RBA, foreign central banks and banks.
This reporting item should be reported gross of any specific provisions.
5.5.5 Total loans to financial corporations
Sum the gross value of loans to Australian and offshore financial corporations.
5.6.(1) Total gross loans and advances – Balance outstanding
Sum the gross value of loans and advances.
5.6.(2) Total gross loans and advances – Specific provision
Sum the specific provisions applying to all loans.
5.6.(3) Total gross loans and advances – General Reserve for Credit Losses
Record the General Reserve for Credit Losses applying to all loans.
Note: The total of the above of which breakdown of the loan portfolio must equal the aggregate loan portfolio balance disclosed above.
5.6.1 Total gross loans and advances of which: Margin lending
Lending for the purpose of purchasing equities, where the underlying security is equities.
5.6.2 Total gross loans and advances of which: Loans held for sale
Loans held for sale are loans (e.g. mortgages) acquired and held by the ADI with the intention of resale in the short term (i.e. within 12 months of acquisition). This item is to be carried at the lower of cost or net fair value.
5.6.3 Total gross loans and advances of which: Revolving credit
Include:
- the gross value of loans of a revolving credit nature.
Exclude:
- loans to Australian householders, for the purpose of housing.
A revolving credit is a loan arrangement in which the borrowing party may repay funds on loan and immediately borrow it again up to an agreed limit.
This reporting item should be reported gross of any specific provisions and General Reserve for Credit Losses.
5.6.4 Total gross loans and advances of which: Credit cards
Include:
- the gross value of credit card liabilities by Australian counterparties.
5.6.5 Total gross loans and advances of which: Housing – Fixed rate
Of the total reported for “housing loans” identify the component that has a fixed interest rate.
5.6.6 Total gross loans and advances of which: Housing – Variable rate
Of the total reported for “housing loans” identify the component that has a variable interest rate.
5.6.7 Total gross loans and advances of which: Term loan – Fixed rate
Include:
- the gross value of term loans to Australian counterparties that have a fixed interest rate.
Exclude:
- loans to householders for the purpose of housing.
5.6.8 Total gross loans and advances of which: Term loan – Variable rate
Include:
- the gross value of term loans to Australian counterparties that have a variable interest rate. Exclude loans to householders for the purpose of housing.
5.6.9 Total gross loans and advances of which: Lease financing
Include:
- the gross value of lease financing to Australian counterparties.
This reporting item should be reported net of unearned revenue and gross of specific provisions for impairment and General Reserve for Credit Losses.
5.6.10 Total gross loans and advances of which: Other loans
Include:
- the gross value of loans to Australian counterparties other than margin lending, loans held for resale, revolving credit loans, credit cards, housing loans, term loans and leasing finance.
5.7 Less: Deferred fee income
Deferred fee income should be reported in this line item and deducted from total gross loans and advances.
5.8 Net loans and advances (net of Specific provision, General Reserve for Credit Losses and deferred fee income)
Report total loans and advances, net of specific provisions, General Reserve for Credit Losses and deferred fee income.
5.9 Intra-company advances
Report all advances and other assets to other offices within the ADI.
6. Other investments
6.1 Parent entity
Report the total amount of equity investments in the parent entity. Defined in accordance with AASB 127 and AASB 3.
6.2 Controlled entities
Report the total amount of equity investments in controlled entities (subsidiaries). Defined in accordance with AASB 127 and AASB 3.
6.3 Associates
Report the total amount of equity investments in associates. Defined in accordance with AASB 128.
6.4 Joint ventures
Report the total amount of interests in joint ventures (entities). Defined in accordance with AASB 131 Interests in Joint Ventures.
6.5 Other
Report any Other investments not included above.
6.6 Total other investments
Sum all reporting line items for Other Investments.
7. Fixed assets
The reporting of all fixed assets items should be in accordance with applicable Australian accounting standards. Do not include property acquired or held available for sale. These assets are to be disclosed in “Other Assets” category under line item “Non-current assets and disposal groups classified as held for sale”.
7.1. Property
Include:
- property (owner-occupied and investment) consistent with the classification and measurement basis used in AASB 116 Property, Plant and Equipment (AASB 116) and AASB 140 Investment Property.
