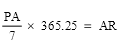Part 1—Preliminary
1 Name
This instrument is the Child Support (Assessment) Regulations 2018.
2 Commencement
(1) Each provision of this instrument specified in column 1 of the table commences, or is taken to have commenced, in accordance with column 2 of the table. Any other statement in column 2 has effect according to its terms.
Commencement information |
Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
Provisions | Commencement | Date/Details |
1. The whole of this instrument | The day after this instrument is registered. | 20 March 2018 |
Note: This table relates only to the provisions of this instrument as originally made. It will not be amended to deal with any later amendments of this instrument.
(2) Any information in column 3 of the table is not part of this instrument. Information may be inserted in this column, or information in it may be edited, in any published version of this instrument.
3 Authority
This instrument is made under the Child Support (Assessment) Act 1989.
4 Schedules
Each instrument that is specified in a Schedule to this instrument is amended or repealed as set out in the applicable items in the Schedule concerned, and any other item in a Schedule to this instrument has effect according to its terms.
5 Definitions
Note: A number of expressions used in this instrument are defined in the Act and in the Child Support (Registration and Collection) Act 1988 (see section 6 of the Act).
In this instrument:
Act means the Child Support (Assessment) Act 1989.
address for service, in relation to a person, includes both:
(a) the person’s address for the physical delivery of notices; and
(b) the person’s address for the electronic delivery of notices.
amenity allowance or gratuity means periodical payments of an incidental nature to a person for any of the following:
(a) the purchase of personal items such as toiletries;
(b) other minor expenses.
Australia‑New Zealand Agreement means the Agreement between the Government of Australia and the Government of New Zealand on Child and Spousal Maintenance done at Canberra on 12 April 2000, a copy of the text of which is set out in Schedule 1 to the Child Support (Registration and Collection) Regulations 2018.
consent has the same meaning as in subsection 5(1) of the Electronic Transactions Act 1999.
electronic communication has the same meaning as in subsection 5(1) of the Electronic Transactions Act 1999.
Governor means the person in charge of a prison, however described.
NDIS amount has the same meaning as in section 9 of the National Disability Insurance Scheme Act 2013.
social security law has the same meaning as in subsection 3(3) of the Social Security (Administration) Act 1999.
Tax Act means the Income Tax Assessment Act 1936.
Part 2—Children who may be covered by the Act
6 Exclusion of certain children
For the purposes of subsection 22(1) of the Act, children are not eligible children if they are in the custody of, or under the guardianship, care and control or supervision of, a person under a child welfare law of:
(a) Western Australia; or
(b) South Australia.
Part 3—Applications to Registrar for administrative assessment of child support
7 Prescribed overseas jurisdictions
For the purposes of paragraphs 29(2)(b), (c) and (d) of the Act, each foreign country, or a part of a foreign country, mentioned in Schedule 2 to the Child Support (Registration and Collection) Regulations 2018 is a prescribed overseas jurisdiction.
8 Actions that may be taken by an overseas authority of a reciprocating jurisdiction for a person
For the purposes of subsections 29B(2) and (3) of the Act, the following actions are prescribed:
(a) making an election of any kind under a provision of the Act;
(b) under Part 6A of the Act, applying to the Registrar to make a determination under section 98S of the Act;
(c) under Part 7 of the Act, filing an application for leave to appeal and appealing against a decision;
(d) under Part 7 of the Act, applying to a court to make an order under section 118 of the Act;
(e) subject to Part VII of the Registration and Collection Act, lodging an objection to a decision;
(f) subject to Part VIIA of the Registration and Collection Act, applying to the AAT for review of a decision;
(g) subject to Part IVA of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975, appealing on a question of law from a decision of the AAT.
9 Excluded reciprocating jurisdictions
For the purposes of section 30A of the Act, the following reciprocating jurisdictions are specified:
(a) Brunei Darussalam;
(b) Cook Islands;
(c) Israel;
(d) Niue;
(e) Papua New Guinea;
(f) Samoa;
(g) the Yukon Territory of Canada.
Part 4—Administrative assessment of child support
10 Taxable income—prescribed provisions and circumstances
