| Name | Unique identifier | Applicable to: | Valid values | Description |
1 | Exposure classification | Y | | - Sovereign
- Financial institution
- Corporate - large - non-IPRE
- Corporate - large - IPRE
- Corporate - SME - non-IPRE
- Corporate - SME - IPRE
- Corporate - other - non-IPRE
- Corporate - other - IPRE
- Retail - SME
- Retail - QRR
- Retail - residential mortgages - owner occupied and principal and interest
- Retail - residential mortgages - five or more investment properties
- Retail - residential mortgages - other
- Retail - other
- Supervisory slotting - project finance
- Supervisory slotting - object finance
- Supervisory slotting - commodities finance
- Supervisory slotting - IPRE
- Exposures to residual value
| Exposures that are excluded from the scope of APS 113 (paragraph 11) would be reported in the relevant table. Exposure classes are as defined in APS 113. Also refer to Prudential Practice Guide APG 113 Internal Ratings-based Approach to Credit Risk as existing at the commencement of this reporting standard for further details on the definitions. Exposures to residual value captures the residual value of IRB lease exposures that expose an ADI to residual value risk. Refer to Attachment A of APS 113. Non-IRB lease exposures and related residual value exposures would be reported under ARS 112.0. |
2 | RWA overlay | Y | | | |
3 | Purchased receivable | Y | | | For purchased receivables, report Yes. For all other exposures, report No. |
4 | Asset value correlation multiplier (AVCM) | Y | | | For financial institution exposures subject to an AVCM of 1.25, report Yes. For all other exposures, report No. |
5 | On/off balance sheet | Y | | - On-balance sheet
- Off-balance sheet
- Not Applicable
| Off-balance sheet exposures include both non-market-related (including undrawn commitments) and market-related off-balance sheet transactions. For Exposures to residual value, report Not Applicable. |
6 | Nature of transaction | Y | | - Direct credit substitutes
- Sale and repurchase agreements and asset sales with recourse
- Lending of securities or posting of securities as collateral
- Forward asset purchases, forward deposits and partly paid shares and securities
- Other off-balance sheet items that are credit substitutes
- Unsettled securities, commodities and foreign exchange transactions accounted for at settlement date
- Other commitments with certain drawdown
- Note issuance and revolving underwriting facilities
- Performance-related contingencies
- Other commitments (40% CCF)
- Other commitments (100% CCF)
- Short-term self-liquidating trade letters of credit arising from the movement of goods
- Intraday limits
- Irrevocable standby commitments under industry support arrangements
- Modelled EAD
- Market-related exposure
- Not Applicable
| Report the nature of the transaction for off-balance sheet exposures only. For all other exposures, report Not Applicable. Transaction types are defined in Attachment C of APS 112. Also refer to Prudential Practice Guide APG 112 Standardised Approach to Credit Risk as existing at the commencement of this reporting standard for further details of the definitions. Select Modelled EAD for exposures that use internal estimates of EAD (e.g. revolving retail exposures). Select Market-related exposure for exposures that expose an ADI to counterparty credit risk (refer to APS 113). |
7 | Weighted average credit conversion factor (CCF) | | | Percentage to 2 decimal places | Report the exposure-weighted average CCF for rows with Modelled EAD in column 6. Note that the average should be calculated as the exposure (after CRM and CCF) weighted average for each relevant row. For all other rows, leave this column blank. |
8 | Slotting category | Y | | - Strong
- Good
- Satisfactory
- Weak
- Default
- Not Applicable
| Report the slotting category for exposures subject to the supervisory slotting approach only. For all other exposures, report Not Applicable. Where the exposure is slotted, for columns 9 to 17, populate the non-numeric columns with Not Applicable and leave the numeric columns blank. |
9 | Internal probability of default (PD) grade | Y | | Text | Report the label assigned to the internal PD grade or pool (e.g. A1, B1, etc.). The allocation of exposures to each PD grade should be made after the application of regulatory floors on PD. For rows to which this column does not apply (e.g. slotted exposures), report Not Applicable. |
10 | Probability of default (PD) | | | Percentage to 5 decimal places | For each internal PD grade or pool in column 9, report the PD estimate for the internal grade or pool. For rows to which this column does not apply (e.g. slotted exposures), leave this column blank. |
11 | Prescribed loss given default (LGD) category | Y | | - Eligible financial collateral (0%)
- Eligible financial receivables (20%)
- Eligible CRE or RRE (20%)
- Other eligible physical collateral (25%)
- Senior unsecured (5%)
- Senior unsecured (25%)
- Senior unsecured (40%)
- Senior unsecured (45%)
- Senior unsecured (50%)
- Subordinated debt (75%)
- Dilution risk (100%)
- Not Applicable