7.2 Plant and equipment
Include:
- furniture, equipment (excluding information technology), re-modelling costs to existing premises, and interest capitalised during the period of construction of buildings in accordance with AASB 116.
7.3 Information technology
Where information technology is treated as an intangible asset for accounting purposes, it must be reported as an intangible asset in this regulatory form.
7.4 Other
Report other fixed assets items not specifically mentioned above; e.g. leasehold improvements and capital leases.
7.5 Fixed assets - Accumulated depreciation/impairment
Report total depreciation/impairment for all fixed assets items here.
7.6 Net fixed assets
Deduct Accumulated depreciation/impairment from the gross values for property, plant and equipment, information technology and other.
8. Intangible assets
Intangible assets have been divided into “intangible assets with a finite life” and “intangible assets with an infinite life” and “goodwill”.
Classification of assets as intangible assets must be in compliance with the Australian accounting authoritative pronouncements. As a guide ADIs are suggested to follow the disclosure adopted in its annual financial report.
8.1 Intangible assets with a finite life
Include:
- total intangible assets with a finite life.
8.2 Accumulated amortisation
Include:
- the total amount of amortisation of intangible assets, over the period from the date of acquisition to the end of the reporting period.
8.3 Net Intangible assets with a finite life
Subtract the “Accumulated amortisation” from the “Intangible assets with a finite life”.
8.4 Intangible assets with an infinite life
Include:
- total intangible assets with an infinite life.
8.5 Impairment
Include:
- the total amount of impairment of intangible assets over the period from the date of acquisition to the end of the reporting period.
8.6 Net Intangible assets with an infinite life
Subtract the “Impairment” from the “Intangible assets with an infinite life”.
8.7 Goodwill
Goodwill (determined in accordance with AASB 3) represents the excess of the cost of the business combination over the acquirer’s interest in the net fair value of the identifiable assets, liabilities and contingent liabilities.
8.8 Impairment
Include:
- the total amount of impairment over the period from the date of acquisition to the end of the reporting period.
8.9 Net goodwill
Include:
- the net amount of goodwill after impairment.
8.10 Net intangible assets
Deduct “Accumulated amortisation” and “Impairment” from the gross values for “Intangible Assets with a finite life”, “Intangible assets with an infinite life” and “Goodwill”.
9. Other assets
9.1 Interest receivable
Include:
- interest accrued for but not yet received.
9.2 Derivative financial instruments
Include:
- all derivatives consistent with the classification and measurement basis used for derivatives by institutions in accordance with AASB 132,AASB 7 and AASB 139. This applies to trading and banking book derivatives. Derivative financial instruments in existence prior to adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are to be reported in accordance with AASB 1 First-time Adoption of Australian Equivalents to International Financial Reporting Standards.
9.3 Amounts receivable from clients - Outstanding security settlements
For those institutions that have broking activity with clients who are other than financial institutions, record the amount due from clients in relation to security settlement transactions. Do not include amounts receivable from financial institutions or clearing houses in relation to security settlements, as these are to be recorded in a separate asset heading “Due from Financial Institutions” and “Due from Clearing Houses”.
9.4 DTA
Tax assets are defined in accordance with Income Taxes (AASB 112).
Recognition of DTA are to be made in accordance with AASB 112.
The amounts calculated and recognised for DTA must be noted separately in the following categories:
9.4.1 DTA – From tax losses
Report all DTA arising out of tax losses in accordance with AASB 112.
9.4.2 DTA – From specific provision and General Reserve for Credit Losses
Report all DTA associated with the provisioning for asset impairment in accordance with AASB 112.
9.4.3 DTA - Other
Report all DTA other than from tax losses, specific provision and general reserve for credit losses.
9.5 Loan/credit card servicing rights
Report the carrying value of purchased loan (e.g. mortgages) and credit card relationships when the reporting entity purchases the right to receive existing loan payments and credit card receivables in consideration for providing lending and credit card services to those customers. Also report any purchased loan/credit card servicing rights arising in the acquisition of an entire financial institution. The carrying value consists of the cost of the servicing right less accumulated amortisation for the right.
9.6 Defined benefit assets
Include:
- defined benefit assets i.e. surplus, consistent with the classification and measurement basis used in AASB 119 Employee Benefits (AASB 119).