(1) For the purposes of paragraphs 56(2)(b) and (c) of the Act, the following provisions and circumstances are prescribed:
(a) sections 78A, 82KJ, 82KK, 82KL and 177F of the Tax Act;
(b) sections 136AD, 136AE and 136AF of the Tax Act as in force immediately before 29 June 2013;
(c) the circumstances in which subsection 170(9B) of the Tax Act, as in force immediately before 29 June 2013, applied.
(2) For the purposes of subsection 57(7) of the Act, the following circumstances are prescribed:
(a) the circumstance in which a tax assessment under the Tax Act could be amended to give effect to the provisions of the Tax Act;
(b) the circumstances mentioned in paragraph (1)(c).
11 Adjusted taxable income—prescribed circumstances
(1) For the purposes of section 58A of the Act, the following circumstances are prescribed in relation to a parent who was unable to provide information about the parent’s adjusted taxable income to the Registrar at the time the relevant administrative assessment was made:
(a) one or more of the following applied in relation to the parent at that time:
(i) the parent did not know that an application for the assessment had been made and accepted;
(ii) the parent had a serious illness or injury;
(iii) the parent was under detention or imprisonment;
(iv) the parent resided in a remote location which made it difficult to contact the Registrar;
(v) a natural disaster prevented the parent from being able to contact the Registrar;
(vi) there was some other exceptional circumstance that prevented the parent from providing the information;
(b) the Registrar confirms that the parent was unable to provide the information at that time because of a circumstance mentioned in paragraph (a);
(c) the parent later provides the information to the Registrar as soon as is practicable in the circumstances.
(2) For the purposes of section 58A of the Act, the following circumstances are prescribed in relation to a parent who resided overseas during the last relevant year of income for the child support period for which the Registrar made the relevant administrative assessment:
(a) the parent was not required to lodge a tax return under the Tax Act;
(b) the parent provides the information about the parent’s adjusted taxable income to the Registrar within a reasonable time in the circumstances.
12 Overseas income—conversion of currency
(1) For the purpose of determining, under Subdivision BA of Division 7 of Part 5 of the Act, an amount of income expressed in foreign currency to be a person’s overseas income, the Registrar must convert the amount into an equivalent amount in Australian currency.
(2) The equivalent amount in Australian currency must be worked out using:
(a) the average exchange rate for the foreign currency for the financial year in which the income was derived, being the average of the international money transfer buying rates published by the Commonwealth Bank of Australia for that currency for that financial year; or
(b) if no such rate is available for the foreign currency for that financial year—an exchange rate for the foreign currency that the Registrar considers appropriate.
13 Prescribed payments
(1) For the purposes of paragraph (a) of the definition of income in subsection 66A(4) of the Act, money received by a person as an NDIS amount is prescribed.
(2) For the purposes of paragraph (b) of the definition of income in subsection 66A(4) of the Act, the following kinds of payments paid to a person are prescribed:
(a) an NDIS amount paid to the person;
(b) payments, in the nature of an amenity allowance or gratuity, authorised by the Governor of a prison, paid to the person if he or she is serving a term of imprisonment in the prison, to the extent that the payment is not for:
(i) work done by the person inside or outside the prison; or
(ii) approved study undertaken by the person inside or outside the prison; or
(iii) participation by the person in any other program approved by the Governor;
(c) disability support pension paid to the person under the social security law;
(d) pension paid to the person as a veteran who is totally and permanently incapacitated as mentioned in paragraph 24(1)(b) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986;
(e) Special Rate Disability Pension paid in relation to the person under Part 6 of Chapter 4 of the Military Rehabilitation and Compensation Act 2004.
(3) Paragraphs (2)(c), (d) and (e) apply in relation to a pension only if the Registrar is satisfied that:
(a) at least 85% of the pension is paid by, or on behalf of, the pension recipient to another person; and
(b) the other person provides ongoing care to the pension recipient in return for the payment.
14 Conversion of annual rates into daily rates of payment
(1) For the purposes of section 69 of the Act, an annual rate of child support is to be converted into a daily rate by using the following formula:

