Schedule 11 Calculation of values for nutrition information panel
Note 1 This instrument is a standard under the Food Standards Australia New Zealand Act 1991 (Cth). The standards together make up the Australia New Zealand Food Standards Code. See also section 1.1.1—3.
Standard 1.2.8 is a standard for nutrition information requirements. This Standard:
● sets out how to calculate average energy content, available carbohydrate and available carbohydrate by difference for sections 1.1.2—2 and 1.2.8—4; and
● sets out how to determine dietary fibre for subsection 1.2.8—7(7) and subsection S5—6(2); and
● lists substances for paragraph 1.2.8—6(9)(a) and subparagraph 1.2.8—14(1)(c)(ii).
Note 2 The provisions of the Code that apply in New Zealand are incorporated in, or adopted under, the Food Act 2014 (NZ). See also section 1.1.1—3.
S11—1 Name
This Standard is Australia New Zealand Food Standards Code – Schedule 11 – Calculation of values for nutrition information panel.
Note Commencement:
This Standard commences on 1 March 2016, being the date specified as the commencement date in notices in the Gazette and the New Zealand Gazette under section 92 of the Food Standards Australia New Zealand Act 1991 (Cth). See also section 93 of that Act.
S11—2 Calculation of average energy content
(1) For section 1.1.2—2, the *average energy content of a food means the energy content AE, in kJ/100 g, calculated using the following equation:
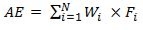
where:
N is the number of *components in the food.
Wi is the average amount of a component of the food measured in g/100 g of the food.
Fi is the energy factor, expressed in kJ/g:
(a) for a general component listed in the table to subsection (2)—indicated in the corresponding row of that table; and
(b) for a specific component listed in the table to subsection (3)—indicated in the corresponding row of that table.
(2) For subsection (1), particular energy factors, in kJ/g, for certain *components are listed below:
Energy factors for general components
Component | Energy factor |
alcohol | 29 |
*carbohydrate (excluding unavailable carbohydrate) | 17 |
unavailable carbohydrate (including dietary fibre) | 8 |
fat | 37 |
protein | 17 |
(3) For subsection (1), and for paragraph 1.2.8—6(9)(a) and subparagraph 1.2.8—14(1)(c)(ii), particular energy factors, in kJ/g, for specific *components are listed below:
Energy factors for specific components
Component | Energy factor |
erythritol | 1 |
glycerol | 18 |
isomalt | 11 |
lactitol | 11 |
maltitol | 13 |
mannitol | 9 |
organic acids | 13 |
polydextrose | 5 |
sorbitol | 14 |
D-Tagatose | 11 |
Xylitol | 14 |
(4) If for Standard 1.2.8 the *average energy content may be expressed in calories/100 g, the number of calories must be calculated in accordance with the following equation:
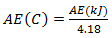
where
AE(C) is the average energy content in calories/100 g;
AE(kJ) is the average energy content in kilojoules/100 g, calculated in accordance with the equation set out in subsection (1).
S11—3 Calculation of available carbohydrate and available carbohydrate by difference
Calculation of available carbohydrate
(1) For section 1.1.2—2(3), available carbohydrate, for a food, is calculated by summing the *average quantity in the food of:
(a) total available sugars and starch; and
(b) if quantified or added to the food—any available oligosaccharides, glycogen and maltodextrins.
Calculation of available carbohydrate by difference
(2) For section 1.1.2—2(3), available carbohydrate by difference, for a food, is calculated by subtracting from 100 the *average quantity in the food, expressed as a percentage, of the following substances:
(a) water;
(b) protein;
(c) fat;
(d) dietary fibre;
(e) ash;
(f) alcohol;
(g) if quantified or added to the food—any other unavailable carbohydrate;
(h) a substance listed in subsection S11—2(3).
S11—4 Methods of analysis for dietary fibre and other fibre content
(1) This section applies for the purposes of subsection 1.2.8—7(7) and section S5—6(2).
(2) The total dietary fibre, and amount of any specifically named fibre, in a food must be determined in accordance with any one or more of the methods contained in following sections of the AOAC:
(a) for total dietary fibre—sections 985.29 or 991.43;
(b) for total dietary fibre (including all resistant maltodextrins)—section 2001.03;
(c) for inulin and fructooligosaccharide—section 997.08;
(d) for inulin—section 999.03;
(e) for polydextrose—section 2000.11.
(3) If the *dietary fibre content of a food has been determined by more than 1 method of analysis, the total dietary fibre content is calculated by:
(a) adding together the results from each method of analysis; and
(b) subtracting any portion of dietary fibre which has been included in the results of more than one method of analysis.
(4) In this section:
AOAC means the Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, eighteenth edition, 2005, published by AOAC International, Maryland USA.
____________________
![]()