9.7 Non-current assets and disposal groups classified as held for sale
Include:
- non-current assets and disposal groups classified as held for sale consistent with classification and measurement basis used in AASB 5 Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations.
9.8 Items in suspense
Report suspense or unreconciled/unidentified transactions/balances here. A list of examples is not provided as these may vary between institutions. It is recommended that the institutions internal procedures be adopted regarding the recording and reporting of these types of balances.
9.9 Other
Include all other assets not separately identified above.
Include
- commodities other than gold bullion;
- valuables;
- artwork; and
- other receivables.
Exclude:
- deposits, loans and other claims on controlled entities and associates.
9.10 Total other assets
Sum all the reporting items listed under “Other assets”.
10.1.1 Total assets of which deposits, debt securities and loans to controlled entities and associates – Subordinated
Report the total amount of investments of a subordinated nature in controlled entities or associates of the reporting entity. Investments in the form of deposits, loans, advances, bonds, notes and debentures should be reported.
A subordinated debt is a debt security that ranks below other debts should a company be wound up. This includes all debt securities both short and long term.
A subordinated loan is a loan that ranks below other debts should a company be wound up.
10.1.2 Total assets of which deposits, debt securities and loans to controlled entities and associates – Secured
Report the total amount of investments of a secured nature in controlled entities or associates of the reporting entity. Investments in the form of deposits, loans, advances, bonds, notes and debentures should be reported.
A secured debt is a debt security that ranks above other debts should a company be wound up. This includes all debt securities both short and long term.
A secured loan is a loan that ranks above other debts should a company be wound up.
10.1.3 Total assets of which deposits, debt securities and loans to controlled entities and associates – Other
Report the total amount of investments other than subordinated or secured in nature, in controlled entities or associates of the reporting entity. Investments in the form of deposits, loans, advances, bonds, notes and debentures should be reported.
10.2.1 Total assets of which deposits, debt securities and loans to the parent entity – Subordinated
Report the total amount of investments of a subordinated nature in the parent entity of the reporting entity. Investments in the form of deposits, loans, advances, bonds, notes and debentures should be reported.
A subordinated debt is a debt security that ranks below other debts should a company be wound up. This includes all debt securities both short and long term.
A subordinated loan is a loan that ranks below other debts should a company be wound up.
10.2.2 Total assets of which deposits, debt securities and loans to the parent entity – Secured
Report the total amount of investments of a secured nature in the parent entity of the reporting entity. Investments in the form of deposits, loans, advances, bonds, notes and debentures should be reported.
A secured debt is a debt security that ranks above other debts should a company be wound up. This includes all debt securities both short and long term.
A secured loan is a loan that ranks above other debts should a company be wound up.
10.2.3 Total assets of which deposits, debt securities and loans to the parent entity – Other
Report the total amount of investments other than subordinated or secured in nature, in the parent entity of the reporting entity. Investments in the form of deposits, loans, advances, bonds, notes and debentures should be reported.
Section B: Liabilities
1. Due to clearing houses
Include:
- amounts due to recognised clearing houses such as the ASXCH and SFXCH in Australia. Include margin calls from stock and derivative exchanges which are payable.
2. Due to financial institutions
Include:
- settlement account balances – Austraclear, and RITS balances with banks and non-bank financial institutions;
- amounts owing to banks and other financial institutions in relation to the payments system;
- items in the course of collection – due to banks and other financial institutions in relation to the payments system;
- amounts due in relation to an involvement in an overseas payments system; and
- securities purchased not delivered/security settlements – record payables for unsettled purchases of securities. This item only arises if securities are recorded on a settlement date basis as opposed to a trade date basis.
This reporting item should be brought to account at the gross value of the outstanding balance. Interest is taken to profit and loss when earned.
Due to RBA/due to central banks
Include:
- settlement account balances due to the RBA and foreign central banks. Funds borrowed from the RBA and other central banks should also be reported in this data item.
Due to banks
Include:
- settlement account balances due to Australian and offshore banks.
Due to other financial institutions
Include:
- settlement account balances due to other financial institutions.
Other financial institutions refer to financial institutions other than central banks and banks.