where:
AR is the annual rate of payment.
DR is the daily rate of payment.
(2) In calculating a conversion, the daily rate must be rounded to 5 decimal places (rounding up if the sixth decimal place is 5 or more).
Part 5—Consent arrangements
15 Conversion of periodic amounts into annual rates
If a child support agreement refers to a periodic amount of payment (the periodic amount), the annual rate of payment (the annual rate) in respect of the periodic amount is to be worked out as follows:
(a) in the case of a daily amount—in accordance with the formula:
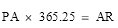
(b) in the case of a weekly amount—in accordance with the formula:

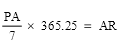
(c) in the case of a periodic amount that is in respect of a period that is a multiple of one week—in accordance with the formula:

(d) in the case of a monthly amount—in accordance with the formula:

(e) in the case of a periodic amount that is in respect of a period that is a multiple of one month—in accordance with the formula:

where:
AR is the annual rate.
NM is the number of months in respect of which the periodic amount is specified.
NW is the number of weeks in respect of which the periodic amount is specified.
PA is the periodic amount.
Part 6—Administration
16 Circumstances in which Registrar’s jurisdiction ceases
For the purposes of section 150DA of the Act, the following are prescribed:
(a) the Australia‑New Zealand Agreement;
(b) Article 5.2 of that Agreement.
Part 7—Miscellaneous
17 Scales of expenses
For the purposes of subsection 161(2) of the Act, the prescribed scales of expenses to be allowed to a person (other than a person who is a payer, payee or a personal representative of a payer or payee) required to attend under section 161 of the Act are as follows:
(a) the amount provided for in the High Court Rules (as in force at the commencement of this section) for expenses of witnesses;
(b) if the person is required to be absent overnight from his or her usual place of residence—such amount as is reasonable for meals and accommodation.
18 Service of orders
For the purposes of subsection 162(2) of the Act, a copy of an order made under subsection 162(1) of the Act must be served on a person in the following manner:
(a) if the person is a natural person:
(i) by delivering the copy to the person personally; or
(ii) by leaving the copy at, or sending the copy by prepaid post to, the address of the person last known to the proper officer of the court; or
(b) if the person is a body corporate—by leaving the copy at, or sending the copy by prepaid post to, the head office, a registered office or a principal office of the body corporate.
19 Service of notices etc.
(1) Any notice or other communication given by or on behalf of the Registrar under the Act may be served on a person:
(a) if the person is a natural person:
(i) by causing it to be personally served on the person; or
(ii) by leaving it at the person’s address for service; or
(iii) if the person has consented to receiving such notices or communications by way of electronic communication—by delivering the notice or other communication by means of electronic communication; or
(iv) by sending it by prepaid post to the person’s address for service; or
(b) if the person is a body corporate:
(i) by leaving it at the person’s address for service; or
(ii) if the person has consented to receiving such notices or communications by way of electronic communication—by delivering the notice or other communication by means of electronic communication; or
(iii) by leaving it at, or sending it by prepaid post to, the head office, a registered office or a principal office of the body corporate.
(2) If service has been attempted by use of prepaid post, then, unless the contrary is proved, service will be taken to have been effected at the time when the notice or other communication would, in the ordinary course of the post, have arrived at the place to which it was addressed.
20 Address for service
(1) The address last notified by a person to the Registrar as the address for service of the person is, for all purposes under the Act and this instrument, that person’s address for service.
(2) If no address for service has been notified to the Registrar but the Registrar’s records contain an address attributed to the person, the last such address in any record held by the Registrar is the person’s address for service under the Act and this instrument.
21 Service of documents in Australia for overseas authority
(1) This section applies if a document is required to be served by an overseas authority of a reciprocating jurisdiction on a person who is in Australia.
(2) The Registrar (or a person authorised to do so on the Registrar’s behalf) may serve the document on behalf of the overseas authority if it is necessary or convenient to do so for the purposes of an international maintenance arrangement with the reciprocating jurisdiction.
22 Giving notices or other communications in reciprocating jurisdictions
For the purposes of section 162B of the Act, a notice or other communication that is required to be given to a person who is a resident of a reciprocating jurisdiction may be given to an overseas authority of the reciprocating jurisdiction, if the Registrar considers that it is desirable or appropriate to do so.
23 Date of making of application etc.
(1) An application for administrative assessment or for the acceptance of a child support agreement is to be taken to have been made on the day on which the application is received in an office of the Human Services Department.
(2) An election under section 60 of the Act, or a revocation under section 62, is to be taken to have been made on the day on which the form of election or revocation is received in an office of the Human Services Department.
(3) If any other matter is required by the Act to be done in an approved form, the form is to be taken to have been received on the day on which the form is received in an office of the Human Services Department.
24 Documents taken to be duly signed
(1) A certificate, notice or other document bearing the written, printed or stamped name (including a facsimile of the signature) of a person who is, or was at any time, the Registrar or a delegate of the Registrar in place of that person’s signature must, unless it is proved that the document was issued without authority, be taken to have been duly signed by that person.
(2) Judicial notice must be taken of the names and signatures of the persons who are, or were at any time, the Registrar or a delegate of the Registrar.