| This column contains the FIRB LGD categories in APS 113 and is applicable to exposures subject to the FIRB approach and the dilution risk LGD category which is applicable to purchased receivable exposures. For all other exposures, report Not Applicable. Senior unsecured LGD categories include senior exposures secured by ineligible collateral under the FIRB approach. For partly secured exposures or exposures with mixed eligible collateral, exposures should be allocated to the relevant FIRB LGD categories as detailed in Attachment B of APS 113. For partly secured exposures, the amount reported in column 19 against a senior unsecured category should be calculated as 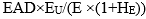 , where E is the committed amount. , where E is the committed amount. The Dilution risk (100%) category is used for purchased receivables only. Refer to Attachment F of APS 113. |
12 | Loan-to-valuation ratio (LVR) | Y | | - 0% to <= 50%
- 50.01% to <= 60%
- 60.01% to <= 70%
- 70.01% to <= 80%
- 80.01% to <= 90% - LMI
- 80.01% to <= 90% - non-LMI
- 90.01% to <= 100% - LMI
- 90.01% to <= 100% - non-LMI
- > 100% - LMI
- > 100% - non-LMI
- Not Applicable
| This column is applicable to Retail - residential mortgages - owner occupied and principal and interest, Retail - residential mortgages - five or more investment properties and Retail - residential mortgages – Other exposures except where the exposure is a purchased receivable. Loan-to-valuation ratio (LVR) and lenders’ mortgage insurance (LMI) are defined in APS 112. Allocate exposures to the appropriate LVR-LMI band based on the exposure’s LVR and the application of eligible LMI. For all other exposures, report Not Applicable. |
13 | Internal LGD grade | Y | | Text | This column captures internal LGD grades and is applicable to exposures subject to the AIRB or the retail IRB approach. For all other exposures, report Not Applicable. For ADIs that use discrete LGD grades for regulatory capital calculation, report the label given to the internal LGD grade (e.g. LGD1, LGD2, etc.). For ADIs that assign continuous LGD estimates for regulatory capital calculation, the estimates must first be grouped into LGD bands for reporting purposes and then report the label given to each band (e.g. LGD1, LGD2, etc.). It is up to the ADI to determine the reasonable number of discrete bands for reporting purposes. The bands may be aligned with bands used internally for other purposes such as pricing. The allocation of exposures to each LGD grade or band should be made after the application of regulatory floors on LGD. For rows to which this column does not apply (e.g. slotted exposures), report Not Applicable. |
14 | Internal LGD estimate | | | Percentage to 3 decimal places | For each internal LGD grade in column 13, report the LGD estimate after the application of regulatory LGD floors. Where an ADI has formed LGD bands in column 13, report the exposure-weighted average LGD for each band after the application of regulatory LGD floors. For rows to which this column does not apply (e.g. slotted exposures), leave this column blank. |
15 | Maturity (M) band | Y | | - <1 year
- Equal to 1 year
- >1 to <=2 years
- >2 to <=3 years
- >3 to <=4years
- >4 to <5 years
- Equal to 5 years
- Not Applicable
| This column is applicable to sovereign, financial institution and corporate exposures except for rows where Exposure after CRM and CCF (column 19) is zero. The <1 year band is for exposures that are exempt from the one-year maturity floor only. The allocation of exposures to each effective maturity band should be made after the application of regulatory caps and floors on effective maturity. For all other exposures, report Not Applicable. |
16 | Weighted average maturity (years) | | | Years to 3 decimal places | Report the exposure-weighted average effective maturity in years for each effective maturity band in column 15. Note that the average should be calculated as the exposure (after CRM and CCF) weighted average at the unique identifier level. For rows to which this column does not apply, including rows where Exposure after CRM and CCF (column 19) is zero, leave this column blank. |
17 | Weighted average firm size | | | Whole dollars | For Corporate - SME - IPRE and Corporate - SME - non-IPRE exposures, except for rows where Exposure after CRM and CCF (column 19) is zero, report the exposure-weighted average consolidated annual revenue for the purpose of calculating the firm-size adjustment. Note that the average should be calculated as the exposure (after CRM and CCF) weighted average for each relevant row. For all other exposures, leave this column blank. |
18 | Exposure before CRM and CCF | | | Whole dollars | For each row other than rows with Yes in column 2, report exposure before credit risk mitigation (CRM) and before CCF. |
19 | Exposure after CRM and CCF | | | Whole dollars | For each row other than rows with Yes in column 2, report exposure after CRM and after CCF. |
20 | Risk weighted assets (RWA) - Internal ratings-based (IRB) | | | Whole dollars | Report the RWA without the 1.1 scaling factor. Refer to Attachment A of APS 113. For RWA overlays, refer to the instructions for column 2. |
21 | Scaled RWA | | | Whole dollars | APRA calculated field. |
22 | Expected loss (EL) amount | | | Whole dollars | Report the EL amount. |
23 | RWA - Standardised | | | Whole dollars | For each row and exposures reported in column 19, report the equivalent standardised RWA calculated in accordance with APS 112. For RWA overlays, report the equivalent standardised RWA where relevant (e.g. an overlay associated with the exposure amount may have a standardised equivalent). |