3. Acceptances
Acceptances comprise undertakings by an ADI to pay bills of exchange drawn on customers. The ADI expects most acceptances to be presented before being reimbursed by the customers. These bills of exchange are not held as part of the ADI’s asset portfolio. Acceptances are accounted for and disclosed as a liability with a corresponding contra asset. The contra asset is recognised to reflect the ADI’s claim against each drawer of the bills of exchange.
Bills of exchange that have been accepted and held in an ADI’s asset portfolio should be excluded from this item. Include these holdings of own acceptances under either Trading Securities or Investment Securities.
Netting is allowed in accordance with the requirements specified in the Australian accounting standards (i.e. only if there is a legal right to set off and there is an intention to settle on a net basis, or realise the assets and settle the liability simultaneously).
Acceptances generate fee income that is taken to profit and loss when earned.
4. Deposits
4.1 Call/on demand deposits: Households/retail
Report call or on demand deposits received from Australian and offshore householders. Household deposits are otherwise referred to as retail deposits.
Include:
- cheque accounts which provide checking facilities of any kind. This account can either be interest bearing or non-interest bearing. This account may be linked with other accounts offering transaction or non-transaction facilities;
- accounts from which payments may be made to third parties – automated teller machines, debit card or another electronic device;
- notice of withdrawal account – a written notice required before funds can be withdrawn or transferred out of the account;
- demand deposits;
- savings deposits;
- money market deposit accounts;
- other savings deposits; and
- 11am accounts and 24-hour money.
Call/on demand deposits: Other
Report call or on demand deposits received from other than Australian and offshore householders.
Include:
- cheque Accounts which provide checking facilities of any kind. This account can either be interest bearing or non-interest bearing. This account may be linked with other accounts offering transaction or non-transaction facilities;
- accounts from which payments may be made to third parties – ATMs, debit card or another electronic device;
- notice of withdrawal account – a written notice required before funds can be withdrawn or transferred out of the account;
- demand deposits;
- savings deposits;
- money market deposit accounts;
- other savings deposits; and
- 11am accounts and 24-hour money.
4.2 Term deposits: Households/retail
Report term deposits received from Australian and offshore householders. Household deposits are otherwise referred to as retail deposits.
Term deposits refer to an account in which money has been placed for a fixed period of time for a stated interest rate.
Term deposits: Other
Report term deposits received from other than Australian and offshore householders.
Term deposits refer to an account in which money has been placed for a fixed period of time for a stated interest rate.
4.3 Deposits: Certificates of deposit
Certificates of deposit are negotiable bearer debt securities. They are issued at a discount to the face value and do not require endorsement when sold.
4.4 Deposits: Other
Report deposits not identified above.
4.5 Total deposit
Sum all the deposit accounts above.
5. Other borrowings
Include:
- securities sold under agreements to repurchase;
- subordinated loans with a residual maturity of 12 months or less;
- short term loans due to controlled entities and associates;
- treasury related short term borrowings from other banks;
- promissory notes with a residual maturity of 12 months or less;
- commercial paper with a residual maturity of 12 months or less; and
- short term debt securities from controlled and associated entities.
Exclude:
- negotiable and TCDs of deposits;
- subordinated loans with a residual maturity greater than 12 months; and
- deposits.
5.1 Securities sold under agreements to repurchase
Where the transferee of the stock effectively receives a lender’s rate of return (i.e. the underlying risks and rewards of ownership of the underlying stock is not effectively transferred), these transactions are to be accounted for as collateralised lending activities (treating stock lending as on balance sheet exposures). Securities sold under agreements to repurchase, represents the payable due to counterparties with whom the stock has been lent and from whom cash has been lodged. Under this method of accounting the bank’s physical stock positions recorded on the balance sheet in either Trading Securities or Investment Securities sections is not affected. This treatment is consistent with AASB 139.
5.2 Promissory notes/commercial paper
Report all borrowings by the reporting entity in the form of commercial paper or promissory notes. Commercial paper or promissory notes are short-term debt securities usually issued with an original term to maturity of less than 180 days.
Include all commercial paper or promissory notes issued with a residual term to maturity of 12 months or less. Commercial paper or promissory notes with a residual maturity greater than 12 months should be reported as “long term debt”.
5.3 Short term loans
Report all borrowings by the reporting entity in the form of short term debt securities, other than certificates of deposits and promissory notes/commercial paper (identified above).
