1 Name
This instrument is the Road Vehicle Standards (Classes of Vehicles that are not Road Vehicles) Determination 2021.
2 Commencement
This instrument commences on the day after it is registered.
3 Authority
This instrument is made under paragraph 6(5)(b) of the Road Vehicle Standards Act 2018.
4 Purpose of this instrument
This instrument sets out classes of vehicles that are not road vehicles for the purposes of the Act.
5 Definitions
(1) In this instrument:
Act means the Road Vehicle Standards Act 2018.
agricultural machine means a vehicle with its own automotive power, built to perform agricultural tasks such as cultivating land, growing and harvesting crops, or rearing livestock.
approach angle means the smallest angle, in a side view, between level ground and a straight line tangent to the front tyre and touching the front of the vehicle (see Figure 1).
breakover angle means the supplement of the largest angle, in a side view, that can be formed by two lines tangent to the front and rear tyres and intersecting at a point on the underside of the vehicle (see Figure 1).
departure angle means the smallest angle, in a side view, between level ground and a straight line tangent to the rear tyre and touching the rear of the vehicle (see Figure 1).
electrically power-assisted cycle means an electrically-powered pedal cycle with a maximum continued rated power of 250W, of which the output is:
(a) progressively reduced as the cycle’s travel speed increases above 6 km/h; and
(b) cut off, where:
(i) the cycle reaches a speed of 25 km/h; or
(ii) the cyclist is not pedalling and the travel speed exceeds 6km/h.
golf cart means a motorised vehicle that:
(a) is designed to transport people and equipment around a golf course; and
(b) is designed to travel on at least four high-flotation tyres; and
(c) has side-by-side seating; and
(d) is not capable of exceeding 25 km/h on level ground; and
(e) has an unladen mass of no more than 350 kg; and
(f) has no road-going features.
high-flotation tyre means a tyre with a large sidewall that is designed to be operated at low inflation pressure in order to maximise the contact patch and prevent the vehicle from sinking into soft terrain such as soil or mud.
light utility vehicle means a motorised off-road vehicle that:
(a) is designed to travel on at least four high-flotation tyres; and
(b) has side-by-side seating; and
(c) is propelled solely by:
(i) one or more electric motors; or
(ii) an internal combustion engine that has a cylinder capacity not exceeding 1,500 cm3; and
(d) has a steering wheel; and
(e) has a tray back designed for carrying loads; and
(f) has an unladen mass of no more than 800 kg; and
(g) has no road-going features.
miniature motorbike (also known as a mini bike or pocket bike) means a vehicle that resembles a motorcycle but is scaled down to approximately half the size, and that:
(a) is designed to carry one person only; and
(b) has a seat height no greater than 600 mm; and
(c) has major dimensions that are scaled down in proportion to the seat height.
motorised mobility device means a wheeled chair that:
(a) is designed to be used by one person only; and
(b) is designed to assist a person who is unable to walk, or has difficulty walking; and
(c) is propelled by an electric motor; and
(d) has a steering control; and
(e) has a maximum governed speed of 10 km/h; and
(f) has a minimum of three wheels.
motorised recreational device means a wheeled device that:
(a) is built to transport a person; and
(b) is ordinarily used for recreation or play; and
(c) is assisted by a motor or motors with a combined maximum power output not exceeding 200 watts.
Example: Motor-assisted rollerblades, roller skates, skateboards and unicycles, and other similar motor-assisted wheeled devices, are examples of motorised recreational devices.
off-road vehicle means a vehicle that has at least four of the following five characteristics when the vehicle is at unladen mass on level ground, with the front wheels in the straight ahead position and the tyres inflated to the manufacturer’s recommended pressure:
(a) approach angle of 28 degrees or more;
(b) breakover angle of 14 degrees or more;
(c) departure angle of 20 degrees or more;
(d) running clearance of 200 mm or more;
(e) distance from the ground to the lowest point of any suspension or drivetrain component of 175 mm or more.
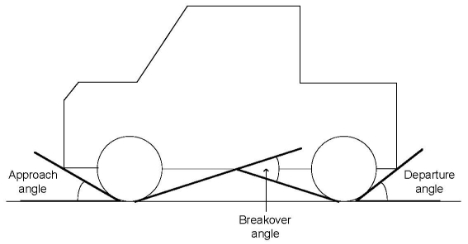
Figure 1: Approach, breakover and departure angles
personal mobility device means a device that:
(a) is designed to carry one person only; and
(b) has one or more wheels; and
(c) is propelled by an electric motor; and
(d) has an effective stopping system, including one or more of the following:
(i) brakes;
(ii) gears;
(iii) motor control; and
(e) is not capable of exceeding 25 km/h on level ground when propelled by motor; and
(f) has a footprint of no more than 1250 mm by 700 mm; and
(g) is not more than 1350 mm in height; and
(h) has an unladen mass of 60 kg or less; and
(i) is not equipped with:
(i) any object or fitting not technically essential to the device that protrudes from any part of the device in a manner that likely increases the risk of bodily injury to any person; or
(ii) any object or fitting that, because it is pointed or has a sharp edge, likely increases the risk of bodily injury to any person.
power-assisted pedal cycle means a vehicle, designed to be propelled through a mechanism primarily using human power, that:
(a) meets the following criteria:
(i) is equipped with one or more auxiliary propulsion electric motors with a combined maximum power output not exceeding 200 watts;
(ii) cannot be propelled exclusively by the motor or motors;
(iii) has a tare mass (including batteries) of less than 50 kg;
(iv) has a height-adjustable seat; or
(b) is an electrically power-assisted cycle;
but does not include a vehicle that has an internal combustion engine.
quad bike means a motorised off-road vehicle that:
(a) is designed to travel on at least four high-flotation tyres; and
(b) has a saddle-type seat designed to be straddled by the user; and
(c) is steered by handlebars.
running clearance means the distance from the ground to the lowest point on the vehicle excluding unsprung mass.
seat height means the vertical distance between the undeformed upper surface of the driver’s seat and the ground on which the vehicle rests, when the vehicle is at unladen mass on level ground.
tare mass has the meaning given by Vehicle Standard (Australian Design Rule – Definitions and Vehicle Categories) 2005¸ as in force from time to time.
tracked vehicle means a vehicle that travels on continuous tracks rather than tyres.
Example: A bulldozer or excavator may be a tracked vehicle.
unladen mass means the mass of the vehicle in running order, unoccupied and unladen, with all fluid reservoirs filled to nominal capacity including fuel, and with all standard equipment.
(2) Each of the following is a road-going feature:
(a) direction indicators;
(b) brake lights;
(c) rear vision mirrors;
(d) provision for mounting a registration plate;
(e) seatbelts;
(f) a fully enclosed cabin with doors.
6 Classes of vehicles that are not road vehicles
The following classes of vehicles are not road vehicles:
(a) agricultural machines;
(b) golf carts;
(c) light utility vehicles;
(d) miniature motorbikes;
(e) motorised mobility devices;
(f) motorised recreational devices;
(g) personal mobility devices;
(h) power-assisted pedal cycles;
(i) quad bikes;
(j) tracked vehicles.

