national measurement act 1960
determination by the national standards commission
Recognized-Value Standard of Measurement
of Density Mercury
In pursuance of paragraphs 8A(1) (a) and (b) of the National Measurement Act 1960, the National Standards Commission hereby determines that the magnitude of the density of mercury dt at a temperature t and a mean pressure p shall be a recognized-value standard of measurement, provided t lies within the range 0°C to 40°C and p lies within the range 0 Pa to 107 Pa.
For the purposes of this Determination -
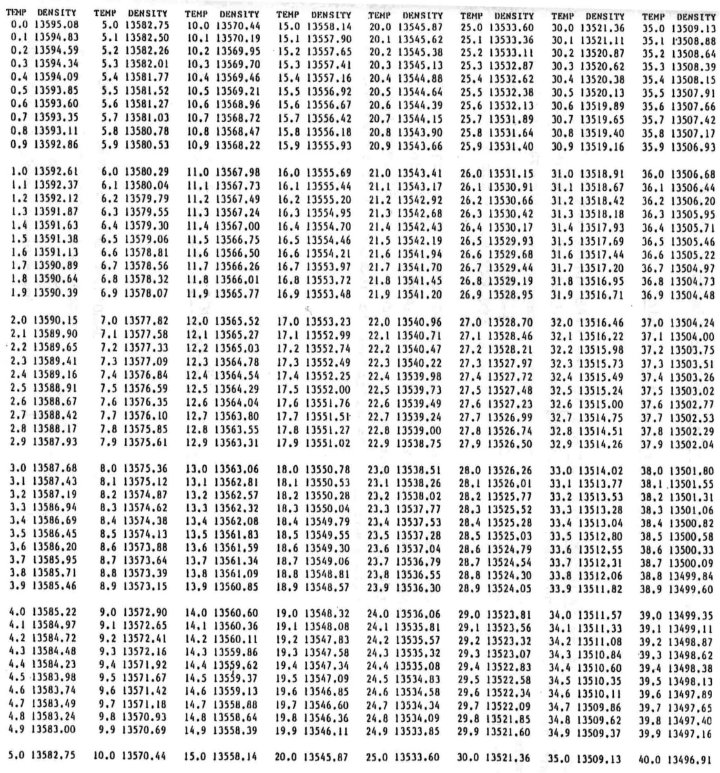
(a) When p is 101 325 Pa and t is one of the temperatures listed in the attached table then the magnitude of the density in kg.m-3 is as stated in the table, which is derived from the following formula:
dt = 13 595.08 / {1 + (18 150.36 t + 0.702 09 t2 + 2.865 5 10-3t3 + 2.621 10-6 t4) 10-8}
where dt is the density in kg.m-3, and
t is the temperature in °C;
(b) When p is 101 325 Pa and t is between two adjacent values of temperature listed in the attached table then the magnitude of the density in kg.m-3 shall be determined from the table by linear interpolation;
(c) When p differs from 101 325 Pa the magnitude of the density in kg.m-3 as stated in the attached table or derived therefrom in accordance with the above linear interpolation shall be algebraically increased by an amount equal to
5.47 10-7 (p – 101 325); and
(d) If the value of t used in the attached table and the above equations does not differ from the true mean temperature of the mercury by more than 0.1°C, if the value of p used in the equation does not differ from the true mean pressure within the mercury by more than 1 000 Pa, and if impurities in the mercury do not exceed 5 part in 106 by mass, the chance is not more than one in one hundred that the density so ascertained differs from the true density by more than 0.3 kg.m-3.
Dated this 21st day of March 1985
The common seal of the national T.J. PETRY
standards commission was hereto
affixed by authority of the Commission
in the presence of
The density of mercury in kilograms per cubic metre as a function of the temperature in degrees Celsius