Include:
- all debt securities issued with a residual term to maturity of 12 months or less. Other debt securities with a residual maturity greater than 12 months should be reported as “long term debt”.
5.3.1 Short term loans - Variable
Report all borrowings by the reporting entity in the form of variable interest rate short term loans.
A loan is considered to be short term if its residual term to maturity is of 12 months or less.
5.3.2 Short term loans - Fixed
Report all borrowings by the reporting entity in the form of fixed interest rate short term loans.
A loan is considered to be short term if its residual term to maturity is of 12 months or less.
5.4 Total other borrowings
Sum the component parts listed under “Other Borrowings”.
6. Income tax liability
Recognition of current and deferred tax liabilities are to be made in accordance with AASB 112.
6.3 Total income tax liability
Sum the income tax liability items relating to Australian business operations.
7. Provisions
7.1 Dividends
A provision for dividends is the allowance that the reporting entity has made in terms of the obligation for declared dividends.
7.2 Employee entitlements
This includes provisions for long service leave, annual leave, staff housing loan benefits, health fund subsidy and other employee entitlements. This should be reported in accordance with the requirements of AASB 119.
7.3 Non-lending losses
Include:
- provision for self insurance;
- frauds;
- litigation, fraud detection and prevention;
- forgeries; and
- non-transferred insurance risks.
7.4 Restructuring costs
Report all provisions raised for the restructuring of an organization.
Include:
- severance, termination and redundancy payments; and
- integration costs.
7.5 Other provisions
Report all other provisions not identified above.
Include:
- specific provision for off-balance sheet credit related commitments;
- leased premises surplus to current requirements; and
- provision for subsidiary integration costs.
7.6 Total provisions
Sum all the “provisions” reporting items.
8. Bonds, notes and long-term borrowings
Bonds, notes and long term borrowings have a residual term to maturity of more than one year. This includes loans and debt securities.
8.1 Debt securities
Report debt securities that have been issued and have a residual term to maturity of more than one year. Measurement is to be consistent with Australian accounting standards.
As a guide include:
- bonds;
- debentures;
- unsecured notes;
- fixed-interest securities;
- MTNs;
- inflation-indexed bonds;
- FRNs;
- other floating-rate debt securities;
- mortgage-backed bonds;
- asset-backed bonds;
- Euro notes;
- Euro bonds;
- Euro medium-term notes;
- non-participating preference shares (a special type where the holder has no entitlement to a share in the residual value on dissolution of the issuing company); and
- subordinated bonds and notes.
As a guide exclude:
- hybrid securities;
- trading derivatives;
- convertible notes prior to conversion;
- negotiable and TCDs;
- subordinated debt issues with a residual maturity of 12 months or less;
- promissory notes with a residual maturity of 12 months or less;
- commercial with a residual maturity of 12 months or less; and
- short term debt securities from controlled and associated entities.
8.2 - 8.3 Loans
Report the face value of all loans and borrowings that have a residual term to maturity of more than one year.
Include:
- secured and unsecured borrowings;
- financial lease agreements;
- term loans;
- mortgages;
- commercial loans;
- equity participation in leveraged leases;
- redeemable preference share finance; and
- loans to controlled entities and associates.
Exclude:
- loan capital (e.g. subordinated loans);
- short term loans due to controlled entities and associates; and
- treasury related short term borrowings from other banks.
8.2 Loans – Variable rate
Report the face value of all variable interest rate loans and borrowings that have a residual term to maturity of more than one year.
8.3 Long term loans – Fixed rate
Report the face value of all fixed interest rate loans and borrowings that have a residual term to maturity of more than one year.
8.4 Total bonds, notes and long term borrowings
Sum the total face value of all "Bonds, notes and long term borrowings" issued.
9. Intra-company borrowings
Report borrowings from other offices within the ADI (including the Australian head office).
10. Creditors and other liabilities
10.1 - 10.2 Defined benefit liabilities
Include:
- defined benefit liabilities i.e. deficit, consistent with the classification and measurement basis used in AASB 119.
Distinctions between current and non-current defined benefit liabilities are to be made in accordance with AASB 101 Presentation of Financial Statements.
10.3 Interest payable
Include;
- interest accrued for but not yet paid.
10.4 Unearned interest
Include:
- interest received but not yet earned.
10.5 Derivative financial instruments
Include:
- all derivatives consistent with the classification and measurement basis used for derivatives by institutions in accordance with AASB 132, AASB 7 and AASB 139. This applies to trading and banking book derivatives. Derivative financial instruments in existence prior to adoption of IFRS are to be reported in accordance with AASB 1 First-time Adoption of Australian Equivalents to International Financial Reporting Standards.
10.6 Amounts payable to client - Outstanding security settlements
For those institutions that have broking activity with clients who are other than financial institutions, record the amount due to clients in relation to security settlement transactions. Do not include amounts payable to financial institutions or clearing houses in relation to security settlements, as these are to be recorded in a separate liability heading “Due to Financial Institutions” and “Due to Clearing Houses”.
10.7 Items in suspense
Report suspense or unreconciled/unidentified transactions/balances here that are in a liability position. A list of examples is not provided as these may vary between institutions. It is recommended that the institution’s internal procedures be adopted regarding the recording and reporting of these types of balances.
10.8 Liabilities included in disposal groups classified as held for sale
Include:
- liabilities included in disposal groups classified as held for sale consistent with paragraph 38 of AASB 5.
10.9 Share capital repayable on demand
Applicable to Credit Unions and Building Societies, this includes members’ shares in co-operatives classified as liabilities consistent with AASB 132 and AASB 7.
10.10 Other
Include:
- other liabilities not separately identified above. E.g. unearned fees and commission received in advance but not recognised as earned for accounting purposes.
Exclude:
- deposits, loans and other liabilities to controlled entities and associates
10.11 Total creditors and other liabilities
Sum the reporting items listed under “Creditors and other liabilities”.
11. Loan capital and hybrid securities
Report the face value of all loan capital and hybrid securities that have been issued in Australia and have a residual term to maturity of more than one year.
Classification is to be consistent with AASB 132 and AASB 7.
As a guide include:
- preference shares;
- convertible notes; and
- subordinated loans of a residual maturity of more than one year.
11.1 Loan capital
As a guide include:
- subordinated loans of a residual maturity of more than one year.
11.2 Hybrid securities
As a guide include:
- preference shares; and
- convertible notes.
11.3 Total loan capital and hybrid securities
Total all loan capital and hybrid securities items listed above.
12. Total liabilities
Sum total liabilities.
12.1.1 Total liabilities of which deposits, debt securities and loans from controlled entities and associates – Subordinated
Report the total amount of liabilities of a subordinated nature from controlled entities or associates of the reporting entity. Liabilities in the form of deposits, loans, advances, bonds, notes and debentures should be reported.
A subordinated debt is a debt security that ranks below other debts should a company be wound up. This includes all debt securities both short and long term.
A subordinated loan is a loan that ranks below other debts should a company be wound up.
12.1.2 Total liabilities of which deposits, debt securities and loans from controlled entities and associates – Secured
Report the total amount of liabilities of a secured nature from controlled entities or associates of the reporting entity. Liabilities in the form of deposits, loans, advances, bonds, notes and debentures should be reported.
A secured debt is a debt security that ranks above other debts should a company be wound up. This includes all debt securities both short and long term.
A secured loan is a loan that ranks above other debts should a company be wound up.
12.1.3 Total liabilities of which deposits, debt securities and loans from controlled entities and associates – Other
Report the total amount of liabilities other than subordinated or secured in nature, from controlled entities or associates of the reporting entity. Liabilities in the form of deposits, loans, advances, bonds, notes and debentures should be reported.
12.2.1 Total liabilities of which deposits, debt securities and loans from the parent entity – Subordinated
Report the total amount of liabilities of a subordinated nature from the parent entity of the reporting entity. Liabilities in the form of deposits, loans, advances, bonds, notes and debentures should be reported.
A subordinated debt is a debt security that ranks below other debts should a company be wound up. This includes all debt securities both short and long term.
A subordinated loan is a loan that ranks below other debts should a company be wound up.
12.2.2 Total liabilities of which deposits, debt securities and loans from the parent entity – Secured
Report the total amount of liabilities of a secured nature from the parent entity of the reporting entity. Liabilities in the form of deposits, loans, advances, bonds, notes and debentures should be reported.
A secured debt is a debt security that ranks above other debts should a company be wound up. This includes all debt securities both short and long term.
A secured loan is a loan that ranks above other debts should a company be wound up.
12.2.3 Total liabilities of which deposits, debt securities and loans from the parent entity – Other
Report the total amount of liabilities other than subordinated or secured in nature, from the parent entity of the reporting entity. Liabilities in the form of deposits, loans, advances, bonds, notes and debentures should be reported.
12.3 Total liabilities of which other secured deposits, debt securities and loans
Report the total amount of liabilities of a secured nature from parties other than the parent, controlled or associated entities of the reporting entity. Liabilities in the form of deposits, loans, advances, bonds, notes and debentures should be reported.
A secured debt is a debt security that ranks above other debts should a company be wound up. This includes all debt securities both short and long term.
A secured loan is a loan that ranks above other debts should a company be wound up.
13. Net assets
Calculated as total assets less total liabilities.
Section C: Shareholders’ equity
1. Share capital
1.1 Ordinary shares
Include:
- ordinary share capital on issue.
1.2 Preference shares
Preference shares have a priority over dividend payments and to the assets of the reporting company.
1.3 Other
Include:
- any other form of share capital not included above (e.g. income securities).
2. Reserves
2.1 General reserves
This is derived from revenue profits and is mostly available for dividend payment.
Exclude:
- from General reserves any portion of General Reserve for Credit Losses that forms part of Shareholders’ Equity. These excluded amounts are to be recorded in the General Reserve for Credit Losses column in the assets section of this form.
2.2 Capital profits reserve
Capital profits reserve represents the realised value of revaluations associated with an asset or class of assets that have been disposed of. These assets have been subject to the fair value basis of measurement and revaluations accounted for in accordance with accounting standard AASB 116. Due to the disposal of these assets, the balance of the asset revaluation reserve (ARR) associated with these assets has been transferred to a capital profits reserve.
2.3.1 ARR – Owner-occupied property
Include:
- the balance of the asset revaluation reserve relating to the revaluation of owner-occupied property.
2.3.2 ARR – Plant and equipment
Include:
- the balance of the asset revaluation reserve relating to the revaluation of plant and equipment.
2.3.3 ARR – Intangibles revaluation surplus
Include:
- the balance of the asset revaluation reserve relating to the revaluation surplus of intangible assets.
2.3.4 ARR – Investments in subsidiaries
Include:
- the balance of the asset revaluation reserve relating to the revaluation of investment in subsidiaries.
2.3.5 ARR – Investments in associates/share of associates
Include:
- the balance of the asset revaluation reserve relating to the revaluation of investments in associates
2.3.6 ARR – Relating to non-current assets or disposal groups held for sale
Include:
- the balance of the asset revaluation reserve relating to revaluation of non-current assets or disposal groups held for sale in accordance with AASB 5.
2.3.7 ARR - Other
Asset revaluation reserve relating to the revaluation of other assets.
2.3.8 Total ARR
Sum the reporting items listed under “ARR”.
2.4 Foreign currency translation reserve
Include:
- the exchange rate differences arising on translation of assets and liabilities in accordance with AASB 121.
2.5.1. Available for sale reserve – Marketable securities
Include:
- available for sale reserve for all marketable securities (debt and equity) consistent with the classification and measurement basis used by institutions in accordance with AASB 130 and AASB 7.
2.5.2. Available for sale reserve – Other
Include:
- available for sale reserve for loans and advances and all other items not separately identified above, consistent with the classification and measurement basis used in AASB 139, AASB 132 and AASB 7.
2.6 Cash flow hedge reserve
Include:
- the effective portion of the gain or loss on the cash flow hedge as required by AASB 139, AASB 132 and AASB 7.
2.7 Share based payments reserve
Include:
- the equity settled share based payments reserve amounts as required by AASB 2: Share-based Payment.
2.8 Other reserves
Include:
- all reserves not separately identified above. Report dividend reinvestment plan reserve in this reporting item.
2.9 Total reserves
Sum the reporting items listed under “Reserves”.
3. Retained profits or accumulated losses at the end of the period
4. Total shareholders’ equity
Sum the reporting items: “Shareholders’ equity”.